AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20260115
1. Controlled Self-Evolution for Algorithmic Code Optimization
🔑 Keywords: Controlled Self-Evolution, feedback-guided genetic evolution, initialization bias, Hierarchical Evolution Memory, LLM backbones
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to address inefficiencies in code generation by improving exploration efficiency and solution quality through Controlled Self-Evolution, involving elements such as diversified initialization and feedback guidance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces Controlled Self-Evolution which incorporates Diversified Planning Initialization, feedback-guided Genetic Evolution, and Hierarchical Evolution Memory to enhance the process.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments show that Controlled Self-Evolution significantly outperforms existing methods in various scenarios, achieving higher efficiency and continuous improvements in code generation. The method is validated on EffiBench-X and is applicable across different LLM backbones.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.07348

2. MAXS: Meta-Adaptive Exploration with LLM Agents
🔑 Keywords: LLM Agents, meta-adaptive reasoning framework, lookahead strategy, trajectory convergence, inference efficiency
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to improve the reasoning capabilities of LLM agents by addressing issues of locally myopic generation and trajectory instability through a meta-adaptive reasoning framework called MAXS.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– MAXS integrates tool execution and reasoning planning using a lookahead strategy and trajectory convergence mechanisms, tested across three base models and five datasets.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MAXS consistently outperforms existing methods in performance and inference efficiency, effectively balancing global effectiveness and computational efficiency with its innovative approach.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.09259

3. Distribution-Aligned Sequence Distillation for Superior Long-CoT Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: AI Native, sequence-level distillation, teacher-student knowledge transfer, reasoning model
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce DASD-4B-Thinking, an open-source reasoning model that achieves state-of-the-art performance in mathematics, scientific reasoning, and code generation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Enhance sequence-level distillation by addressing limitations in current teacher-student knowledge transfer frameworks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DASD-4B-Thinking outperforms several larger models using significantly fewer training samples and is released publicly for community research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.09088

4. SkinFlow: Efficient Information Transmission for Open Dermatological Diagnosis via Dynamic Visual Encoding and Staged RL
🔑 Keywords: SkinFlow, Visual Information Transmission Efficiency, Virtual-Width Dynamic Vision Encoder, Reinforcement Learning, Diagnostic Accuracy
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a novel framework, SkinFlow, for dermatological vision-language modeling to improve diagnostic accuracy through optimized visual information transmission efficiency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a Virtual-Width Dynamic Vision Encoder (DVE) and a two-stage Reinforcement Learning strategy to handle complex pathological data without physical expansion of parameters.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SkinFlow establishes a new state-of-the-art on the Fitzpatrick17k benchmark, outperforming massive general-purpose models, demonstrating superior diagnostic reasoning with improved Top-1 and Top-6 accuracy.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.09136

5. OpenDecoder: Open Large Language Model Decoding to Incorporate Document Quality in RAG
🔑 Keywords: OpenDecoder, Retrieval-Augmented Generation, Relevance Score, Ranking Score, Query Performance Prediction
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces OpenDecoder, aiming to improve the robustness of retrieval-augmented generation models by enhancing the evaluation of retrieved information’s quality.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– OpenDecoder explicitly assesses retrieved information using three criteria: relevance score, ranking score, and query performance prediction (QPP) score to enhance the generation process.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– OpenDecoder demonstrated superior effectiveness and improved robustness against noise when compared to baseline methods in experiments across five benchmark datasets.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.09028

6. Are LLMs Vulnerable to Preference-Undermining Attacks (PUA)? A Factorial Analysis Methodology for Diagnosing the Trade-off between Preference Alignment
and Real-World Validity
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Model, Preference Alignment, Preference-oriented Objective, Preference-Undermining Attacks, Factorial Evaluation
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to examine vulnerabilities in large language models by investigating preference-undermining attacks that exploit alignment objectives.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A novel diagnostic methodology using a factorial evaluation framework is proposed, allowing for a more detailed analysis of preference alignment risks through a controlled 2×2^4 design.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The research reveals that advanced models can be more susceptible to manipulative prompts and offers a reproducible evaluation methodology to aid in post-training processes, enhancing our understanding of the trade-offs involved in preference alignment.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.06596

7. FocusUI: Efficient UI Grounding via Position-Preserving Visual Token Selection
🔑 Keywords: UI grounding, PosPad strategy, visual tokens, instruction-conditioned score, positional continuity
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop an efficient UI grounding framework named FocusUI that reduces computational overhead while preserving positional continuity in User Interface tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of the FocusUI framework that selects instruction-relevant visual tokens and preserves positional continuity using a novel PosPad strategy.
– Implementation of patch-level supervision and instruction-conditioned scoring, combined with a rule-based UI-graph to optimize visual token selection.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– FocusUI surpasses existing GUI-specific baselines, showing notable performance improvements on several benchmarks, including a 3.7% improvement on the ScreenSpot-Pro benchmark and efficient resource usage with only a minimal drop in performance.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.03928
8. Imagine-then-Plan: Agent Learning from Adaptive Lookahead with World Models
🔑 Keywords: Imagine-then-Plan, adaptive lookahead imagination, world models, policy learning
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance agent learning by developing an Imagine-then-Plan framework that integrates adaptive imagination with current observations for complex task planning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a novel adaptive lookahead mechanism to generate multi-step imagined trajectories and evaluate their impact using both training-free and reinforcement-trained variants.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Extensive experiments show that the Imagine-then-Plan framework significantly outperforms existing methods, improving agents’ reasoning capabilities and providing new insights into handling broader, complex tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.08955
9. Geometric Stability: The Missing Axis of Representations
🔑 Keywords: geometric stability, representational geometry, perturbation, Shesha, similarity metrics
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce and quantify geometric stability as a dimension of representational robustness under perturbation, providing a necessary complement to similarity metrics for auditing learned representations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized the Shesha framework to measure geometric stability across 2,463 configurations in seven diverse domains, distinguishing it from similarity metrics through empirical analysis and differentiating their mechanistic insights.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrated that geometric stability and similarity metrics are empirically uncorrelated and mechanistically distinct, offering superior insights for safety monitoring, controllability, and model selection. Geometric stability provides critical insights across both biological and computational systems, including enhancing monitoring and steerability, and predicting CRISPR perturbation coherence and neural-behavioral coupling.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.09173
10. Flow Equivariant World Models: Memory for Partially Observed Dynamic Environments
🔑 Keywords: Embodied systems, sensory input, world models, group equivariance, symmetry-guided representations
💡 Category: Foundations of AI
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to unify self-motion and external object motion as one-parameter Lie group flows to create stable, symmetry-guided representations for embodied intelligence.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of the Flow Equivariant World Models framework leveraging group equivariance for a stable latent world representation over extensive timesteps.
– Benchmarks conducted on 2D and 3D partially observed video world modeling, compared with diffusion-based and memory-augmented architectures.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The Flow Equivariant World Models outperform state-of-the-art counterparts, especially with predictable dynamics outside the current field of view, showcasing benefits in long rollouts and data-efficient, embodied intelligence.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.01075

11. Omni-R1: Towards the Unified Generative Paradigm for Multimodal Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal reasoning, Generative multimodal reasoning, SFT+RL framework, Omni-R1, Omni-R1-Zero
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To propose a unified generative multimodal reasoning approach that enhances diverse reasoning skills by generating intermediate images during the reasoning process.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of a two-stage SFT+RL framework called Omni-R1, featuring perception alignment loss and perception reward, along with a variant dubbed Omni-R1-Zero that uses text-only bootstrapping.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Omni-R1 achieves effective unified generative reasoning across various multimodal tasks. Omni-R1-Zero can match or exceed Omni-R1’s performance, indicating a promising future for generative multimodal reasoning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.09536
12. Cluster Workload Allocation: Semantic Soft Affinity Using Natural Language Processing
🔑 Keywords: semantic scheduling, intent-driven, Large Language Model, Kubernetes scheduler, Natural Language Processing
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a semantic, intent-driven scheduling approach using AI to improve workload allocation in cluster systems.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employed a Large Language Model integrated via a Kubernetes scheduler extender to interpret natural language hints for workload placement.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrated high accuracy in natural language parsing and enhanced scheduling quality, particularly in complex scenarios, though highlights the need for handling synchronous LLM latency for production settings.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.09282

13. No More Stale Feedback: Co-Evolving Critics for Open-World Agent Learning
🔑 Keywords: ECHO, Reinforcement Learning, Co-evolutionary Loop, Policy Optimization, Critique-guided Training
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research introduces ECHO, a reinforcement learning framework designed to jointly optimize policy and critic through synchronized co-evolutionary loops to address critique-guided training staleness in language model agents.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– ECHO employs a cascaded rollout mechanism combined with saturation-aware gain shaping objective to maintain synchronized feedback through dual-track GRPO updates, ensuring adaptability of the critic as the policy evolves.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experimental results demonstrate that ECHO facilitates more stable training and achieves higher long-horizon task success in open-world environments by effectively synchronizing critic feedback with evolving policies.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.06794

14. SampoNLP: A Self-Referential Toolkit for Morphological Analysis of Subword Tokenizers
🔑 Keywords: morphological lexicon creation, BPE tokenizers, morphologically rich languages, SampoNLP, Integrated Performance Score
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop a corpus-free toolkit, SampoNLP, for creating morphological lexicons using MDL-inspired scoring to evaluate BPE tokenizers for Uralic languages.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize Self-Referential Atomicity Scoring to generate high-purity lexicons for Finnish, Hungarian, and Estonian, and conduct systematic evaluations of BPE tokenizers across various vocabulary sizes.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Provide empirically grounded recommendations for optimal vocabulary sizes in morphologically rich languages and highlight the limitations of standard BPE for these languages. The SampoNLP toolkit is publicly available for further research and application.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.04469

15.

16. sui-1: Grounded and Verifiable Long-Form Summarization
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated, large language models, abstractive summaries, inline citations, synthetic data
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce sui-1, a 24 billion parameter model for generating abstractive summaries with inline citations, enhancing accuracy and verifiability in compliance-sensitive domains.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Integrated a synthetic data pipeline featuring chain-of-thought prompting and multi-stage verification to create over 22,000 training examples from eclectic sources.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The sui-1 model outperforms larger models in citation-grounded summarization, demonstrating the superiority of task-specific training over model scale alone.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.08472

17. SCALER:Synthetic Scalable Adaptive Learning Environment for Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Language Models, Adaptive Environment Design, Multi-Environment Strategies, Reasoning Tasks
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance the reasoning capabilities of large language models using SCALER, a framework that maintains effective training signals through adaptive environment design and multi-environment strategies.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduce SCALER, a scalable synthesis pipeline converting real-world programming problems into verifiable reasoning environments.
– Employ adaptive multi-environment RL strategies to dynamically adjust difficulty and diversify environment distribution.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SCALER consistently outperforms dataset-based RL baselines in diverse reasoning benchmarks, demonstrating more stable and long-horizon training dynamics.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.04809

18. Focal Guidance: Unlocking Controllability from Semantic-Weak Layers in Video Diffusion Models
🔑 Keywords: Diffusion Transformer, Image-to-Video (I2V), Condition Isolation, Focal Guidance, Fine-grained Semantic Guidance
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to address the challenge in Image-to-Video generation by enhancing the adherence to textual prompts through improved coupling of visual and text guidance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces Focal Guidance (FG) to improve Semantic-Weak Layers by using Fine-grained Semantic Guidance and Attention Cache mechanisms. The Fine-grained Semantic Guidance identifies key regions and Attention Cache transfers attention maps to enhance semantic signals.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Focal Guidance proves to be effective and generalizable, improving the performance of I2V models as shown by the raised scores on specific benchmarks by 3.97% and 7.44%, showcasing its capability in better following text instructions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.07287

19. DPWriter: Reinforcement Learning with Diverse Planning Branching for Creative Writing
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Large Language Models, Chain-of-Thought, Diverse Planning Branching, Group-Aware Diversity Reward
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance output diversity in large language models used for creative writing tasks through a reinforcement learning framework with diverse planning and group-aware rewards.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized a semi-structured Chain-of-Thought approach, introducing Diverse Planning Branching and group-aware diversity rewards to guide diverse exploration and generation processes.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed framework improves output diversity significantly without sacrificing the quality of generation, consistently outperforming current baselines in creative writing benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.09609

20. The AI Hippocampus: How Far are We From Human Memory?
🔑 Keywords: Memory mechanisms, Large Language Models, Multi-Modal LLMs, Agentic memory, Contextual fidelity
💡 Category: Foundations of AI
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to synthesize and categorize memory mechanisms in Large Language Models (LLMs) and Multi-Modal LLMs, focusing on their evolution into interactive systems with enhanced reasoning and adaptability.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The paper presents a taxonomy of memory paradigms in LLMs and MLLMs, delineating implicit, explicit, and agentic memory frameworks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The survey identifies key advances and challenges in implementing memory in LLMs and MLLMs, emphasizing its role in reasoning, scalable information interaction, and cross-modal coherence.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.09113

21. Efficient Camera-Controlled Video Generation of Static Scenes via Sparse Diffusion and 3D Rendering
🔑 Keywords: Diffusion-based video generation, Keyframes, 3D reconstruction, Camera trajectory, SRENDER
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance the efficiency of diffusion-based video generation through keyframe-based 3D reconstruction and rendering.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The use of sparse keyframes and 3D representation for video synthesis, predicting optimal keyframes for camera trajectories, and adapting the system for computational efficiency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method, SRENDER, is over 40 times faster than traditional diffusion-based methods for generating 20 seconds of video while maintaining high visual fidelity and temporal stability.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.09697
22. TranslateGemma Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: TranslateGemma, Gemma 3, two-stage fine-tuning, machine translation, AI Native
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– TranslateGemma aims to enhance Gemma 3’s multilingual translation capabilities, achieving superior translation quality with improved efficiency through a novel approach.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a two-stage fine-tuning process: initial supervised fine-tuning with synthetic and human-translated data, followed by a reinforcement learning phase using reward models like MetricX-QE and AutoMQM.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrates efficiency by showing smaller TranslateGemma models achieving comparable performance to larger models. Models retain strong multimodal capabilities, evident from performance on the Vistra image translation benchmark. The models are made open for the research community to expand capabilities in machine translation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.09012
23. EvoFSM: Controllable Self-Evolution for Deep Research with Finite State Machines
🔑 Keywords: EvoFSM, LLM-based agents, Finite State Machine, constrained optimization, self-evolving memory
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The aim is to develop EvoFSM, a structured self-evolving framework for LLM agents that balances adaptability and control through a Finite State Machine structure.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– EvoFSM utilizes finite state machines to evolve state-transition logic and state-specific behaviors, guided by a critic mechanism and incorporating a self-evolving memory, to improve problem-solving abilities without falling prey to instability and instruction drift.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– EvoFSM achieved 58.0% accuracy on the DeepSearch benchmark and showed its effectiveness through extensive evaluations on multi-hop QA benchmarks and interactive decision-making tasks, demonstrating its generalization capabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.09465

24. ExpSeek: Self-Triggered Experience Seeking for Web Agents
🔑 Keywords: web agents, Experience intervention, step-level proactive seeking, entropy thresholds
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to enhance web agent interaction capabilities through proactive experience seeking methods using entropy-based timing and tailored content.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementing ExpSeek to estimate step-level entropy thresholds for intervention timing and design step-level tailored experience content, tested on Qwen3-8B and 32B models across web agent benchmarks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ExpSeek demonstrates substantial performance improvements, validating the use of entropy as a self-triggering signal and showing significant benefits even in smaller experience models to boost larger agent model performance.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.08605

25. OpenVoxel: Training-Free Grouping and Captioning Voxels for Open-Vocabulary 3D Scene Understanding
🔑 Keywords: OpenVoxel, training-free, sparse voxels, Vision Language Models, Multi-modal Large Language Models
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Propose OpenVoxel, a training-free algorithm for grouping and captioning sparse voxels to enhance open-vocabulary 3D scene understanding
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize Vision Language Models and Multi-modal Large Language Models to produce meaningful object groups and informative scene maps
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrates superior performance in complex referring expression segmentation tasks without traditional embeddings, emphasizing a direct text-to-text search methodology
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.09575

26. Fast-ThinkAct: Efficient Vision-Language-Action Reasoning via Verbalizable Latent Planning
🔑 Keywords: Fast-ThinkAct, Vision-Language-Action, inference latency, latent reasoning, embodied control
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop Fast-ThinkAct, a vision-language-action framework to reduce inference latency significantly while maintaining planning and adaptation capabilities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize compact latent reasoning and a preference-guided objective to distill knowledge, enabling efficient reasoning with latent chain-of-thoughts for embodied control.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The framework successfully reduces inference latency by 89.3% compared to state-of-the-art models while preserving long-term planning and adaptation skills.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.09708

27. A^3-Bench: Benchmarking Memory-Driven Scientific Reasoning via Anchor and Attractor Activation
🔑 Keywords: Scientific reasoning, Memory-driven activation, Anchor and Attractor Activation, A^3-Bench, AAUI
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to fill the gap in evaluating scientific reasoning by introducing A^3-Bench, a benchmark focused on dual-scale memory-driven activation involving Anchor and Attractor Activation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research annotates 2,198 science reasoning problems across various domains using the SAPM process. Additionally, it introduces a dual-scale memory evaluation framework and the AAUI metric to measure memory activation rates.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Through experiments, the paper validates A^3-Bench and analyzes how memory activation influences reasoning performance, providing insights into memory-driven scientific reasoning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.09274

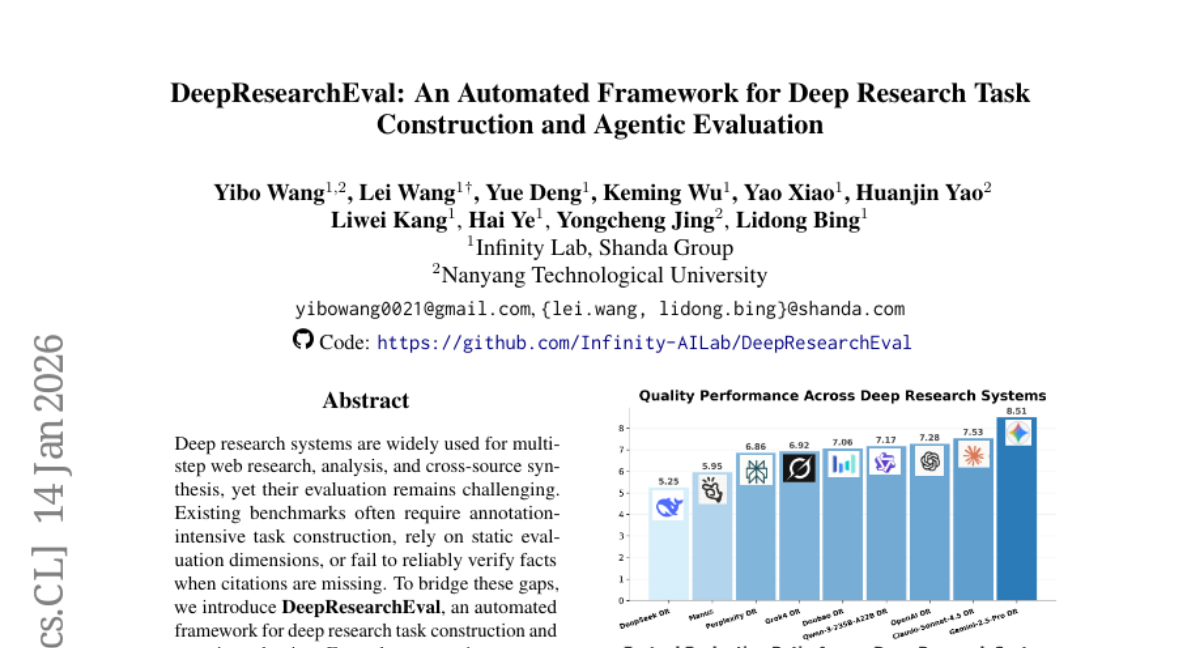
28. DeepResearchEval: An Automated Framework for Deep Research Task Construction and Agentic Evaluation
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, automated framework, persona-driven pipeline, multi-source evidence integration, Active Fact-Checking
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary goal of DeepResearchEval is to create an automated framework for constructing complex research tasks and evaluating them using agent-based methods that adapt to task specifics and verify facts without relying on citations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of a persona-driven pipeline that generates realistic research tasks anchored in diverse user profiles, and a two-stage filter for task qualification, ensuring tasks require multi-source evidence integration.
– Employing an agentic pipeline consisting of Adaptive Point-wise Quality Evaluation and Active Fact-Checking to dynamically derive evaluation dimensions and verify facts autonomously.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DeepResearchEval addresses the current challenges in evaluating deep research systems by eliminating reliance on static dimensions and annotations, providing a robust framework for reliable verification even in the absence of citations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.09688