AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20260129

1. Harder Is Better: Boosting Mathematical Reasoning via Difficulty-Aware GRPO and Multi-Aspect Question Reformulation
🔑 Keywords: Mathematical Reasoning, Reinforcement Learning, Difficulty-Aware Group Policy Optimization, Multi-Aspect Question Reformulation
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance mathematical reasoning in large models through a dual framework that addresses limitations in current reinforcement learning methods, particularly focusing on more challenging questions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research introduces MathForge, which combines a Difficulty-Aware Group Policy Optimization (DGPO) algorithm and a Multi-Aspect Question Reformulation (MQR) strategy to improve mathematical reasoning by prioritizing harder questions from both algorithmic and data perspectives.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MathForge significantly outperforms existing methods in various mathematical reasoning tasks, demonstrating the effectiveness of integrating DGPO and MQR to tackle challenging questions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.20614

2. Innovator-VL: A Multimodal Large Language Model for Scientific Discovery
🔑 Keywords: Scientific Multimodal Large Language Model, Data Efficiency, Generalization, Transparent Methodology, Supervised Fine-tuning
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Innovator-VL aims to advance understanding and reasoning across various scientific domains, while maintaining strong performance in general vision tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study employed a transparent and reproducible training pipeline, including data collection, preprocessing, supervised fine-tuning, and reinforcement learning, to optimize scientific intelligence with reduced data requirements.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Innovator-VL achieves competitive performance in scientific tasks and general vision capabilities using fewer than five million curated samples, demonstrating that effective reasoning can be achieved through principled data selection rather than massive pretraining.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.19325

3. Spark: Strategic Policy-Aware Exploration via Dynamic Branching for Long-Horizon Agentic Learning
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement learning, long-horizon tasks, adaptive branching exploration, decision-making signals, generalization
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Spark, a reinforcement learning framework, to improve resource allocation and sampling efficiency for long-horizon tasks by branching at critical decision points.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Leverage adaptive branching exploration activated at critical decision points to explore promising trajectories and enhance precise resource allocation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrated success in diverse tasks, showcasing superior success rates and robust generalization with fewer training samples, even in unseen scenarios.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.20209

4. Reinforcement Learning via Self-Distillation
🔑 Keywords: Self-Distillation Policy Optimization, Reinforcement Learning, Rich Feedback, Sample Efficiency, Verifiable Rewards
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards by using rich textual feedback to improve sample efficiency and accuracy in language model training.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces Self-Distillation Policy Optimization (SDPO), which leverages tokenized feedback to create a dense learning signal without an external teacher, treating the model as a self-teacher.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SDPO outperforms strong RLVR baselines in sample efficiency and accuracy across various environments. It also shows enhanced performance in standard RLVR settings and can accelerate discovery in difficult tasks with fewer attempts.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.20802

5. SERA: Soft-Verified Efficient Repository Agents
🔑 Keywords: AI Native, coding agents, private codebases, supervised fine-tuning, synthetic trajectories
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to demonstrate the practical advantages of Soft-Verified Efficient Repository Agents (SERA) in facilitating cost-effective specialization of coding agents to private codebases through supervised fine-tuning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors developed SERA using Soft Verified Generation (SVG), a method that generates thousands of trajectories from a single code repository, making it significantly cheaper and efficient compared to reinforcement learning and previous synthetic data methods.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SERA achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source models and is substantially cheaper to create, showing considerable potential to accelerate research on open coding agents and the specialization of models to private codebases, while all models and data are made openly available to support the research community.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.20789

6. RIR-Mega-Speech: A Reverberant Speech Corpus with Comprehensive Acoustic Metadata and Reproducible Evaluation
🔑 Keywords: Reverberant Speech, Acoustic Annotations, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research introduces a large-scale reverberant speech corpus with detailed acoustic annotations to facilitate standardized comparison and reproduction of speech processing research.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study presents RIR-Mega-Speech, a corpus created by convolving LibriSpeech utterances with roughly 5,000 simulated room impulse responses. Each file has acoustic conditions like RT60, direct-to-reverberant ratio (DRR), and clarity index well-documented and reproducible.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The research highlights the impact of reverberation on recognition, with WER increasing with RT60 and decreasing with DRR; this represents a consistent finding with prior studies and intends to provide a reproducible standardized resource for the community.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.19949

7. Training Reasoning Models on Saturated Problems via Failure-Prefix Conditioning
🔑 Keywords: failure-prefix conditioning, Reinforcement Learning, informative failures, token efficiency, robustness
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance reinforcement learning by leveraging failure-prefix conditioning to improve exploration and robustness in saturated problems.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method reallocates exploration by focusing training on prefixes from rare incorrect reasoning trajectories, allowing models to encounter informative failures effectively and maintaining token efficiency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Failure-prefix conditioning improves performance similar to training on medium-difficulty problems and enhances robustness, though with a minor compromise on adherence to initial correct reasoning.
– An iterative approach to refresh failure prefixes during training provides further performance gains after reaching a plateau.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.20829

8. Group Distributionally Robust Optimization-Driven Reinforcement Learning for LLM Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Model, GDRO, Reinforcement Learning, Online Difficulty Classifier, EMA-debiased multiplicative-weights bandit sampler
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To dynamically adapt training distributions for large language models by classifying prompt difficulty and reallocating computational resources to improve reasoning performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of the Multi-Adversary Group Distributionally Robust Optimization (GDRO) framework.
– Use of an Online Difficulty Classifier to partition prompts based on difficulty.
– Implementation of two GDRO post-training games: Prompt-GDRO and Rollout-GDRO, focusing on upweighting hard tasks and reallocating rollouts efficiently.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed GDRO framework shows significant average relative gains in pass@8 accuracy, achieving +10.6% with Prompt-GDRO and +10.1% with Rollout-GDRO compared to the GRPO baseline, demonstrating the framework’s effectiveness in optimizing reasoning performance.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.19280

9. Shallow-π: Knowledge Distillation for Flow-based VLAs
🔑 Keywords: Knowledge Distillation, Vision-Language-Action Models, Transformer Depth, Real-Time Robotic Deployment, AI Native
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces Shallow-pi, a knowledge distillation framework designed to reduce the transformer depth in vision-language-action (VLA) models, aiming to achieve faster inference with minimal performance loss in robotic applications.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Shallow-pi aggressively reduces the transformer layers from 18 to 6 while maintaining performance through knowledge distillation, validated through industrial-scale experiments on multiple robot platforms, including humanoid systems, in complex and dynamic environments.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Shallow-pi achieves over two times faster inference with less than one percent drop in success rate on standard manipulation benchmarks, establishing state-of-the-art performance in reduced VLA models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.20262
10. Persona Prompting as a Lens on LLM Social Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: Persona prompting, Large Language Models, rationale quality, model bias
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study explores how Persona prompting affects Large Language Models’ rationales on socially sensitive tasks, with a focus on classification accuracy and explanation quality, while addressing demographic biases.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research involves simulating different demographic personas with datasets annotated with word-level rationales, measuring their alignment with human annotations, and assessing the impact of Persona prompting on model bias and human alignment.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study finds that Persona prompting improves classification accuracy in tasks like hate speech detection but degrades the quality of rationales. It also notes that simulated personas do not align well with real-world demographics and that models consistently exhibit demographic biases and over-flag content as harmful, despite using Persona prompting.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.20757

11.

12. SketchDynamics: Exploring Free-Form Sketches for Dynamic Intent Expression in Animation Generation
🔑 Keywords: Free-form sketching, Vision-language model, AI-generated summary, Motion graphics, 3D animation
💡 Category: Human-AI Interaction
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to bridge human intention and digital output in animation workflows through free-form sketching and AI.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implemented a vision-language model interface and conducted a three-stage user study with 24 participants to refine the system.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Findings indicate the potential of free-form sketching with AI to effectively communicate motion and guide video refinement, highlighting its applicability in 3D animation and video generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.20622

13. SE-DiCoW: Self-Enrolled Diarization-Conditioned Whisper
🔑 Keywords: SE-DiCoW, Speaker-attributed ASR, Diarization, Cross-attention, tcpWER
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to enhance speaker-attributed automatic speech recognition (ASR) by addressing limitations in the Diarization-Conditioned Whisper (DiCoW) system, specifically focusing on improving cross-attention conditioning in multi-speaker environments.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The methodology involves using speaker diarization outputs to identify enrollment segments, which are then employed as fixed conditioning in cross-attention layers at each encoder stage. Additionally, improvements are made in data segmentation, model initialization, and augmentation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SE-DiCoW significantly reduces transcription error rates, achieving a 52.4% reduction in macro-averaged tcpWER compared to the original DiCoW system on the EMMA MT-ASR benchmark.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.19194

14. GDCNet: Generative Discrepancy Comparison Network for Multimodal Sarcasm Detection
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal sarcasm detection, semantic incongruities, large language models, Generative Discrepancy Comparison Network, Multimodal LLMs
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance multimodal sarcasm detection by addressing semantic incongruities across modalities using a new model.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces the Generative Discrepancy Comparison Network (GDCNet) that leverages descriptive and factually grounded image captions generated by Multimodal LLMs as stable semantic anchors to capture cross-modal conflicts.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The GDCNet has demonstrated superior accuracy and robustness in multimodal sarcasm detection, setting a new state-of-the-art performance on the MMSD2.0 benchmark.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.20618

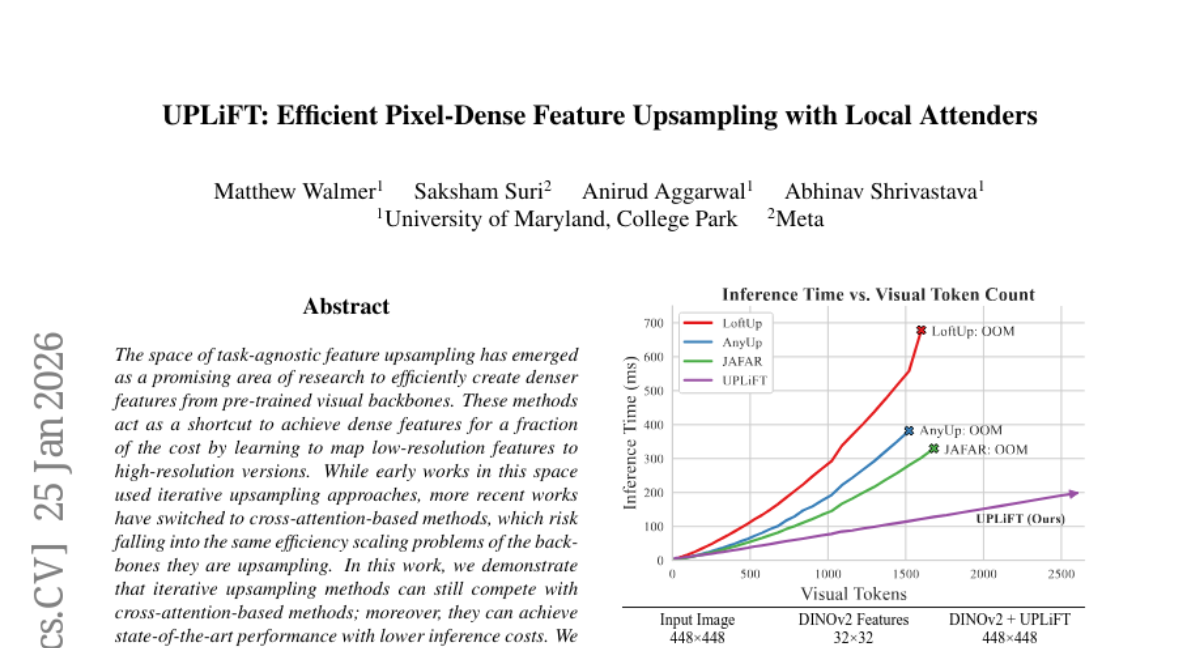
15. UPLiFT: Efficient Pixel-Dense Feature Upsampling with Local Attenders
🔑 Keywords: Iterative Upsampling, UPLiFT, Local Attender, Cross-Attention, Pixel-dense Feature Upsamplers
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To demonstrate that iterative upsampling methods can compete with cross-attention-based methods in feature upsampling, achieving state-of-the-art performance with lower inference costs.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The introduction of the UPLiFT architecture, which uses the Local Attender operator for efficient and dense feature generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– UPLiFT achieves competitive performance with state-of-the-art models for VAE feature upsampling, offering a versatile and efficient approach to creating denser features at reduced costs.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.17950
16. OmegaUse: Building a General-Purpose GUI Agent for Autonomous Task Execution
🔑 Keywords: GUI agents, autonomous task execution, data-construction pipeline, Mixture-of-Experts, ScreenSpot-V2
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to develop OmegaUse, a general-purpose GUI agent model to enhance autonomous task execution on mobile and desktop platforms.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced a novel data-construction pipeline using a combination of bottom-up autonomous exploration and top-down taxonomy-guided generation.
– Implemented a decoupled training paradigm utilizing Supervised Fine-Tuning and Group Relative Policy Optimization.
– Utilized a Mixture-of-Experts architecture to balance computational efficiency and reasoning capacity.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– OmegaUse achieves state-of-the-art performance across GUI benchmarks, scoring 96.3% on ScreenSpot-V2 and a leading 79.1% step success rate on AndroidControl.
– Demonstrated strong performance on OS-Nav, with 74.24% step success on ChiM-Nav and 55.9% average success on Ubu-Nav.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.20380

17. VERGE: Formal Refinement and Guidance Engine for Verifiable LLM Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: neurosymbolic framework, Large Language Models, SMT solvers, logical correctness, verification-guided answers
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance logical correctness in Large Language Models by integrating them with SMT solvers using a neurosymbolic framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework involves decomposing LLM outputs into atomic claims, autoformalizing them into first-order logic, and verifying their logical consistency through automated theorem proving.
– It introduces multi-model consensus via formal semantic equivalence checking, semantic routing for appropriate verification strategies, and precise logical error localization using Minimal Correction Subsets.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The framework achieves significant improvements in logical correctness, delivering formal guarantees and advancing trustworthy AI with an 18.7% performance uplift at convergence compared to single-pass approaches.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.20055

18. Linear representations in language models can change dramatically over a conversation
🔑 Keywords: Language model representations, Linear directions, Interpretability, Context-adaptive behavior
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Explore how linear representation directions in language models change dynamically during conversations, affecting how information, particularly factual content, is encoded.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Investigating the evolution of linear representations along dimensions during simulated conversations, assessing changes in factuality, robustness across model families and layers, and analyzing effects of steering representational directions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Representation changes are content-dependent and robust, posing challenges for interpretability and steering; these dynamics highlight key areas for future research in understanding model adaptations to context.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.20834

19. DeepSeek-OCR 2: Visual Causal Flow
🔑 Keywords: DeepEncoder V2, visual tokens, 2D image understanding, causal reasoning
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Explore the feasibility of using DeepEncoder V2 to dynamically reorder visual tokens based on semantic content for 2D image understanding.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduce a new paradigm that employs two-cascaded 1D causal reasoning structures to achieve effective 2D image understanding.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DeepEncoder V2 offers a novel architectural approach with the potential for genuine 2D reasoning by enabling intelligent reordering of visual tokens prior to language model-based content interpretation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.20552
20. Advancing Open-source World Models
🔑 Keywords: LingBot-World, world simulator, long-term memory, real-time interactivity
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To present LingBot-World, an open-source world simulator with high-fidelity dynamics, long-term memory, and real-time interactivity across diverse environments.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of a world model with the ability to maintain high fidelity and robust dynamics, support minute-level horizons, and enable real-time interactivity with low latency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LingBot-World bridges the gap between open-source and closed-source technologies by providing a versatile tool for applications in content creation, gaming, and robot learning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.20540