AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20260123
1. EvoCUA: Evolving Computer Use Agents via Learning from Scalable Synthetic Experience
🔑 Keywords: EvoCUA, AI Native, Policy Optimization, Data Generation, Evolutionary Cycle
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce EvoCUA, a native computer-use agent model that merges autonomous task generation with policy optimization to enhance performance in complex tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed a verifiable synthesis engine for diverse task generation with executable validators.
– Designed scalable infrastructure for asynchronous sandbox rollouts.
– Employed iterative evolving learning to dynamically regulate policy updates.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– EvoCUA achieved a new state-of-the-art success rate of 56.7% on the OSWorld benchmark.
– Demonstrated superior performance over previous models, showing generalizability and scalability across foundation models of different scales.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.15876

2. HERMES: KV Cache as Hierarchical Memory for Efficient Streaming Video Understanding
🔑 Keywords: HERMES, real-time responses, KV cache, hierarchical memory framework, video understanding
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of this research is to propose HERMES, a training-free architecture designed to achieve real-time and accurate understanding of video streams, overcoming limitations of current Multimodal Large Language Models in handling streaming video inputs.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research involves the use of a hierarchical memory framework based on KV cache reuse, allowing for efficient streaming video understanding. It eliminates the need for additional computations with incoming user queries, ensuring real-time responses.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– HERMES offers significant improvements in response times, achieving 10 times faster TTFT than previous state-of-the-art models. Despite reducing video tokens by up to 68%, it maintains superior or comparable accuracy across various benchmarks, outperforming existing solutions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.14724

3. LLM-in-Sandbox Elicits General Agentic Intelligence
🔑 Keywords: LLM-in-Sandbox, code sandbox, general intelligence, Reinforcement Learning, sandbox exploration
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to enable large language models (LLMs) to perform tasks across diverse domains by exploring a code sandbox environment, achieving general intelligence without the need for additional training.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– LLM-in-Sandbox employs a virtual code sandbox to allow LLMs to enhance their generalization capabilities and perform tasks spontaneously, such as accessing external resources and executing scripts. Additionally, LLM-in-Sandbox Reinforcement Learning (RL) method is used to train models for effective sandbox exploration.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The LLM-in-Sandbox framework demonstrates robust generalization across various domains including mathematics, physics, chemistry, biomedicine, and more, in both training-free and post-trained settings. The research also includes an analysis of computational efficiency and system perspectives, facilitating real-world deployment by open-sourcing it as a Python package.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.16206

4. Stable-DiffCoder: Pushing the Frontier of Code Diffusion Large Language Model
🔑 Keywords: Stable-DiffCoder, block diffusion, continual pretraining, code modeling, structured code modeling
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to demonstrate the superior performance of Stable-DiffCoder, a block diffusion code model, compared to autoregressive baselines for code modeling tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes block diffusion continual pretraining with warmup and clipped noise schedule, coupled with supervised fine-tuning to enhance code modeling capabilities.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Stable-DiffCoder outperforms autoregressive counterparts in code benchmarks, enhances structured code modeling for editing and reasoning, and effectively supports low-resource coding languages through data augmentation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.15892

5. Learning to Discover at Test Time
🔑 Keywords: Test-Time Training, Reinforcement Learning, Continual Learning, OpenAI gpt-oss-120b
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to discover optimal solutions for specific scientific problems through Test-Time Training to Discover (TTT-Discover), focused on individual challenges rather than generalization.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes reinforcement learning during test time, enabling the LLM to continue training with experience specific to the test problem, prioritizing promising solutions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– TTT-Discover sets a new state of the art in various fields including mathematics, GPU kernel engineering, algorithm design, and biology, with solutions reviewed by experts, achieved using an open model and reproducible with publicly available code.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.16175

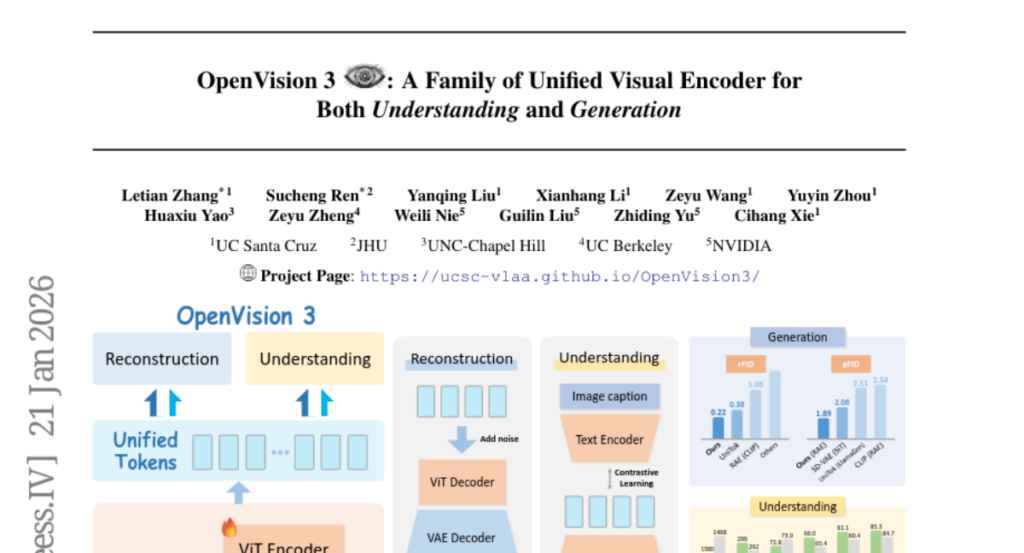
6. OpenVision 3: A Family of Unified Visual Encoder for Both Understanding and Generation
🔑 Keywords: OpenVision 3, VAE-compressed image latents, ViT encoder, contrastive learning, unified modeling
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to develop OpenVision 3, an advanced vision encoder that learns a unified visual representation for both image understanding and generation by integrating VAE-compressed image latents with ViT architecture and optimizing reconstruction and semantic signals.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– OpenVision 3 leverages a ViT encoder trained with VAE-compressed image latents, combining reconstruction with semantic optimization through contrastive learning and image-captioning objectives in a shared latent space.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The unified design demonstrates effective performance for multimodal understanding and generating tasks, validated by extensive downstream evaluations, surpassing standard CLIP-based encoders in generative frameworks like RAE.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.15369
7. Terminal-Bench: Benchmarking Agents on Hard, Realistic Tasks in Command Line Interfaces
🔑 Keywords: Terminal-Bench 2.0, AI agents, long-horizon tasks, computer terminal environments, real-world tasks
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To evaluate AI agents’ capabilities in real-world scenarios using a challenging benchmark called Terminal-Bench 2.0.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Curated a hard benchmark composed of 89 tasks in computer terminal environments, each featuring a unique environment, human-written solution, and comprehensive tests for verification.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Frontier models and agents score less than 65% on the benchmark; error analysis is conducted to identify areas for improvement. Dataset and evaluation harness are published for future research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.11868

8. PROGRESSLM: Towards Progress Reasoning in Vision-Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language Models, ProgressLM-45K, ProgressLM-3B, progress reasoning, training-free prompting
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– This paper aims to evaluate and improve the ability of Vision-Language Models to reason about task progress from partial observations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced Progress-Bench as a benchmark for progress reasoning evaluation.
– Employed a two-stage progress reasoning approach using both training-free prompting and a training-based method with the ProgressLM-45K dataset.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study reveals that most Vision-Language Models struggle with task progress estimation, and are sensitive to modality and viewpoint changes.
– The training-based approach, ProgressLM-3B, provided significant improvements even with a small model size, highlighting areas where progress reasoning succeeds or fails.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.15224

9. 360Anything: Geometry-Free Lifting of Images and Videos to 360°
🔑 Keywords: 360° panoramas, diffusion transformers, perspective-to-equirectangular mapping, Circular Latent Encoding, zero-shot camera estimation
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to develop a geometry-free framework for transforming perspective images and videos into 360° panoramas, bypassing the need for camera metadata.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers employ pre-trained diffusion transformers and treat both input and target as token sequences to map perspectives to equirectangular spaces purely through data-driven means. They also introduce Circular Latent Encoding to resolve seam artifacts.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The framework, named 360Anything, achieves state-of-the-art performance in generating 360° panoramas from images and videos. It surpasses existing methods that rely on ground-truth camera information and demonstrates enhanced geometric understanding in zero-shot camera FoV and orientation estimation benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.16192

10. ActionMesh: Animated 3D Mesh Generation with Temporal 3D Diffusion
🔑 Keywords: 3D diffusion models, temporal axis, rig-free animations, geometric accuracy, temporal consistency
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces AI Native ActionMesh to enhance animated 3D mesh generation by incorporating a temporal axis to extend 3D diffusion models, ensuring high-quality, rig-free animations from various input types.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a temporal 3D diffusion model to generate synchronized latent sequences of time-varying 3D shapes.
– Implements a temporal 3D autoencoder to convert independent shape sequences into deformations of a reference shape, facilitating animation construction.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The ActionMesh framework achieves state-of-the-art performance in geometric accuracy and temporal consistency, allowing for rapid iteration and practical applications like texturing and retargeting.
– Evaluated on standard video-to-4D benchmarks, the model delivers animated 3D meshes with unprecedented speed and quality.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.16148
11. LLM Prompt Evaluation for Educational Applications
🔑 Keywords: Prompt Engineering, Large Language Models, Metacognitive Learning Strategies, Tournament-Style Evaluation, Glicko2 Rating System
💡 Category: AI in Education
🌟 Research Objective:
– To design and evaluate LLM prompts that produce personalized and pedagogically aligned outputs for educational applications.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementing a tournament-style evaluation framework using the Glicko2 rating system to compare six distinct prompt templates across format, dialogue support, and appropriateness.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– A prompt template focused on strategic reading significantly outperformed others, highlighting the importance of evidence-based prompt development in educational contexts.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.16134

12. Numba-Accelerated 2D Diffusion-Limited Aggregation: Implementation and Fractal Characterization
🔑 Keywords: DLA, Numba, JIT compilation, fractal dimension, non-equilibrium statistical mechanics
💡 Category: Foundations of AI
🌟 Research Objective:
– To simulate two-dimensional Diffusion-Limited Aggregation (DLA) using a high-performance framework called dla-ideal-solver, exploring the Laplacian growth instability.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of Numba-accelerated Python with just-in-time (JIT) compilation to achieve high computational throughput while maintaining flexibility.
– Investigation of the standard fractal dimension across different injection geometries and walker concentrations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Confirmation of a crossover from standard fractal dimension (approx 1.71) to Eden-like compact growth (approx 1.87) in high-density environments.
– Establishment of a reproducible, open-source testbed for studying phase transitions in non-equilibrium statistical mechanics.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.15440

13. Agentic Uncertainty Quantification
🔑 Keywords: Dual-Process Agentic UQ, Uncertainty-Aware Memory, Uncertainty-Aware Reflection, closed-loop benchmarks, trajectory-level calibration
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to enhance reasoning reliability in AI agents by addressing the issue known as the “Spiral of Hallucination” through a unified Dual-Process framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework consists of two mechanisms: System 1 (Uncertainty-Aware Memory) and System 2 (Uncertainty-Aware Reflection), which work together to convert verbalized uncertainty into active control signals.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed training-free AUQ framework demonstrates superior performance and ensures trajectory-level calibration in AI agents, representing a significant advancement towards more reliable AI systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.15703

14. Wigner’s Friend as a Circuit: Inter-Branch Communication Witness Benchmarks on Superconducting Quantum Hardware
🔑 Keywords: Quantum circuits, IBM Quantum hardware, inter-branch communication witnesses, coherence witnesses, device noise
💡 Category: Quantum Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To implement and benchmark a circuit family for estimating operational inter-branch communication witnesses on IBM Quantum hardware, focusing on correlations in classical measurement records.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of a five-qubit instance of the protocol as an inter-register message-transfer pattern within a single circuit, evaluating its performance under realistic device noise and compilation constraints.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The experiment demonstrated population-based visibility of 0.877 and coherence witnesses of 0.840 and -0.811 along orthogonal axes, with a phase-sensitive magnitude of approximately 1.17. These results highlight the complementary sensitivity of coherence witnesses to off-diagonal noise.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.16004

15.

16. MirrorBench: An Extensible Framework to Evaluate User-Proxy Agents for Human-Likeness
🔑 Keywords: Large language models (LLMs), conversational systems, user proxy agents, MIRRORBENCH, lexical-diversity metrics
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to evaluate large language models as user simulators using a reproducible benchmark framework to generate human-like conversational responses across various tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers present MIRRORBENCH, a modular and extensible benchmarking framework incorporating typed interfaces, metadata-driven registries, and multi-backend support. The system evaluates user proxies with both lexical-diversity metrics and LLM-judge-based metrics across four open datasets.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MIRRORBENCH provides variance-aware results and identifies systematic gaps between user proxies and genuine human users, offering an open-source framework for consistent, principled evaluation of user proxies.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.08118
17. From Passive Metric to Active Signal: The Evolving Role of Uncertainty Quantification in Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Uncertainty, Active Control Signal, Advanced Reasoning, Autonomous Agents, Reinforcement Learning
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to address reliability challenges in Large Language Models (LLMs) by leveraging uncertainty as an active control signal across various AI methodologies.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizing uncertainty as an active control signal in advanced reasoning, autonomous agents, and reinforcement learning, supported by Bayesian methods and conformal prediction frameworks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Emphasizing the importance of mastering uncertainty as a crucial trend for developing scalable, reliable, and trustworthy AI systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.15690
18. Agentic Confidence Calibration
🔑 Keywords: Agentic Confidence Calibration, Holistic Trajectory Calibration, AI agents, Interpretability, Transferability
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces Agentic Confidence Calibration to address the unique challenges posed by AI agent systems, such as compounding errors and uncertainty in complex tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Proposes a novel framework, Holistic Trajectory Calibration (HTC), which incorporates process-level features and employs a simple, interpretable model to improve reliability.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– HTC surpasses strong baselines in calibration and discrimination and provides interpretability, transferability, and generalization across different domains without retraining.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.15778

19. VIOLA: Towards Video In-Context Learning with Minimal Annotations
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal Large Language Models, low-resource video domains, In-Context Learning, label-efficient framework, confidence-aware retrieval
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce VIOLA, a framework designed to efficiently adapt multimodal large language models to low-resource video domains by reducing the need for extensive expert annotations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize density-uncertainty-weighted sampling to maximize annotation budget efficiency while ensuring diverse and informative data selection.
– Develop a confidence-aware retrieval mechanism to effectively use unlabeled data and avoid noise propagation in model adaptation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The VIOLA framework significantly outperforms various baseline methods in low-resource settings, demonstrating its ability to achieve robust adaptation with minimal annotation costs across multiple benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.15549

20. Cosmos Policy: Fine-Tuning Video Models for Visuomotor Control and Planning
🔑 Keywords: Cosmos Policy, robot policy, latent diffusion process, action generation, model-based planning
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary objective of the study is to adapt a pretrained video model into an effective robot policy through a single stage of post-training, enabling direct action generation and planning without any architectural modifications.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers introduce Cosmos Policy, which utilizes a large pretrained video model known as Cosmos-Predict2. The model is adapted by executing single-stage post-training on robot demonstration data, exploiting spatiotemporal priors and latent diffusion processes to encode robot actions and future state images directly.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Cosmos Policy demonstrates state-of-the-art performance on simulation benchmarks (LIBERO, RoboCasa) and real-world bimanual manipulation tasks, outperforming existing diffusion policies and vision-language-action models. Additionally, it refines its world model and value function through policy rollout data, achieving higher success rates in complex tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.16163
21. VideoMaMa: Mask-Guided Video Matting via Generative Prior
🔑 Keywords: VideoMaMa, zero-shot generalization, video diffusion models, scalable pseudo-labeling, Matting Anything in Video
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to tackle the challenge of generalizing video matting models to real-world videos despite limited labeled data by presenting the Video Mask-to-Matte Model (VideoMaMa).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– VideoMaMa uses pretrained video diffusion models to transform coarse segmentation masks into accurate alpha mattes, enabling zero-shot generalization and facilitating the creation of a scalable pseudo-labeling pipeline.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The research highlights the importance of large-scale pseudo-labeled video matting and demonstrates the effectiveness of the new Matting Anything in Video (MA-V) dataset in advancing the robustness and scalability of video matting research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.14255
22. Towards Automated Kernel Generation in the Era of LLMs
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, Large language models, Kernel generation, AI Systems and Tools, Agent-based systems
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address scalability challenges in hardware-specific code development by automating kernel generation and optimization using large language models and agent-based systems.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A structured overview of existing LLM-based approaches and agentic optimization workflows.
– Systematic compilation of datasets and benchmarks for learning and evaluation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Recent advances in LLMs and LLM-based agents offer new possibilities for scalable kernel development.
– A comprehensive reference is established for future research and automated kernel optimization through the outlined challenges and directions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.15727

23. Rethinking Composed Image Retrieval Evaluation: A Fine-Grained Benchmark from Image Editing
🔑 Keywords: Composed Image Retrieval, Image Editing, Multimodal Models, Benchmarks, Modality Biases
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a new fine-grained composed image retrieval benchmark using image editing to reveal capability gaps in existing models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize image editing techniques for precise control in synthesizing queries across diverse categories.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Significant capability gaps exist in current multimodal embedding models, revealing limitations in current benchmarks such as modality biases and insufficient categorical coverage.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.16125

24. Qwen3-TTS Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: Qwen3-TTS, multilingual, voice cloning, dual-track LM architecture, speech tokenizers
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To present the Qwen3-TTS series, a family of advanced multilingual text-to-speech models with capabilities such as voice cloning and controllable speech generation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a dual-track LM architecture and specialized speech tokenizers for efficient streaming synthesis.
– Training on over 5 million hours of speech data across 10 languages.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The Qwen3-TTS series shows state-of-the-art performance in both objective and subjective benchmarks, supporting applications with extreme bitrate reduction and ultra-low-latency streaming.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.15621

25. SAMTok: Representing Any Mask with Two Words
🔑 Keywords: Multi-modal LLMs, Discrete Mask Tokenization, Pixel-wise Capabilities, State-of-the-art, Reinforcement Learning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enable pixel-wise capabilities in multi-modal LLMs through SAMTok by leveraging discrete mask tokenization and standard training methods.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes SAMTok, a discrete mask tokenizer, to convert region masks into language tokens for pixel-wise learning.
– Implements standard next-token prediction and simple reinforcement learning without architectural changes.
– Trains on diverse masks with a mask encoder and residual vector quantizer.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieves state-of-the-art performance on various vision-language tasks, providing a scalable solution for equipping MLLMs with robust pixel-wise capabilities.
– Introduces a textual answer-matching reward to enhance reinforcement learning efficiency for mask generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.16093

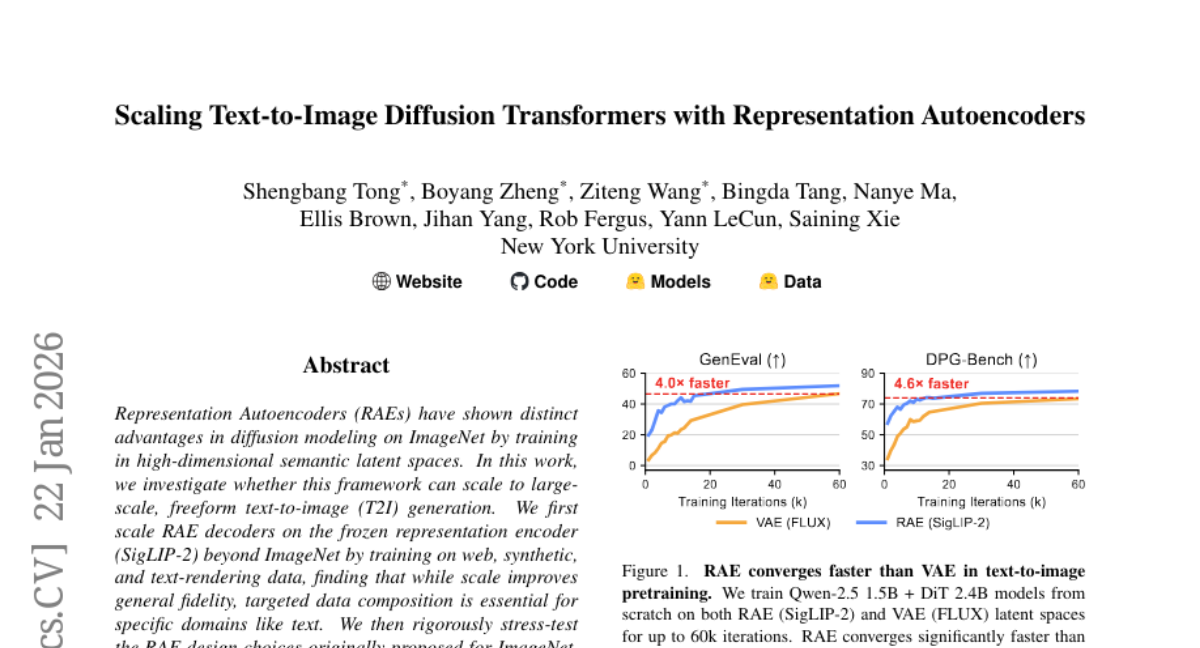
26. Scaling Text-to-Image Diffusion Transformers with Representation Autoencoders
🔑 Keywords: Representation Autoencoders, Text-to-Image Generation, Semantic Latent Spaces, Diffusion Modeling, AI Native
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To investigate the scalability and performance of Representation Autoencoders (RAEs) in large-scale text-to-image generation and assess their effectiveness compared to VAEs.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Evaluating RAE decoders scaled on the frozen representation encoder with varied data types, testing RAE design choices, and conducting controlled comparisons between RAEs and state-of-the-art FLUX VAEs across multiple scales.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RAEs outperform VAEs in terms of stability and performance, with faster convergence and better generation quality in large-scale text-to-image tasks, while maintaining stability during extended training. They provide a simplified and stronger foundation for multimodal reasoning in shared representation spaces.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.16208
27. BayesianVLA: Bayesian Decomposition of Vision Language Action Models via Latent Action Queries
🔑 Keywords: Information Collapse, Bayesian decomposition, Latent Action Queries, conditional Pointwise Mutual Information, Vision-Language-Action
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address the language-action grounding issues in robot manipulation by preventing information collapse and enhancing out-of-distribution generalization using a Bayesian framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized Bayesian decomposition to create a dual-branch architecture, estimating a vision-only prior and a language-conditioned posterior to maximize the conditional Pointwise Mutual Information between actions and instructions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– BayesianVLA significantly improves generalization without requiring new data, as evidenced by an 11.3% improvement on OOD benchmarks, demonstrating robust language grounding in action.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.15197

28. The Flexibility Trap: Why Arbitrary Order Limits Reasoning Potential in Diffusion Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Diffusion Large Language Models, reasoning potential, arbitrary order generation, reinforcement learning, Group Relative Policy Optimization
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To investigate the impact of arbitrary order generation in diffusion large language models (dLLMs) on reasoning capabilities and optimize the generation method for better reasoning performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Analyzing the effects of using arbitrary order generation in dLLMs and proposing the use of JustGRPO, a minimalist approach employing Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), to enhance reasoning without forfeiting parallel decoding.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Arbitrary order generation in its current form limits the reasoning ability of dLLMs by bypassing high-uncertainty tokens necessary for effective exploration. JustGRPO, a more structured approach, achieves superior accuracy in reasoning tasks while maintaining the benefits of dLLMs.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.15165
