AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20260126

1. LongCat-Flash-Thinking-2601 Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: Mixture-of-Experts, agentic reasoning, domain-parallel expert training, asynchronous reinforcement learning, real-world noise
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a 560-billion-parameter Mixture-of-Experts model achieving state-of-the-art performance on agentic benchmarks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize a unified training framework combining domain-parallel expert training with fusion.
– Extend asynchronous reinforcement learning for stable and efficient multi-environment training.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The model demonstrates strong generalization to complex tool interactions and robust behavior in real-world environments.
– Enhanced robustness is achieved by incorporating real-world noise patterns into the training process.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.16725

2. TwinBrainVLA: Unleashing the Potential of Generalist VLMs for Embodied Tasks via Asymmetric Mixture-of-Transformers
🔑 Keywords: TwinBrainVLA, Vision-Language Model (VLM), robotic control, Asymmetric Mixture-of-Transformers, proprioception
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of the research is to resolve the tension between maintaining high-level semantic understanding and learning fine-grained sensorimotor skills in robotic control using a novel model called TwinBrainVLA.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– TwinBrainVLA coordinates a generalist and a specialist VLM through an asymmetric mixture-of-transformers mechanism, combining a frozen “Left Brain” for visual reasoning with a trainable “Right Brain” for embodied perception.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments reveal that TwinBrainVLA surpasses state-of-the-art baselines in manipulation performance while preserving comprehensive visual understanding, suggesting a promising path for developing versatile robots that balance semantic understanding and physical dexterity.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.14133

3. Memory-V2V: Augmenting Video-to-Video Diffusion Models with Memory
🔑 Keywords: Memory-V2V, video-to-video diffusion models, cross-consistency, dynamic tokenization, DiT backbone
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance multi-turn video editing by introducing Memory-V2V, which maintains cross-consistency through explicit memory mechanisms and efficient token compression.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Memory-V2V employs an external cache for accurate retrieval and dynamic tokenization to condition the current editing on prior results. A learnable token compressor within the DiT backbone is proposed to compress redundant tokens while preserving essential visual cues.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The research demonstrates that Memory-V2V significantly improves cross-consistency and computational efficiency in video editing, with a 30% speedup, while maintaining or improving task-specific performance compared to state-of-the-art baselines.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.16296
4. Jet-RL: Enabling On-Policy FP8 Reinforcement Learning with Unified Training and Rollout Precision Flow
🔑 Keywords: Quantized RL training, FP8 precision, numerical mismatch, Jet-RL, stability issues
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to address the challenges in Quantized Reinforcement Learning training, specifically focusing on optimizing training stability and efficiency using FP8 precision.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A comprehensive analysis of FP8 RL training is conducted, proposing a unified FP8 precision framework known as Jet-RL. Extensive experiments compare Jet-RL with traditional BF16-training + FP8-rollout strategies.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Jet-RL demonstrates significant improvements, achieving up to 33% speedup in the rollout phase, 41% speedup in the training phase, and a 16% overall speedup, while maintaining stable convergence and minimal accuracy degradation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.14243

5. DSGym: A Holistic Framework for Evaluating and Training Data Science Agents
🔑 Keywords: Data Science Agents, DSGym, AI Native, Benchmarks, Execution-verified
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce DSGym, a standardized framework for evaluating and training data science agents within self-contained execution environments.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of DSGym with a modular architecture to add tasks and tools, along with a curated task suite DSGym-Tasks, including DSBio and DSPredict for expanded coverage.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DSGym provides a comprehensive testbed for rigorous end-to-end measurement of data science agents’ abilities, outperforming existing models like GPT-4o on standardized benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.16344

6. GameTalk: Training LLMs for Strategic Conversation
🔑 Keywords: GameTalk, large language models, multi-turn interactions, reward shaping, fine-tuning methods
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To train large language models (LLMs) for strategic decision-making through multi-turn dialogue by optimizing global objectives across complete conversations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The adaptation of fine-tuning methods like GRPO, DPO, and STaR to incorporate reward signals dependent on the full interaction.
– Evaluation on a set of complex games focusing on reasoning, coordination, and opponent modeling.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– GameTalk outperforms untrained models in complex game scenarios, with DPO showing the most significant improvements, highlighting conversational fine-tuning as a promising approach for LLMs in interactive environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.16276

7. Endless Terminals: Scaling RL Environments for Terminal Agents
🔑 Keywords: Endless Terminals, reinforcement learning, autonomous pipeline, procedural generation, PPO
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop an autonomous pipeline, Endless Terminals, to generate procedural terminal tasks that enhance agent performance on various benchmarks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implement a four-stage pipeline to generate tasks, build environments, and train agents using PPO with binary rewards and minimal interaction loops.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Models trained on Endless Terminals demonstrate substantial performance improvements on both synthetic and human-curated benchmarks, outperforming models with more complex structures.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.16443

8. Knowledge is Not Enough: Injecting RL Skills for Continual Adaptation
🔑 Keywords: Parametric Skill Transfer, Large Language Models, Supervised Fine-Tuning, Skill Vector, Knowledge Adaptation
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research introduces Parametric Skill Transfer (PaST) to facilitate efficient knowledge adaptation in large language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework combines supervised fine-tuning with skill vector injection to achieve modular skill transfer for knowledge adaptation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PaST shows better performance in question answering and tool-use tasks, outperforming existing methods by significant margins in experiments on SQuAD, LooGLE, and ToolBench benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.11258

9. Guidelines to Prompt Large Language Models for Code Generation: An Empirical Characterization
🔑 Keywords: Prompt Optimization, Code Generation, Software Engineering, Large Language Models, Prompt Engineering
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To derive and evaluate prompt optimization guidelines for code generation tasks in software engineering.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– An iterative, test-driven approach was used to refine code generation prompts, analyzing outcomes to identify improvement patterns.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Ten specific guidelines were identified for improving prompts, focusing on better I/O specification, conditions, examples, and clarity. An assessment with practitioners revealed insights into usage and perceived usefulness, influencing the development of LLM-aided software tools.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.13118

10.

11. VISTA-PATH: An interactive foundation model for pathology image segmentation and quantitative analysis in computational pathology
🔑 Keywords: VISTA-PATH, semantic segmentation, histopathology image, foundation models, human-in-the-loop
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce VISTA-PATH, an interactive pathology segmentation model designed for precise multi-class segmentation and clinical interpretation in digital pathology.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize visual context, semantic descriptions, expert feedback, and optional spatial prompts to enable accurate segmentation across heterogeneous pathology images.
– Curate a large-scale dataset, VISTA-PATH Data, comprising over 1.6 million image-mask-text triplets, spanning 9 organs and 93 tissue classes.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– VISTA-PATH consistently outperforms existing segmentation models.
– Supports dynamic refinement with human-in-the-loop feedback, improving tissue microenvironment analysis and producing strong correlations with patient survival using the Tumor Interaction Score.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.16451

12. Dancing in Chains: Strategic Persuasion in Academic Rebuttal via Theory of Mind
🔑 Keywords: Theory of Mind, AI-Generated Summary, Supervised Fine-Tuning, Reinforcement Learning, RebuttalAgent
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of the research is to introduce RebuttalAgent, the first framework to apply Theory of Mind to academic rebuttals, transforming them into a strategic communication process.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The methods involve a ToM-Strategy-Response pipeline utilizing supervised fine-tuning for initial training, followed by reinforcement learning with a self-reward mechanism to enable efficient automated evaluation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study concludes that RebuttalAgent significantly outperforms the base model by an average of 18.3% on automated metrics and surpasses advanced proprietary models in both automated and human evaluations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.15715

13. ChartVerse: Scaling Chart Reasoning via Reliable Programmatic Synthesis from Scratch
🔑 Keywords: ChartVerse, Vision Language Models, Rollout Posterior Entropy, answer-first paradigm, Chain-of-Thought
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance Vision Language Model (VLM) performance by creating a scalable framework, ChartVerse, to generate complex charts and reliable reasoning data.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces the Rollout Posterior Entropy metric to assess chart complexity and utilizes a complexity-aware chart coder to synthesize diverse charts.
– Implements truth-anchored inverse QA synthesis with an answer-first paradigm to ensure accurate and consistent reasoning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ChartVerse-8B achieves state-of-the-art performance, excelling its teacher model and comparing favorably to stronger alternatives.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.13606

14. Mecellem Models: Turkish Models Trained from Scratch and Continually Pre-trained for the Legal Domain
🔑 Keywords: Turkish Legal Domain, Domain Adaptation, Encoder Models, Continual Pre-training, Retrieval Performance
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop specialized Turkish legal language models through domain adaptation strategies to improve legal text processing.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize ModernBERT-based bidirectional encoder models pre-trained on a large Turkish corpus.
– Implement a checkpoint selection strategy to optimize retrieval performance.
– Apply continual pre-training with controlled curriculum learning for decoder models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieved top-3 rankings on the Turkish retrieval leaderboard with efficient models.
– Demonstrated cost-effective single-stage pre-training approach with high production efficiency.
– Realized a 36.2% perplexity reduction in Turkish legal text through domain adaptation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.16018

15. MeepleLM: A Virtual Playtester Simulating Diverse Subjective Experiences
🔑 Keywords: Human-AI collaboration, constructive critique, player experience, creative co-designers, Mechanics-Dynamics-Aesthetics
💡 Category: Human-AI Interaction
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance Human-AI collaboration in board game design by offering constructive critique that aligns with player experiences, bridging the gap in current AI systems.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research involved curating a dataset of 1,727 rulebooks and 150K reviews, using Mechanics-Dynamics-Aesthetics (MDA) reasoning to bridge written rules and player experience, and developing MeepleLM to simulate feedback from diverse player archetypes.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MeepleLM outperforms existing commercial models in community alignment and critique quality, serving as a reliable virtual playtester, and representing a key advancement in audience-aligned Human-AI collaboration.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.07251

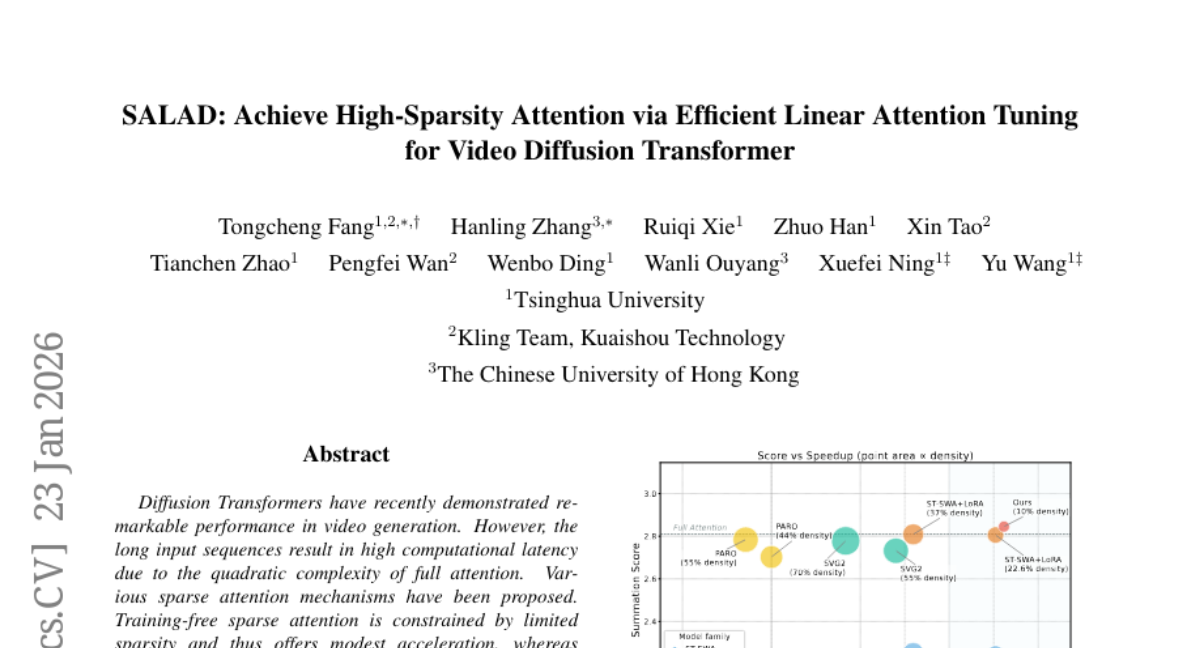
16. SALAD: Achieve High-Sparsity Attention via Efficient Linear Attention Tuning for Video Diffusion Transformer
🔑 Keywords: Diffusion Transformers, video generation, sparse attention, linear attention, input-dependent gating mechanism
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Enhance Diffusion Transformers for video generation to improve sparsity and speed while maintaining quality.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced SALAD, a method combining linear and sparse attention branches with an input-dependent gating mechanism for balancing.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieved 90% sparsity and 1.72x inference speedup, maintaining generation quality comparable to full attention, with efficient finetuning using minimal data.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.16515
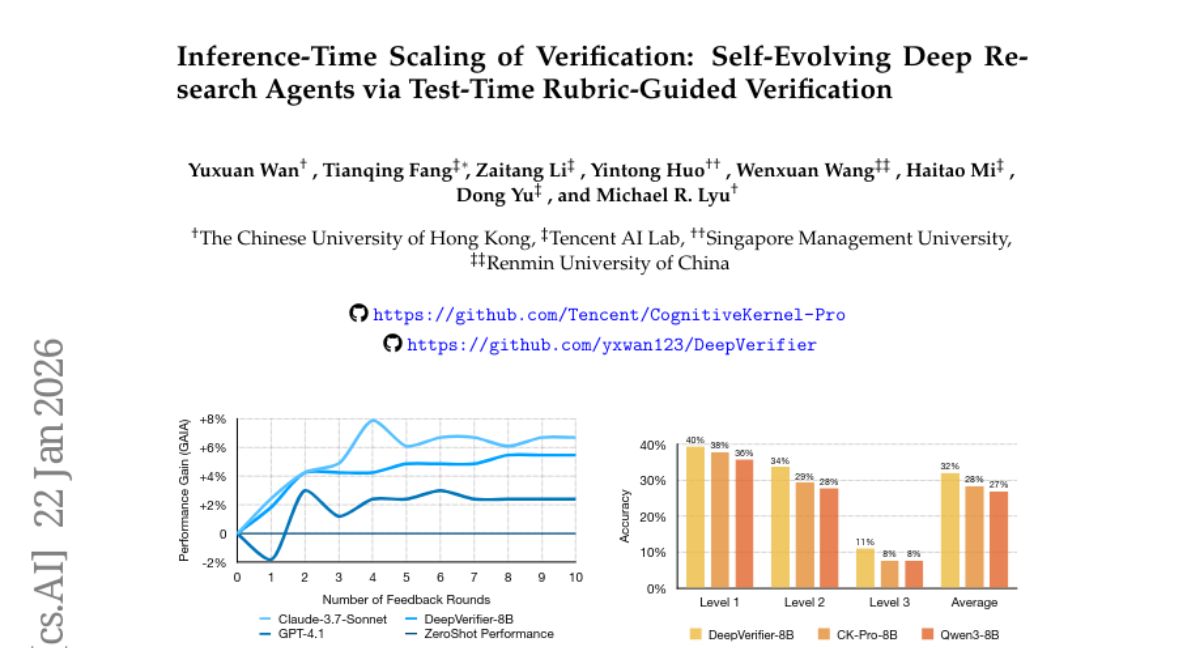
17. Inference-Time Scaling of Verification: Self-Evolving Deep Research Agents via Test-Time Rubric-Guided Verification
🔑 Keywords: Deep Research Agents, self-evolving, rubric-based feedback, verification, inference-time scaling
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To propose a self-evolving framework for Deep Research Agents that enhances performance through iterative verification and rubric-based feedback during inference.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of DeepVerifier, a rubric-based outcome reward verifier, which integrates as a plug-and-play module during test-time inference.
– Development of DRA Failure Taxonomy to classify agent failures systematically, informing rubric design.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– This novel approach enables agents to self-improve by iteratively refining responses, achieving an F1 score improvement of 12%-48% compared to baseline methods.
– The implementation of test-time scaling achieves accuracy gains of 8%-11% on challenging datasets, facilitating agent self-evolution without additional training.
– Release of DeepVerifier-4K, a curated dataset, to support open-source advancements in robust verification capabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.15808
18. VisGym: Diverse, Customizable, Scalable Environments for Multimodal Agents
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language Models, multi-step visual interactions, perception-memory-action integration, symbolic puzzles, feedback
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address the challenges faced by Vision-Language Models (VLMs) in multi-step visual interaction tasks, especially in integrating perception, memory, and action over long horizons.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced VisGym, a gymnasium of 17 environments to evaluate and train VLMs, spanning tasks like symbolic puzzles, real-image understanding, and navigation with adjustable difficulty and feedback mechanisms.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Frontier models struggle in interactive environments, with lower success rates in complex tasks; models perform worse with unbounded histories than with truncated windows, necessitating new methods like goal observations and textual feedback to improve outcomes.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.16973
19. SWE-Pruner: Self-Adaptive Context Pruning for Coding Agents
🔑 Keywords: SWE-Pruner, Task-aware pruning, Neural skimmer, Token reduction
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop a self-adaptive context pruning framework called SWE-Pruner to enhance coding agents by reducing token usage while preserving performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implement task-aware adaptive pruning using a lightweight neural skimmer with 0.6B parameters, designed to select relevant lines based on an explicit goal.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SWE-Pruner achieved substantial token reduction (23-54%) in agent tasks and up to 14.84x compression in single-turn tasks, with minimal impact on performance.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.16746
