AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20260109

1. GDPO: Group reward-Decoupled Normalization Policy Optimization for Multi-reward RL Optimization
🔑 Keywords: Multi-reward reinforcement learning, GRPO, GDPO, training stability
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to address the issues of reward normalization collapse in GRPO and to demonstrate the effectiveness of the newly proposed GDPO method in multi-reward reinforcement learning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers introduce GDPO, which involves decoupling the normalization of individual rewards to maintain their relative differences, thereby improving training stability and optimization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– GDPO consistently outperforms GRPO in various tasks, such as tool calling, math reasoning, and coding reasoning, showcasing its effectiveness and generalizability in optimizing multi-reward reinforcement learning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.05242

2. RL-AWB: Deep Reinforcement Learning for Auto White Balance Correction in Low-Light Night-time Scenes
🔑 Keywords: Nighttime color constancy, Deep reinforcement learning, White balance, Illumination estimation
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To solve the challenge of nighttime color constancy by combining statistical methods with deep reinforcement learning to improve white balance under low-light conditions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of RL-AWB framework, integrating statistical algorithms with deep reinforcement learning, and development of a multi-sensor nighttime dataset for cross-sensor evaluation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method demonstrates superior generalization capability across both low-light and well-illuminated images.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.05249
3. RoboVIP: Multi-View Video Generation with Visual Identity Prompting Augments Robot Manipulation
🔑 Keywords: Visual Identity Prompting, Manipulation Data, Image Diffusion Models, Visuomotor Policy Models
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance manipulation data augmentation for robot policies by implementing visual identity prompting.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizing exemplar images as conditioning inputs in image diffusion models to provide explicit visual guidance.
– Building a scalable pipeline to curate a visual identity pool from large robotics datasets.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method yields consistent performance gains in training downstream vision-language-action and visuomotor policy models in both simulation and real-world settings.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.05241
4. AT^2PO: Agentic Turn-based Policy Optimization via Tree Search
🔑 Keywords: Agentic Reinforcement Learning, Tree Search, Turn-wise Credit Assignment, Policy Optimization, Multi-turn Tasks
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research introduces AT²PO, a framework that enhances multi-turn agentic reinforcement learning by addressing exploration diversity, credit assignment, and policy optimization challenges.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a turn-level tree structure for Entropy-Guided Tree Expansion and Turn-wise Credit Assignment to improve strategic exploration and fine-grained reward propagation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrates improvements over state-of-the-art baselines across seven benchmarks, with up to 1.84 percentage points in average, validating the framework’s components’ effectiveness.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.04767

5. The Illusion of Specialization: Unveiling the Domain-Invariant “Standing Committee” in Mixture-of-Experts Models
🔑 Keywords: Mixture of Experts, domain specialization, COMMITTEEAUDIT, Standing Committee, routing behavior
💡 Category: Foundations of AI
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to challenge the assumption of domain specialization in Mixture of Experts models by analyzing centralized routing behavior across different domains and architectures using the COMMITTEEAUDIT framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of the COMMITTEEAUDIT framework to analyze routing behavior at the level of expert groups across three representative models and the MMLU benchmark.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Discovery of a domain-invariant Standing Committee that dominates routing behavior, revealing a structural bias towards centralized computation. This suggests that specialization is less pervasive than previously believed, potentially affecting current training objectives and their efficiency.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.03425

6. VideoAuto-R1: Video Auto Reasoning via Thinking Once, Answering Twice
🔑 Keywords: AI Native, VideoAuto-R1, reason-when-necessary strategy, verifiable rewards, confidence score
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To explore the necessity and advantages of Chain-of-thought reasoning in video understanding tasks compared to direct answering.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed VideoAuto-R1 framework using a Thinking Once, Answering Twice paradigm, employing verifiable rewards during training and confidence-based reasoning activation during inference.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– VideoAuto-R1 achieves state-of-the-art accuracy with improved efficiency, reducing response length significantly. While explicit reasoning is beneficial, it is not always necessary for perception-oriented tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.05175

7. Agent-as-a-Judge
🔑 Keywords: Agent-as-a-Judge, LLM-as-a-Judge, tool-augmented verification, multi-agent collaboration, agentic evaluation
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to explore agent-based evaluation systems that address the limitations of large language models in assessing complex, multi-step tasks by proposing a new agentic evaluation framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The methods involve the development and use of planning, tool-augmented verification, multi-agent collaboration, and persistent memory to improve evaluation robustness and verification.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study provides a comprehensive survey highlighting a paradigm shift towards agent-as-a-judge systems, identifies key dimensions and challenges, and offers a roadmap for future research in agentic evaluation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.05111

8. DocDancer: Towards Agentic Document-Grounded Information Seeking
🔑 Keywords: Document Question Answering, Open-source, Information-seeking problem, Tool-driven agent framework, Data synthesis pipeline
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce DocDancer, an open-source document question answering agent that addresses limitations in current models by using a tool-driven framework and information-seeking problem formulation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employ an Exploration-then-Synthesis data synthesis pipeline to overcome the scarcity of high-quality training data for document question answering tasks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The trained models demonstrate effectiveness on long-context document understanding benchmarks, providing insights for agentic tool design and synthetic data utilization.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.05163

9. DiffCoT: Diffusion-styled Chain-of-Thought Reasoning in LLMs
🔑 Keywords: Chain-of-Thought, diffusion principles, denoising process, causal consistency, error-correction
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to enhance Chain-of-Thought reasoning by introducing DiffCoT, which reformulates reasoning as an iterative denoising process using diffusion principles.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– DiffCoT integrates diffusion principles through a sliding-window mechanism to enable unified generation and correction of reasoning steps while maintaining token-level autoregression and causal consistency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Extensive experiments demonstrate that DiffCoT consistently outperforms existing methods in CoT reasoning benchmarks, improving robustness and error-correction capabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.03559

10. Guardians of the Hair: Rescuing Soft Boundaries in Depth, Stereo, and Novel Views
🔑 Keywords: HairGuard, soft boundaries, depth refinement, generative scene painter, novel view synthesis
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to recover fine-grained soft boundary details in 3D vision tasks using HairGuard, a specialized framework that enhances both depth refinement and view synthesis techniques.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A novel data curation pipeline is introduced to leverage image matting datasets for training, alongside a depth fixer network to identify and refine soft boundary regions accurately.
– The framework employs a gated residual module for precise depth refinement, depth-based forward warping for maintaining high-fidelity textures, and a generative scene painter to fill disoccluded regions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Extensive experiments show that HairGuard outperforms state-of-the-art models in monocular depth estimation, stereo conversion, and novel view synthesis, particularly improving detail in soft boundary regions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.03362

11. Memorization in 3D Shape Generation: An Empirical Study
🔑 Keywords: memorization, 3D generative models, data modality, diffusion model, guidance scale
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a framework for quantifying memorization in 3D generative models and to identify how data modality and model design influence this memorization.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study designed an evaluation framework and conducted controlled experiments using a Vecset diffusion model to assess memorization in existing methods and analyze the effects of data and modeling parameters.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Data modality and diversity, as well as finer-grained conditioning, influence memorization significantly. Modeling strategies like moderate guidance scale and techniques such as longer Vecsets and rotation augmentation can mitigate memorization without compromising the quality of generated results.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.23628
12. Scaling Behavior Cloning Improves Causal Reasoning: An Open Model for Real-Time Video Game Playing
🔑 Keywords: Behavior cloning, video game playing, foundation model, human gameplay, scaling laws
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To explore how scaling model size and training data improve performance and causal reasoning in behavior cloning for 3D video games.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of an open recipe for training a video game playing foundation model capable of real-time inference on consumer GPUs, supported by releasing data, training code, and pretrained checkpoints.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrates that increasing both data and model size enhances the ability for causal reasoning, with the model achieving performance comparable to human gameplay in various 3D video games.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.04575

13. PyramidalWan: On Making Pretrained Video Model Pyramidal for Efficient Inference
🔑 Keywords: Pyramidal Models, Diffusion Process, Pretrained Models, Inference Efficiency
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to convert a pretrained diffusion model into a pyramidal one through low-cost fine-tuning without compromising output quality.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employ hierarchical resolution processing and investigate various strategies for step distillation to enhance the inference efficiency of pyramidal models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The converted pyramidal models maintain output quality and improve inference efficiency, providing a promising approach compared to existing systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.04792

14. Beyond Binary Preference: Aligning Diffusion Models to Fine-grained Criteria by Decoupling Attributes
🔑 Keywords: Diffusion Models, Expert Alignment, Hierarchical Evaluation Criteria, Domain Knowledge, Complex Preference Optimization
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to enhance the alignment of diffusion models with complex human expertise through a hierarchical, fine-grained evaluation framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study constructs hierarchical evaluation criteria and applies a two-stage alignment framework leveraging Supervised Fine-Tuning and Complex Preference Optimization to reformulate alignment objectives.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The implementation, particularly in painting generation, significantly improves generation quality and alignment with expert knowledge, demonstrating the potential for fine-grained criteria alignment.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.04300

15. Towards Open-Vocabulary Industrial Defect Understanding with a Large-Scale Multimodal Dataset
🔑 Keywords: Industrial Multimodal Defect Dataset, multimodal learning, vision-language foundation model, data-efficient foundation model adaptation, domain-adaptive
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces IMDD-1M, a comprehensive dataset aimed at advancing multimodal learning for manufacturing quality inspection.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study develops a diffusion-based vision-language foundation model trained from scratch, tailored for industrial applications, capable of efficient adaptation with minimal task-specific data.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The newly developed model demonstrates that with less than 5% of task-specific data, it can match the performance of expert models, paving the way for scalable, domain-adaptive, and knowledge-grounded manufacturing intelligence.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.24160

16. Safety at One Shot: Patching Fine-Tuned LLMs with A Single Instance
🔑 Keywords: Safety alignment, large language models, convergence, low-rank structure
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to demonstrate that safety alignment of large language models can be fully recovered using just one safety example while maintaining their utility.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors identified low-rank gradient structures that facilitate quick convergence and efficient safety alignment correction across various language models and datasets.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– It was found that employing a single safety example enables full recovery of safety alignment without compromising the model’s utility, even within a few epochs and regardless of the number of harmful examples used.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.01887

17. VERSE: Visual Embedding Reduction and Space Exploration. Clustering-Guided Insights for Training Data Enhancement in Visually-Rich Document Understanding
🔑 Keywords: VERSE, Vision-Language Models, latent representations, synthetic data, F1 performance
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce VERSE, a methodology for analyzing and improving Vision-Language Models in understanding visually-rich documents.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Visualization of latent representations to assess model feasibility and pinpoint problematic regions.
– Generation of synthetic data to enhance model performance, validated through training on the MERIT Dataset.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– VERSE helps identify visual features in error-prone clusters, boosting F1 performance without harming generalization.
– Optimized on-premise models with VERSE can match or exceed the performance of popular SaaS solutions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.05125

18.

19. LEMAS: Large A 150K-Hour Large-scale Extensible Multilingual Audio Suite with Generative Speech Models
🔑 Keywords: LEMAS-Dataset, Multilingual Speech Synthesis, Word-Level Timestamps, Non-Autoregressive Flow-Matching, Autoregressive Decoder
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to introduce the LEMAS-Dataset, the largest open-source multilingual speech corpus with word-level timestamps, and demonstrate its effectiveness in high-quality speech synthesis and editing using specialized models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research employs two benchmark models: LEMAS-TTS using a non-autoregressive flow-matching framework for robust zero-shot multilingual synthesis, and LEMAS-Edit using an autoregressive decoder-only architecture for seamless speech editing.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experimental results show that models trained on the LEMAS-Dataset achieve high-quality synthesis and editing performance, confirming the dataset’s quality and potential for advancing prompt-based speech generation systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.04233

20. Learning User Preferences Through Interaction for Long-Term Collaboration
🔑 Keywords: MultiSessionCollab, AI-generated summary, memory systems, user preferences, Human-AI Interaction
💡 Category: Human-AI Interaction
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to evaluate agents’ ability to learn and adapt to user preferences through MultiSessionCollab, emphasizing the importance of memory systems for improving long-term collaboration.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of long-term collaborative agents with persistent memory for refining user preferences and leveraging user simulator behavior for agent training.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Agents equipped with memory systems improve long-term collaboration, evidenced by higher task success rates, more efficient interactions, reduced user effort, and enhanced user experience in real-world settings.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.02702

21. Enhancing Object Detection with Privileged Information: A Model-Agnostic Teacher-Student Approach
🔑 Keywords: Learning Using Privileged Information, Object Detection, Teacher-Student Architecture, Model-Agnostic Methodology, Inference Complexity
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To explore the integration of the Learning Using Privileged Information paradigm in object detection to enhance accuracy using additional training-time information without increasing inference complexity.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces a model-agnostic methodology for incorporating privileged information like bounding box masks and saliency maps into object detectors via a teacher-student architecture.
– Experiments conducted across five state-of-the-art object detection models using multiple public benchmarks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LUPI-trained models show significant improvement in detection accuracy without increasing inference complexity, particularly for medium and large objects.
– Intermediate weighting of teacher guidance optimally balances learning, confirming LUPI’s efficacy in advancing object detection systems in various settings.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.02016

22. ReHyAt: Recurrent Hybrid Attention for Video Diffusion Transformers
🔑 Keywords: Recurrent Hybrid Attention, softmax attention, linear attention, video generation, scalability
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a Recurrent Hybrid Attention mechanism, ReHyAt, that melds the benefits of softmax and linear attention to enable scalable and efficient video generation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implemented chunk-wise recurrent reformulation and constant memory usage with ReHyAt, facilitating efficient distillation from existing softmax-based models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ReHyAt reduces attention cost from quadratic to linear while maintaining state-of-the-art video quality, significantly lowering training costs and unlocking scalability for long-duration and on-device video generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.04342

23. AgentDevel: Reframing Self-Evolving LLM Agents as Release Engineering
🔑 Keywords: release engineering, large language model agents, AI-generated summary, regression-aware release pipeline, implementation-blind LLM critic
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary objective is to reframe large language model (LLM) agent improvement using release engineering, treating them as shippable artifacts.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employ a regression-aware release pipeline, introduce AgentDevel featuring implementation-blind LLM critic, script-based executable diagnosis, and flip-centered gating.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– AgentDevel ensures stable improvements with fewer regressions while producing auditable and reproducible artifacts, providing a practical discipline for LLM agent development.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.04620

24. Multi-Scale Local Speculative Decoding for Image Generation
🔑 Keywords: Multi-Scale Local Speculative Decoding, autoregressive image generation, semantic quality, perceptual fidelity, spatially informed verification
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To accelerate autoregressive image generation by integrating multi-resolution drafting with spatially informed verification while preserving semantic quality and perceptual fidelity.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a novel framework, MuLo-SD, that uses a low-resolution drafter and learned up-samplers to propose candidate image tokens, verified by a high-resolution target model.
– Implemented a local rejection and resampling mechanism focusing on spatial neighborhoods for efficient correction of draft errors.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MuLo-SD achieves up to 1.7 times speedup over strong speculative decoding baselines like EAGLE-2 and LANTERN, maintaining competitive semantic alignment and perceptual quality, as validated using GenEval, DPG-Bench, and FID/HPSv2 on the MS-COCO 5k validation split.
– The approach sets a new state-of-the-art in speculative decoding for image synthesis, effectively combining efficiency with fidelity.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.05149
25. One Sample to Rule Them All: Extreme Data Efficiency in RL Scaling
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, One-shot Learning, Polymath Learning, Sample Engineering, Large Language Models
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To demonstrate the effectiveness of one-shot learning using a single, strategically designed training sample within reinforcement learning to enhance the reasoning abilities of large language models across various disciplines.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of a polymath learning framework that optimally selects one training sample integrating multidisciplinary elements to achieve high reasoning performance across multiple domains, including physics, chemistry, and biology.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– A single math reasoning sample can significantly boost performance in various domains when applied through reinforcement learning, challenging traditional training methods that use large datasets.
– Sample quality and design, particularly those integrating multidiscipline elements, are pivotal for improving reasoning capabilities, suggesting a shift towards precision sample engineering over simply increasing data volume.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.03111

26. ProFuse: Efficient Cross-View Context Fusion for Open-Vocabulary 3D Gaussian Splatting
🔑 Keywords: 3D Scene Understanding, 3D Gaussian Splatting, Open-Vocabulary, Semantic Fusion, Geometric Refinement
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Enhance 3D scene understanding by integrating semantic information into 3D Gaussian Splatting with minimal overhead and no render-supervised fine-tuning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced ProFuse, a context-aware framework with a dense correspondence-guided pre-registration phase, using cross-view clustering and weighted aggregation to create 3D Context Proposals.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ProFuse efficiently achieves open-vocabulary 3D scene understanding, completing semantic attachment quickly, in about five minutes per scene, which is twice as fast as the state-of-the-art methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.04754

27. Re-Align: Structured Reasoning-guided Alignment for In-Context Image Generation and Editing
🔑 Keywords: In-Context Image Generation, Editing, Structured Reasoning, Reinforcement Learning, Multimodal Models
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research introduces Re-Align, a framework designed to bridge the gap between understanding and generation in image generation and editing tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes structured reasoning through the In-Context Chain-of-Thought paradigm to decouple semantic guidance and reference association.
– Implements a reinforcement learning training scheme using a surrogate reward to align structured reasoning text with generated images.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The Re-Align framework demonstrates superior performance over competitive methods of similar scale and resources in the tasks of image generation and editing.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.05124

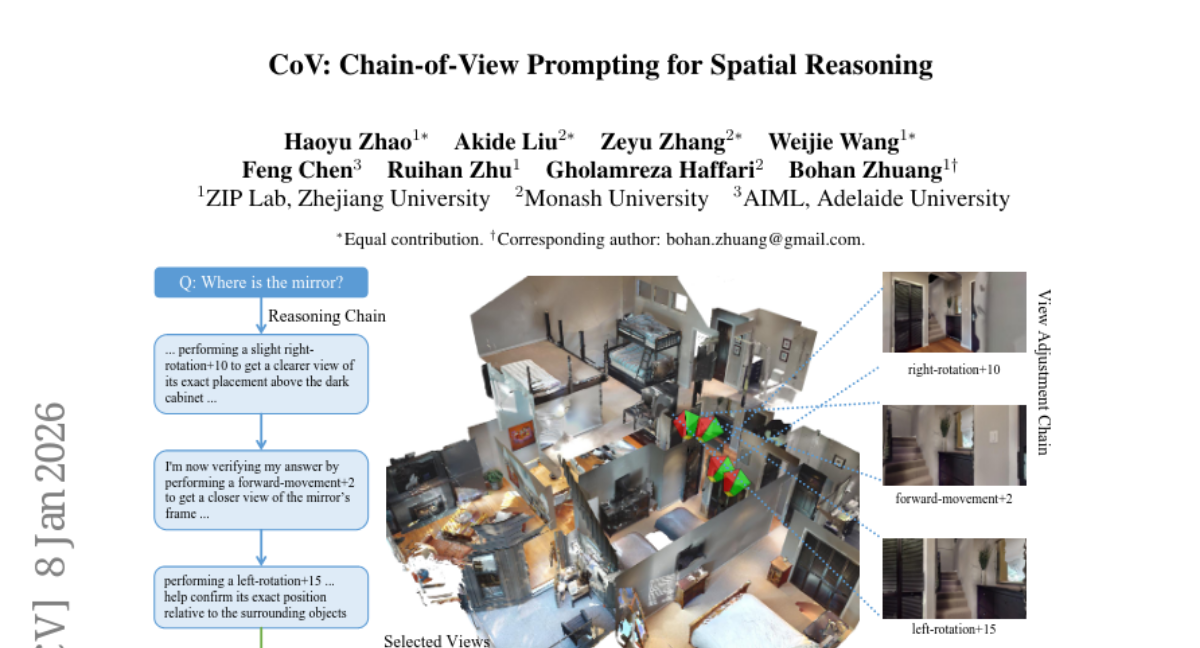
28. CoV: Chain-of-View Prompting for Spatial Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: Chain-of-View prompting, Embodied question answering, Vision-language models, Spatial reasoning, 3D environment
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance spatial reasoning in embodied question answering within 3D environments by enabling vision-language models to actively explore and select question-aligned views.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a Chain-of-View (CoV) prompting framework that employs a View Selection agent to select relevant anchor views and iteratively adjusts camera positions through a coarse-to-fine exploration approach.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CoV achieved significant improvements in spatial reasoning with an average gain of +11.56% in LLM-Match and further scaling benefits by increasing action budgets. This model-agnostic approach proves effective in enhancing question-aligned view selection and reasoning without additional training.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.05172
29. Plenoptic Video Generation
🔑 Keywords: PlenopticDreamer, AI-generated summary, generative video re-rendering, spatio-temporal coherence, camera-guided video retrieval
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– PlenopticDreamer aims to achieve consistent multi-view video re-rendering through synchronized generative hallucinations, focusing on improving temporal coherence and visual fidelity.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework trains a multi-in-single-out video-conditioned model autoregressively, utilizing a camera-guided retrieval strategy to select salient videos as conditional inputs. Techniques like progressive context-scaling, self-conditioning, and long-video conditioning are employed to enhance performance.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PlenopticDreamer exhibits state-of-the-art results in video re-rendering, offering superior view synchronization, high-fidelity visuals, precise camera control, and diverse view transformations, as demonstrated on benchmarks like Basic and Agibot.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.05239
30. VerseCrafter: Dynamic Realistic Video World Model with 4D Geometric Control
🔑 Keywords: 4D Geometric Control, Video world models, Probabilistic 3D occupancy, Video diffusion model, Automatic data engine
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce VerseCrafter, a 4D-aware video world model to achieve unified control over camera and object dynamics using a novel 4D geometric control representation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize a static background point cloud and per-object 3D Gaussian trajectories for representing the world state, combined with conditioning signals for a pretrained video diffusion model to generate view-consistent videos.
– Develop an automatic data engine to extract 4D controls from in-the-wild videos, addressing the scarcity of large-scale training data with explicit 4D annotations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The new approach allows for precise adherence to specified dynamics in high-fidelity video generation, overcoming limitations of traditional 2D image plane operations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.05138
31. Few Tokens Matter: Entropy Guided Attacks on Vision-Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Vision-language models, Adversarial attacks, High-entropy tokens, Semantic degradation, Transferability
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To explore the impact of selective adversarial attacks targeting high-entropy tokens on the semantic degradation of vision-language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Concentrating adversarial perturbations on high-entropy tokens to assess the transferability and vulnerability across diverse VLM architectures.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Selective attacks result in significant semantic degradation with smaller budgets, converting a substantial portion of benign outputs into harmful ones, and reveal new weaknesses in VLM safety mechanisms with high attack success rates and transferability.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2512.21815

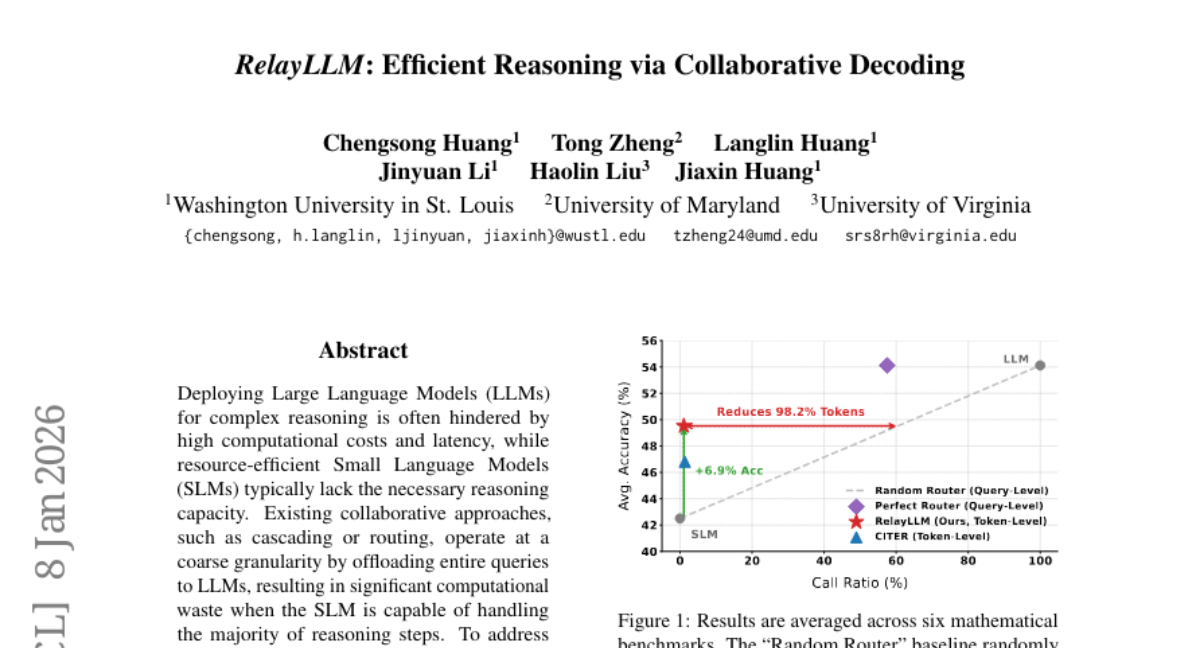
32. RelayLLM: Efficient Reasoning via Collaborative Decoding
🔑 Keywords: RelayLLM, Large Language Models, Small Language Models, collaborative decoding, Group Relative Policy Optimization
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper proposes RelayLLM, a framework for efficient collaborative reasoning that reduces computational waste and improves accuracy through dynamic token-level invocation between small and large language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– RelayLLM employs a two-stage training framework consisting of a warm-up phase and Group Relative Policy Optimization to train the model in balancing independence with strategic use of large language models for critical tokens.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RelayLLM significantly closes the performance gap between small and large language models, achieving an average accuracy of 49.52% by invoking large models for only 1.07% of generated tokens, resulting in a 98.2% cost reduction compared to traditional approaches.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.05167
33. Token-Level LLM Collaboration via FusionRoute
🔑 Keywords: FusionRoute, multi-LLM collaboration, lightweight router, logit addition
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Address the challenge of balancing efficiency and performance in large language models by introducing FusionRoute, a token-level multi-LLM collaboration framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a lightweight router to dynamically select the optimal expert and augment their outputs with complementary logits to improve token distribution.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– FusionRoute demonstrated superior performance over existing sequence- and token-level collaboration methods and model merging, especially in tasks involving mathematical reasoning, code generation, and instruction following, while maintaining competitive efficiency.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.05106

34. Learnable Multipliers: Freeing the Scale of Language Model Matrix Layers
🔑 Keywords: learnable multipliers, weight decay, stochastic gradient noise, large language model training, muP multipliers
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address the issue of weight decay-induced normalization artifacts during the training of large language models by introducing learnable multipliers.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of learnable scalar, per-row, and per-column multipliers to adjust the scale of weight matrices, enabling optimization of the weight decay-noise equilibrium norm.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The introduction of learnable multipliers not only surpasses traditional methods and a well-tuned muP baseline but also reduces computational overhead and shows improved performance in downstream evaluations when tested with both Adam and Muon optimizers.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.04890
