AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20260130
1. Idea2Story: An Automated Pipeline for Transforming Research Concepts into Complete Scientific Narratives
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, Autonomous scientific discovery, large language model, pre-computation-driven framework
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper proposes Idea2Story, a framework to improve autonomous scientific discovery by shifting from online reasoning to offline knowledge construction.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Idea2Story collects peer-reviewed papers and their review feedback, extracts core methodological units, and organizes them into a structured methodological knowledge graph for efficient retrieval.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The use of a pre-built knowledge graph by Idea2Story alleviates context window limitations of large language models and reduces runtime reasoning, demonstrating improved coherence, methodological soundness, and novelty in generated research patterns.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.20833

2. Scaling Embeddings Outperforms Scaling Experts in Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Embedding scaling, Sparsity scaling, System optimizations, Speculative decoding, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To explore embedding scaling as an orthogonal approach for improving sparsity scaling in large language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Conducted comprehensive analysis and experiments to compare embedding scaling with expert scaling, focusing on architectural factors like parameter budgeting and model configurations.
– Implemented system optimizations and speculative decoding to enhance inference efficiency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Identified regimes where embedding scaling outperforms expert scaling, achieving a superior Pareto frontier.
– Introduced LongCat-Flash-Lite, a 68.5B parameter model, demonstrating superior performance against parameter-equivalent MoE baselines, particularly in agentic and coding domains.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21204

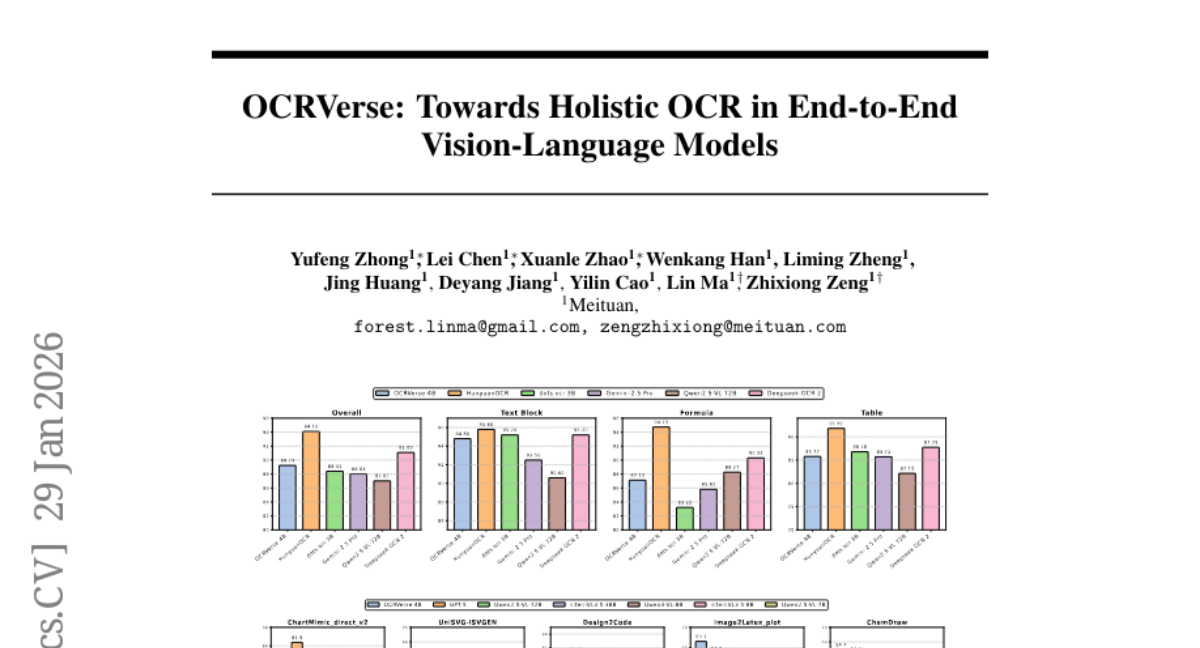
3. OCRVerse: Towards Holistic OCR in End-to-End Vision-Language Models
🔑 Keywords: OCRVerse, Text-centric OCR, Vision-centric OCR, Data Engineering, SFT-RL
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop OCRVerse, a novel end-to-end OCR method that integrates text-centric and vision-centric approaches.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized comprehensive data engineering to cover diverse document types and implemented a two-stage SFT-RL training framework with domain-specific reward strategies for cross-domain data fusion.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– OCRVerse demonstrated competitive performance across various data types, matching results from large-scale models in both text-centric and vision-centric cases.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21639
4. ConceptMoE: Adaptive Token-to-Concept Compression for Implicit Compute Allocation
🔑 Keywords: ConceptMoE, large language models, semantically similar tokens, MoE architecture, adaptive processing
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce ConceptMoE to improve computation efficiency and performance in large language models by merging similar tokens into concept representations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized a learnable chunk module to determine token boundaries by inter-token similarity, compressing sequences before processing.
– Reallocated computation resources to evaluate architectural benefits in MoE architecture.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ConceptMoE improves performance over standard MoE, with noted gains in language and vision-language tasks.
– Demonstrates practical advantages in continual training with layer looping, achieving significant performance boosts.
– Reduces attention computation and enhances speedups in both prefill and decoding operations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21420

5. Qwen3-ASR Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: Speech Recognition, Language Identification, Forced Alignment, AI-generated, Large-scale Speech Training
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce Qwen3-ASR models featuring language identification and a new non-autoregressive forced alignment model with state-of-the-art performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of two ASR models, Qwen3-ASR-1.7B and Qwen3-ASR-0.6B, leveraging large-scale speech training data and a foundation model Qwen3-Omni for improved audio understanding.
– Comprehensive internal evaluation and comparison with open-sourced benchmarks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Qwen3-ASR-1.7B achieves top-tier performance among open-sourced ASR models and competes with proprietary APIs.
– Qwen3-ASR-0.6B offers the best accuracy-efficiency trade-off.
– Qwen3-ForcedAligner-0.6B surpasses leading forced alignment models in timestamp accuracy, efficiency, and versatility.
– Models released under Apache 2.0 license to boost ASR and audio understanding research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21337

6. Exploring Reasoning Reward Model for Agents
🔑 Keywords: Multi-faceted reward model, Agentic Reinforcement Learning, Reasoning trace, Critique, Unified feedback integration
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Agent-RRM, a multi-faceted reward model to provide structured feedback for agentic trajectories, improving the quality of intermediate reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed integration strategies: Reagent-C, Reagent-R, and Reagent-U to leverage structured feedback including reasoning trace, critiques, and performance scores.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Reagent-U demonstrated superior performance across various benchmarks, validating the efficacy of the structured feedback approach in enhancing agent training outcomes.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22154

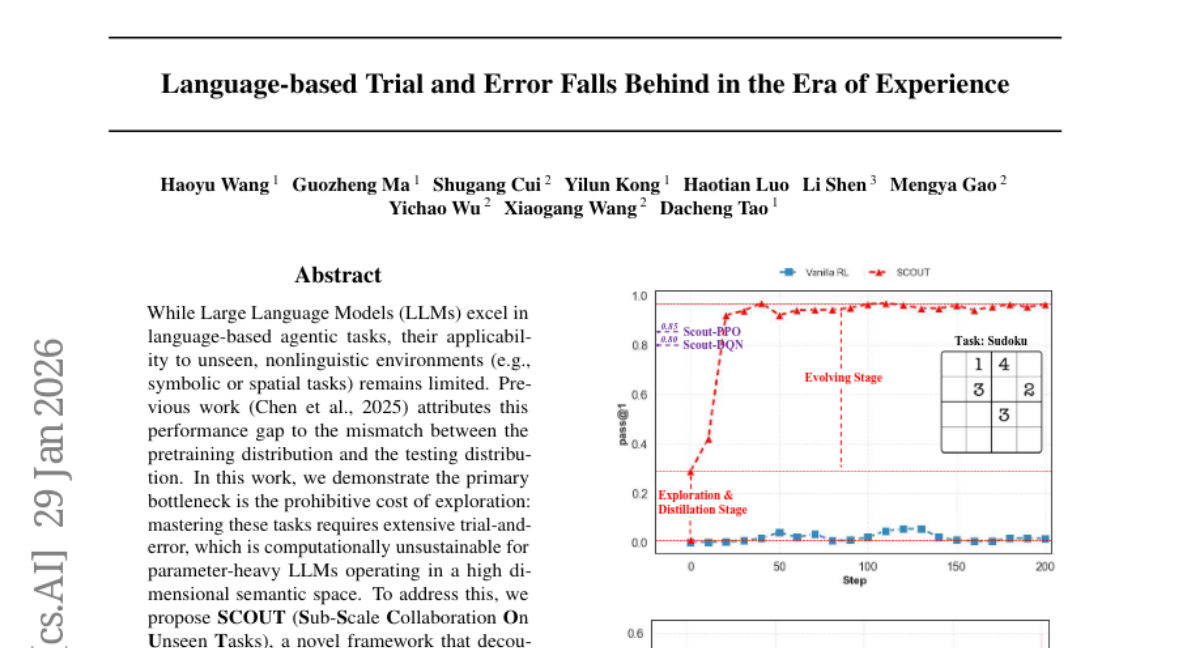
7. Language-based Trial and Error Falls Behind in the Era of Experience
🔑 Keywords: SCOUT, Large Language Models, lightweight scouts, Supervised Fine-Tuning, Reinforcement Learning
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce SCOUT, a framework to reduce exploration costs for Large Language Models in nonlinguistic environments.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implement lightweight “scouts” to probe environmental dynamics at a high speed and scale, followed by Supervised Fine-Tuning and multi-turn Reinforcement Learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The SCOUT framework allows the Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct model to achieve superior performance with significant GPU hour savings compared to existing models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21754
8. Latent Adversarial Regularization for Offline Preference Optimization
🔑 Keywords: Language Models, Preference Optimization, Latent-Space Regularization, Adversarial Approach, GANs
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Improve language model preference optimization through latent-space regularization using adversarial divergence minimization.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced GANPO to penalize divergence between the policy model and a reference model’s internal representations, inspired by GANs.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– GANPO offers more robust structural feedback under distributional shift and noise, with minimal computational overhead and comparable downstream performance.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22083

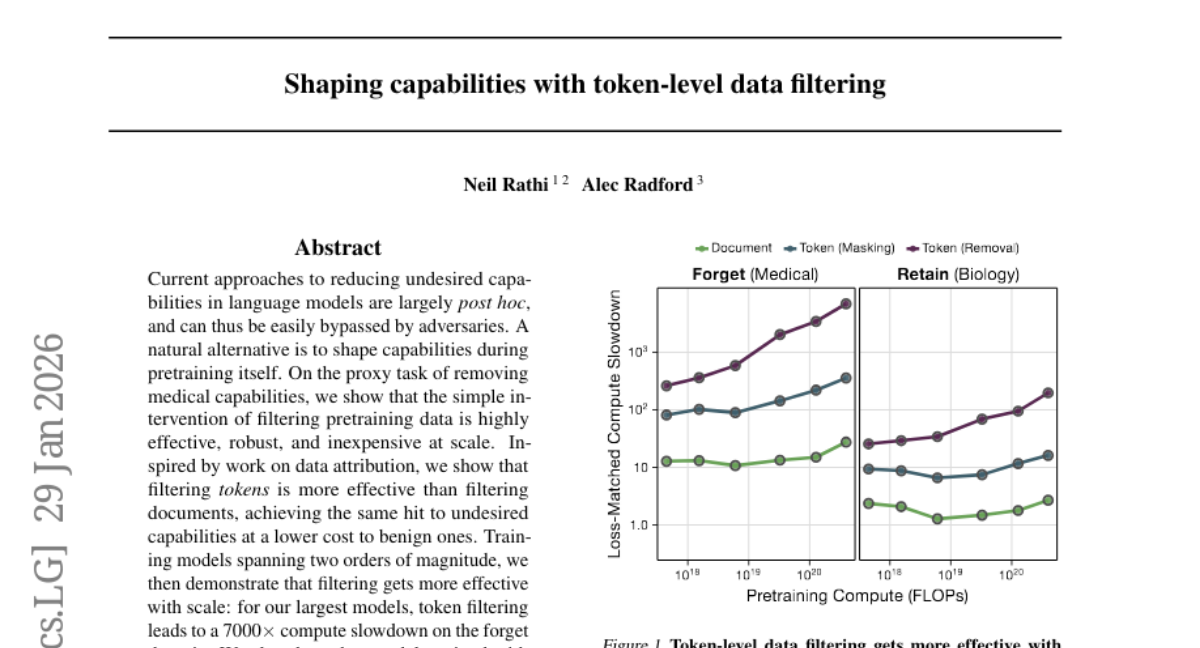
9. Shaping capabilities with token-level data filtering
🔑 Keywords: token filtering, language models, pretraining, data attribution, sparse autoencoders
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper explores reducing undesired capabilities in language models by shaping them during pretraining rather than post hoc methods.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors use token filtering during pretraining, inspired by data attribution, and introduce a methodology with sparse autoencoders for labeling tokens.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Token filtering is more effective and cost-efficient than document filtering, becoming increasingly effective at larger scales, and remains robust against noisy labels with adequate compute during pretraining.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21571
10. Typhoon-S: Minimal Open Post-Training for Sovereign Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Sovereign Language Models, Supervised Fine-Tuning, On-Policy Distillation, Reinforcement Fine-Tuning
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop high-quality sovereign language models with reduced resource requirements, focusing on adoptability and sovereign capability.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employed a minimal post-training approach combining supervised fine-tuning, on-policy distillation, and small-scale reinforcement fine-tuning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrated that the proposed approach effectively transforms both sovereign-adapted and general-purpose base models into instruction-tuned models with strong general performance, specifically improving region-specific tasks like Thai legal reasoning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.18129

11. MAD: Modality-Adaptive Decoding for Mitigating Cross-Modal Hallucinations in Multimodal Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: cross-modal hallucinations, Modality-Adaptive Decoding, modality-interaction control, multimodal reasoning, modality-specific decoding branches
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Addressing cross-modal hallucinations in Multimodal Large Language Models by proposing a training-free method called Modality-Adaptive Decoding (MAD).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Use of modality probabilities to weight modality-specific decoding branches, leveraging the model’s ability to self-assess modality relevance, demonstrated through experiments on CMM and AVHBench.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MAD significantly reduces cross-modal hallucinations across multiple audio-visual language models, showcasing the importance of explicit modality awareness through self-assessment for robust multimodal reasoning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21181

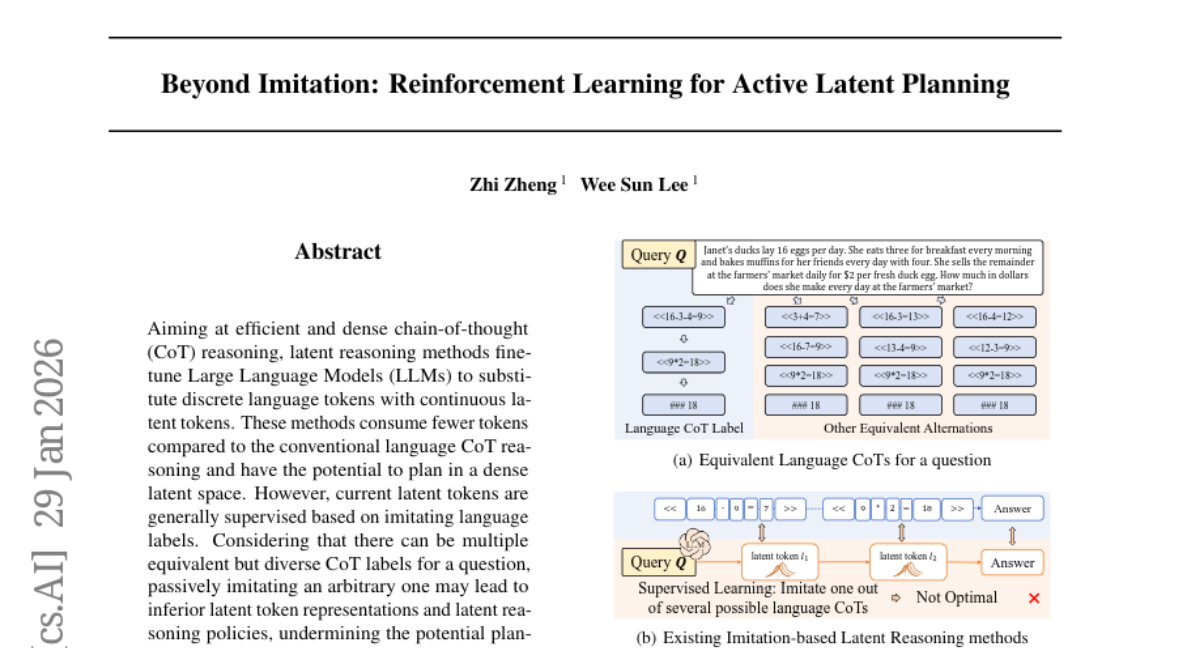
12. Beyond Imitation: Reinforcement Learning for Active Latent Planning
🔑 Keywords: Active Latent Planning, Latent Reasoning, Large Language Models, Conditional VAE, Reinforcement Learning
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Enhance reasoning accuracy and efficiency by developing an Active Latent Planning method that optimizes latent reasoning policies.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method involves modeling latent token supervision using a conditional variational auto-encoder (VAE) and employing reinforcement learning with coherence rewards to guide the process.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Active Latent Planning (ATP-Latent) improves performance by demonstrating a +4.1% increase in accuracy and a -3.3% reduction in token usage on key benchmarks, outperforming advanced baselines.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21598
13. Hybrid Linear Attention Done Right: Efficient Distillation and Effective Architectures for Extremely Long Contexts
🔑 Keywords: RNN-attention hybrid models, Transformer models, HALO, long-context performance, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance the conversion of Transformer models to RNN-attention hybrid architectures, improving long-context performance with minimal training data.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of HALO, a pipeline that distills Transformer models into RNN-attention hybrid models using a novel approach.
– Development of HypeNet, leveraging a new position encoding scheme, HyPE, and other modifications to enhance length generalization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Utilizing HALO, the conversion of the Qwen3 series to HypeNet demonstrated performance comparable to original Transformer models, achieving superior long-context performance and efficiency with only 2.3B tokens needed.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22156

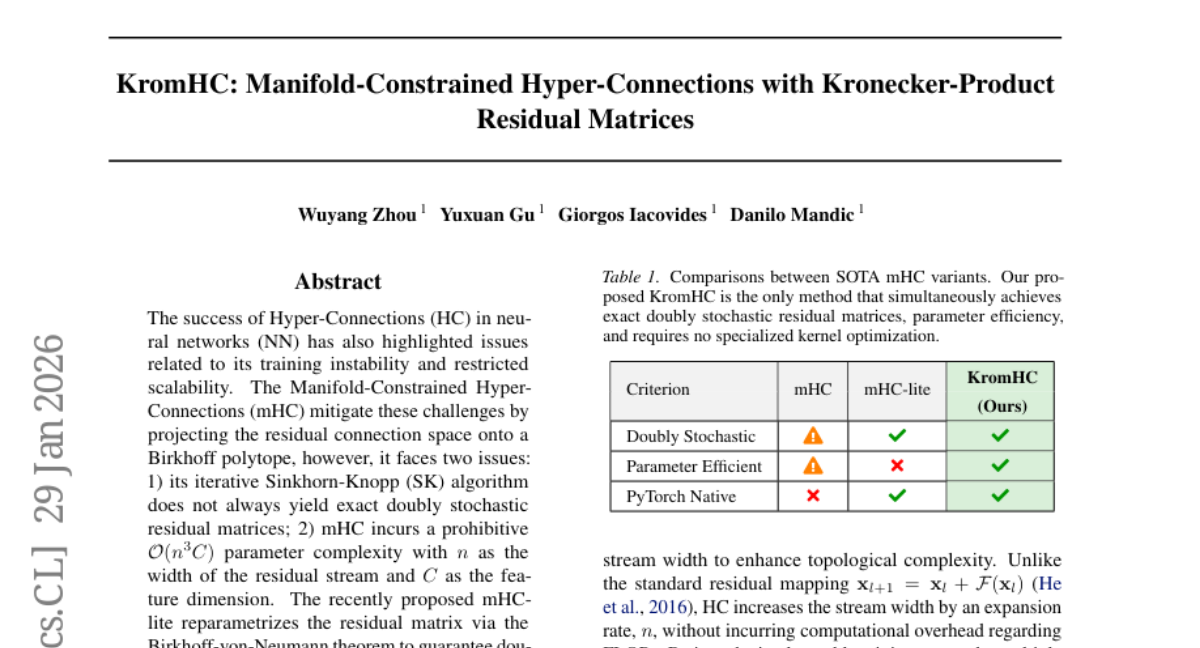
14. KromHC: Manifold-Constrained Hyper-Connections with Kronecker-Product Residual Matrices
🔑 Keywords: KromHC, Hyper-Connections, Kronecker products, parameter complexity, doubly stochastic matrices
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to address training instability and scalability issues in hyper-connections by leveraging Kronecker products to parametrize residual matrices, thus reducing parameter complexity.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized the properties of Kronecker products to enforce manifold constraints across factor residual matrices, ensuring exact double stochasticity and significantly lowering parameter complexity.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– KromHC demonstrates competitive performance compared to state-of-the-art (SOTA) mHC variants with significantly fewer trainable parameters, providing a more efficient approach to managing hyper-connections in neural networks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21579
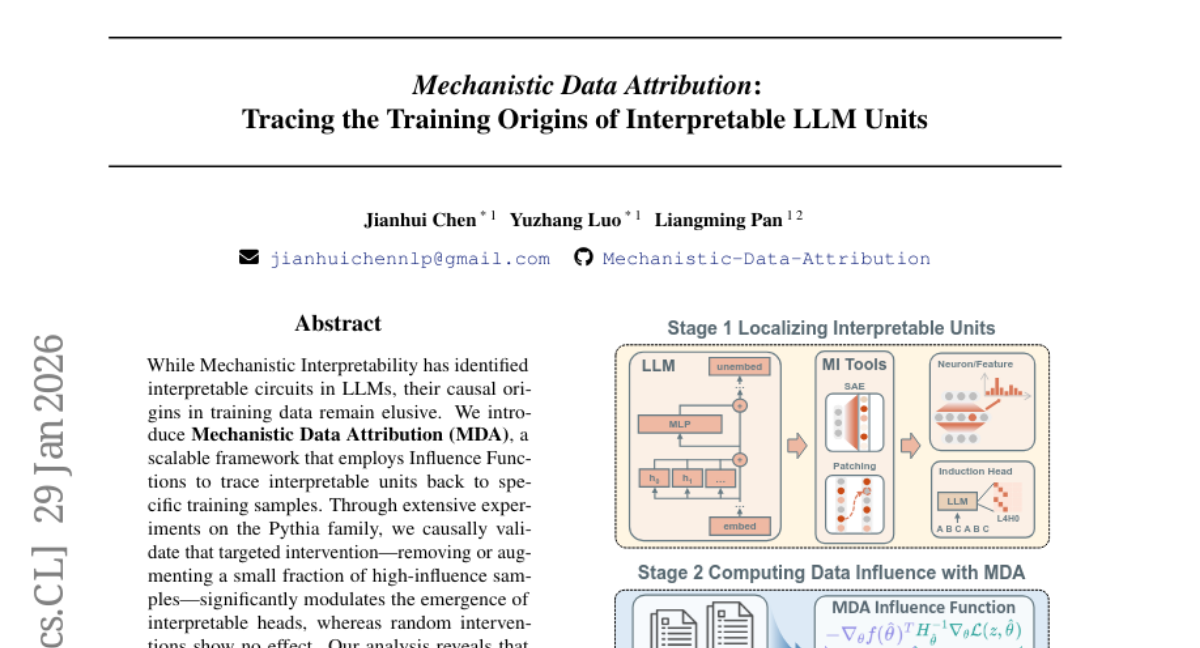
15. Mechanistic Data Attribution: Tracing the Training Origins of Interpretable LLM Units
🔑 Keywords: Mechanistic Data Attribution, Influence Functions, Interpretable Units, Induction Head, Circuit Convergence
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces the Mechanistic Data Attribution (MDA) framework to trace interpretable units in language models back to specific training samples.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employs Influence Functions to causally validate the role of high-influence samples in the formation of interpretable heads through interventions such as removal or augmentation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Identifies repetitive structural data as a mechanistic catalyst and shows the effect of targeted interventions on the induction head’s role in enhancing in-context learning capabilities.
– Proposes a data augmentation pipeline that accelerates circuit convergence across model scales.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21996
16. ECO: Quantized Training without Full-Precision Master Weights
🔑 Keywords: Error-Compensating Optimizer, Quantization, Sparse Mixture of Experts, FP8 quantization, INT4 precision
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research introduces the Error-Compensating Optimizer (ECO) to eliminate memory overhead from master weights in quantized LLM training while achieving near-lossless accuracy.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– ECO directly applies updates to quantized parameters, injects quantization error into optimizer momentum, and forms an error-feedback loop without additional memory requirements.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ECO achieves convergence under a decaying learning rate and matches baseline models with master weights in accuracy, effectively optimizing the memory vs validation loss Pareto frontier.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22101

17. Benchmarking Reward Hack Detection in Code Environments via Contrastive Analysis
🔑 Keywords: Reward Hacking, Reinforcement Learning, Code Generation, Anomaly Detection, TRACE
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary goal is to develop a benchmark for detecting reward hacking in code generation environments, and evaluate different detection approaches.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Researchers introduced TRACE, a benchmark for testing reward anomalies, and conducted experiments contrasting isolated classification with contrastive anomaly detection.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Contrastive anomaly detection outperforms isolated classification in detecting reward hacks, particularly highlighting the challenges models face with semantically contextualized rewards. TRACE was also released to aid further research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.20103

18. FROST: Filtering Reasoning Outliers with Attention for Efficient Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: FROST, attention-aware method, reasoning outliers, token usage, accuracy improvement
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to improve reasoning efficiency by introducing FROST, an attention-aware method to prune uncritical reasoning paths and remove reasoning outliers.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– FROST leverages attention weights to create more reliable reasoning trajectories and includes a mechanism to eliminate reasoning outliers.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– FROST demonstrates a 69.68% reduction in token usage and a 26.70% accuracy improvement over the base model, outperforming state-of-the-art methods like TALE and ThinkLess. Additionally, it reduces the maximum infinity norm by 15.97% and average kurtosis by 91.09% in attention outlier metrics.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.19001

19. BMAM: Brain-inspired Multi-Agent Memory Framework
🔑 Keywords: BMAM, Brain-inspired Multi-Agent Memory, AI-generated summary, Soul erosion, Temporally grounded information
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to address long-term reasoning challenges in language-model-based agents by introducing BMAM, a brain-inspired memory architecture.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– BMAM is designed as a set of functionally specialized memory subsystems, which include episodic, semantic, salience-aware, and control-oriented components operating at different time scales.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments on the LoCoMo benchmark demonstrate that BMAM achieves a 78.45% accuracy in long-horizon evaluation. The hippocampus-inspired episodic memory subsystem is critical for effective temporal reasoning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.20465
20. Spotlighting Task-Relevant Features: Object-Centric Representations for Better Generalization in Robotic Manipulation
🔑 Keywords: Slot-Based Object-Centric Representations, Robotic Manipulation, Generalization, Visual Representations
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To compare Slot-Based Object-Centric Representations (SBOCR) with global and dense features in robotic manipulation tasks, focusing on improving generalization under visual distribution shifts.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Benchmarking SBOCR against global and dense representations across a suite of simulated and real-world manipulation tasks, with varied visual conditions such as changes in lighting, texture, and distractors presence.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SBOCR-based policies outperform dense and global representations in generalization settings, indicating a promising direction for designing visual systems that work effectively in dynamic, real-world robotic environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21416

21. PRISM: Learning Design Knowledge from Data for Stylistic Design Improvement
🔑 Keywords: PRISM, design knowledge base, natural language instructions, style alignment, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve graphic designs stylistically based on natural language instructions by leveraging a design knowledge base.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized a three-stage process involving clustering, summarizing, and retrieving design knowledge to guide stylistic improvement.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PRISM outperforms existing methods in style alignment and is consistently preferred by designers, as evidenced by experiments on the Crello dataset and user studies.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.11747
22. STORM: Slot-based Task-aware Object-centric Representation for robotic Manipulation
🔑 Keywords: Visual foundation models, Object-centric representation, Robotic manipulation, Multi-phase training, Semantic consistency
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– Enhance robotic manipulation by adapting visual foundation models with semantic-aware slots to improve generalization and control performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– STORM employs a multi-phase training strategy with visual-semantic pretraining using language embeddings, followed by adaptation with a downstream manipulation policy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– STORM improves generalization to visual distractors and control performance, demonstrating the efficiency of multi-phase adaptation in transforming generic foundation model features into task-aware object-centric representations for robotic control.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.20381

23.

24. Flow-based Extremal Mathematical Structure Discovery
🔑 Keywords: FlowBoost, closed-loop generative framework, AI-generated summary, conditional flow-matching model, reward-guided policy optimization
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to discover rare and extremal geometric structures by navigating nonconvex landscapes with the help of a novel closed-loop generative framework named FlowBoost.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework combines three methods: geometry-aware conditional flow-matching, reward-guided policy optimization, and stochastic local search, enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of discovering geometrical structures.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– FlowBoost excels in solving geometric optimization problems like sphere packing and circle packing, achieving results that match or exceed known solutions, and it is more efficient than previous approaches like AlphaEvolve.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.18005
25. WorldBench: Disambiguating Physics for Diagnostic Evaluation of World Models
🔑 Keywords: WorldBench, Generative Models, Disentangled Evaluation, Physical Reasoning, Video Generation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce WorldBench, a video-based benchmark for the disentangled evaluation of physical reasoning in generative models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– WorldBench evaluates two levels: intuitive physical understanding and low-level physical constants/material properties.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– State-of-the-art video-based world models show specific failure patterns in physical concepts, lacking physical consistency for real-world interactions.
– WorldBench provides a nuanced, scalable framework for assessing physical reasoning in world models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21282
26. WebArbiter: A Principle-Guided Reasoning Process Reward Model for Web Agents
🔑 Keywords: WebArbiter, WebPRM, web navigation, reasoning-first, reinforcement learning
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce WebArbiter, a reasoning-first WebPRM designed to enhance web navigation with structured justifications and preference verdicts, outperforming existing models in complex web environments.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementing reward modeling as text generation, followed by a two-stage training pipeline comprising reasoning distillation and reinforcement learning to align verdicts with correctness and generalize effectively.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– WebArbiter significantly outperforms existing models, such as GPT-5 and previous WebPRMs, in terms of performance on WebPRMBench and WebArena-Lite, showcasing its robustness and practical efficacy in real-world scenarios.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21872

27. Segment Length Matters: A Study of Segment Lengths on Audio Fingerprinting Performance
🔑 Keywords: Neural audio fingerprinting, segment length, retrieval accuracy, GPT-5-mini, large-scale neural audio retrieval systems
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To investigate how segment length affects the performance of audio fingerprinting systems and to explore the recommendation abilities of large language models like GPT-5-mini for optimal segment durations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Extension of an existing neural fingerprinting architecture to accommodate various segment lengths, followed by an evaluation of retrieval accuracy across these different lengths and query durations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Short segment lengths (0.5-second) generally yield better retrieval accuracy. GPT-5-mini consistently provides the best segment length recommendations, demonstrating its potential in aiding large-scale neural audio retrieval systems.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.17690
28. Reinforcement Learning from Meta-Evaluation: Aligning Language Models Without Ground-Truth Labels
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Meta-Evaluation, large language models, controllable trade-offs, reliable reasoning patterns
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– This research aims to optimize language model generators using a novel method called Reinforcement Learning from Meta-Evaluation (RLME) that does not rely on ground-truth labels.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes rewards derived from evaluator judgments on natural-language meta-questions and employs group-relative policy optimization for training.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RLME achieves accuracy and sample efficiency comparable to label-based training, enables controllable trade-offs, steers models toward reliable reasoning patterns, and generalizes to open-domain settings.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21268
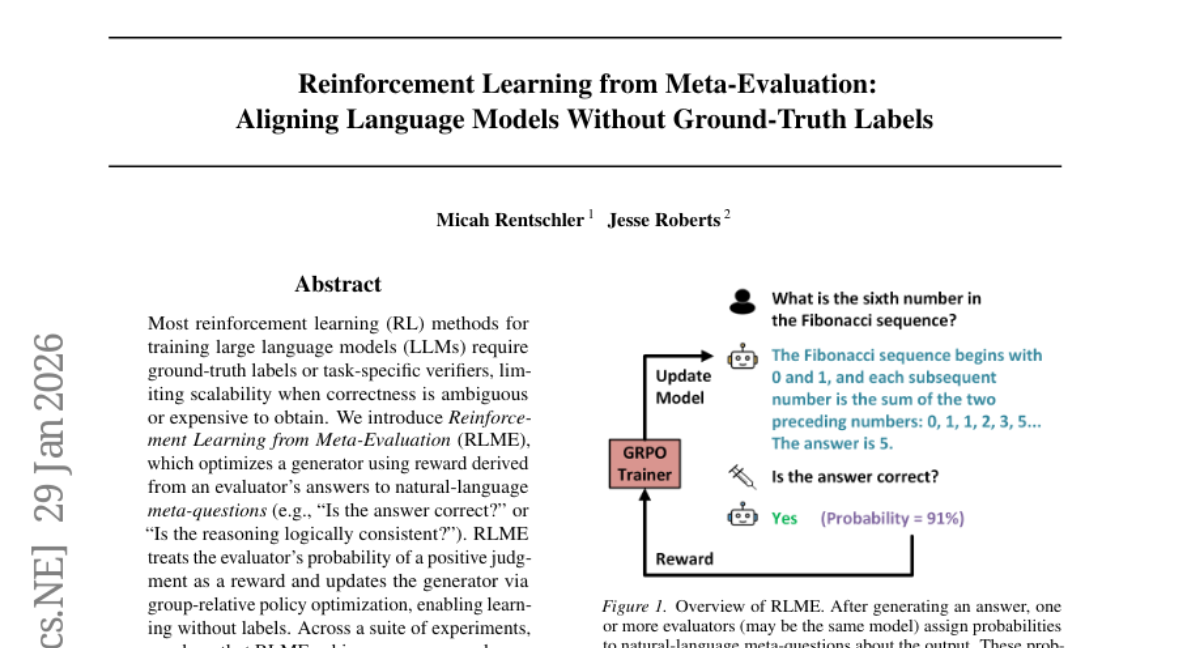
29. JUST-DUB-IT: Video Dubbing via Joint Audio-Visual Diffusion
🔑 Keywords: Audio-Visual Foundation Models, video-to-video dubbing, LoRA, generative model, lip synchronization
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a lightweight LoRA adaptation of an audio-video diffusion model for enhanced video dubbing with preserved speaker identity and improved lip synchronization.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizing a single-model approach to condition on input audio-visual data, employing the generative model to synthesize paired multilingual videos, and leveraging language switching within a single clip to maintain synchronization and quality.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed approach demonstrates superior performance in high-quality video dubbing with enhanced visual fidelity, lip synchronization, and robustness against real-world dynamics when compared to existing methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22143
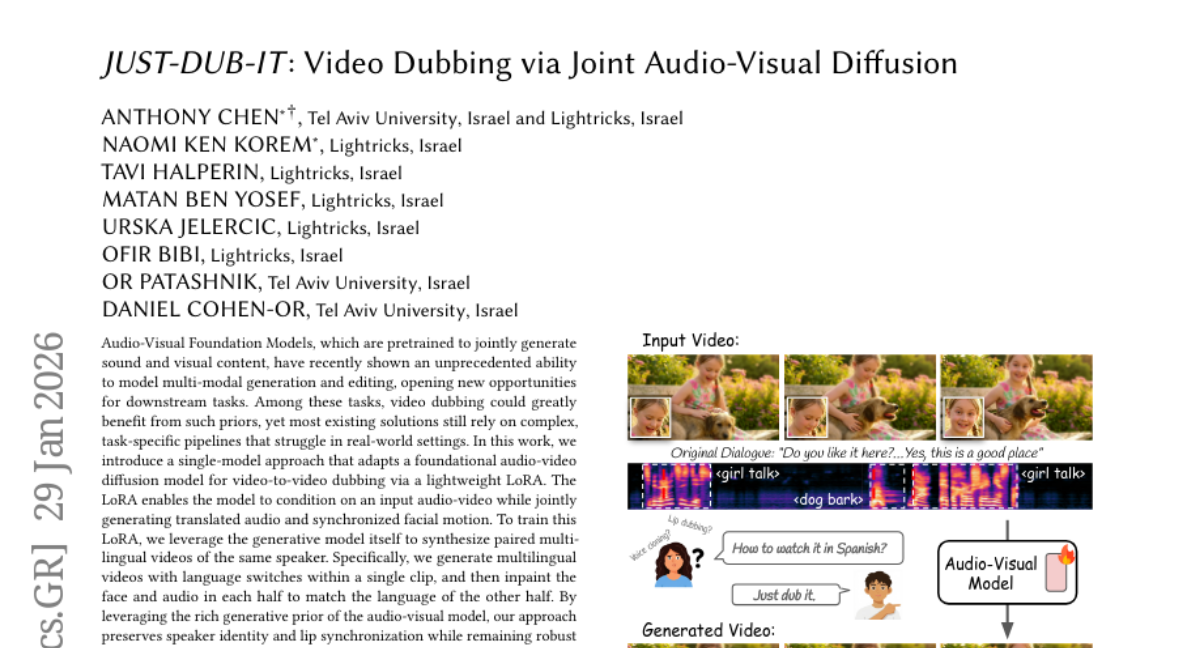
30. Generation Enhances Understanding in Unified Multimodal Models via Multi-Representation Generation
🔑 Keywords: Unified Multimodal Models, visual understanding, post-training methods, intrinsic representations
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– This research aims to enhance Unified Multimodal Models (UMMs) by training them to generate multiple visual representations to improve understanding and generation capabilities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduce UniMRG, an architecture-agnostic post-training method that trains UMMs to generate multiple intrinsic representations such as pixel reconstruction, geometry, and segmentation, alongside existing visual understanding objectives.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study finds that UniMRG notably enhances fine-grained perception, reduces hallucinations, and improves spatial understanding while simultaneously boosting generation capabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21406
31. MetricAnything: Scaling Metric Depth Pretraining with Noisy Heterogeneous Sources
🔑 Keywords: Metric Depth Estimation, Scalability, Sparse Metric Prompt, Vision Foundation Models, Visual Encoder
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to enhance metric depth estimation by presenting a scalable pretraining framework called Metric Anything, which leverages diverse 3D data and sparse metric prompts to achieve superior performance across multiple vision tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The approach introduces the Sparse Metric Prompt that decouples spatial reasoning from sensor and camera biases, using about 20M image-depth pairs across multiple sources to demonstrate scaling trends in metric depth estimation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Metric Anything excels in prompt-driven tasks like depth completion, super-resolution, and Radar-camera fusion, and achieves state-of-the-art results on monocular depth estimation and 3D reconstruction. Utilizing the pretrained model as a visual encoder enhances multimodal language model capabilities in spatial intelligence. The project is open-sourced to support community research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22054
32. Self-Improving Pretraining: using post-trained models to pretrain better models
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Pretraining, Safety, Factuality, Language Models
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a reinforcement learning-based pretraining method to enhance safety, factuality, and quality in large language model generations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employ reinforcement learning to improve token generation by evaluating original, model rollout, and rewritten suffixes during pretraining.
– Use a post-trained model to judge quality, safety, and factuality, rewarding high-quality rollouts as the model improves.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The method results in 36.2% improvement in factuality and 18.5% in safety relative to standard pretraining, with up to 86.3% win rate improvements in overall generation quality.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21343

33. FineInstructions: Scaling Synthetic Instructions to Pre-Training Scale
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Synthetic Instruction-Response Pairs, Instruction Tuning, Pre-training, Response Quality
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop a procedure to transform unstructured pre-training data into large-scale synthetic instruction-response pairs to improve the performance of large language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize ~18M instruction templates created from user-written queries and match them with human-written documents, generating synthetic training data at scale.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The FineInstructions dataset allows large language models to be effectively pre-trained from scratch using the instruction-tuning objective, outperforming traditional and other synthetic pre-training methods on benchmarks measuring response quality.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22146
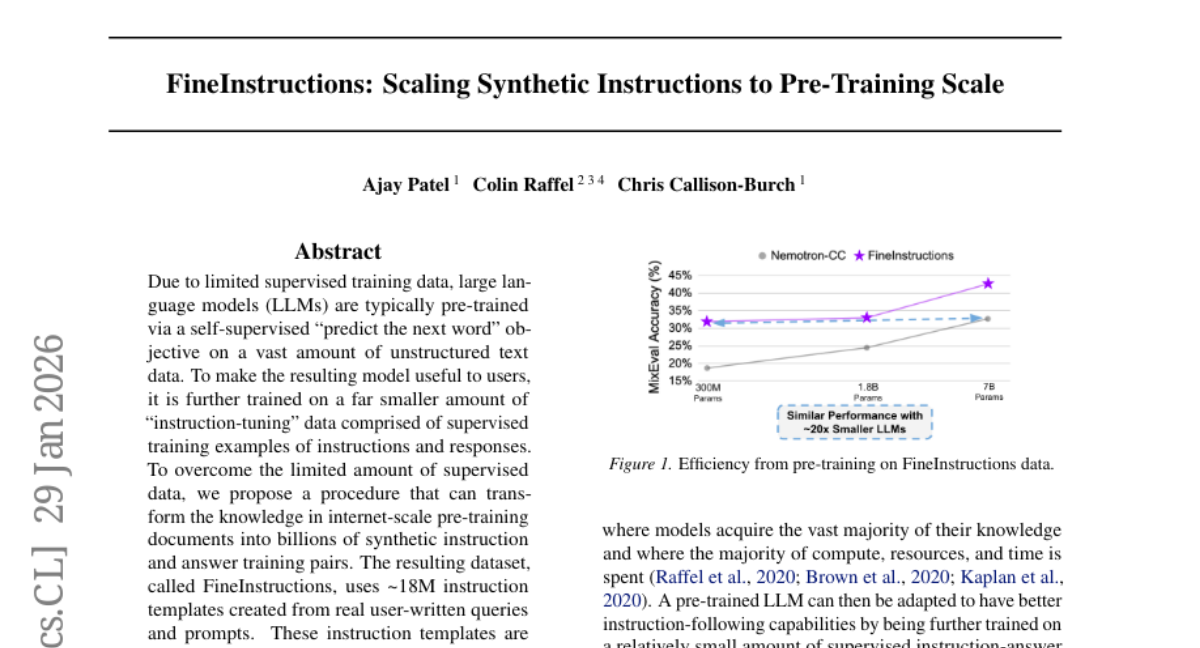
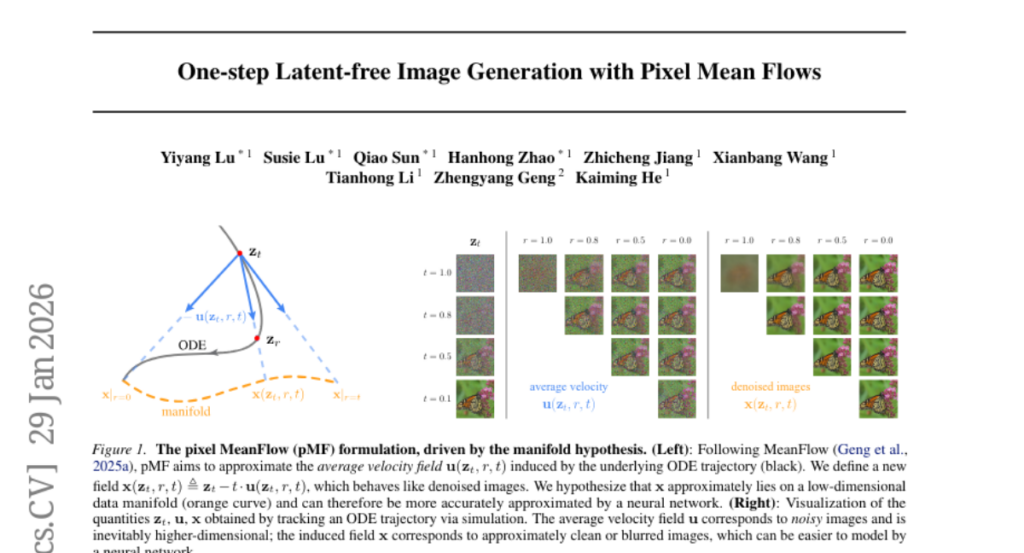
34. One-step Latent-free Image Generation with Pixel Mean Flows
🔑 Keywords: Pixel MeanFlow, ImageNet, latent-free, diffusion/flow-based models, x-prediction
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a one-step latent-free image generation method using a strategy that separates the network output space from the loss space.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced “Pixel MeanFlow” which formulates the network output and loss space separately and employs x-prediction on a low-dimensional image manifold.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieved strong results for one-step generation on ImageNet with impressive scores at resolutions of 256×256 (2.22 FID) and 512×512 (2.48 FID).
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22158
35. DeepSearchQA: Bridging the Comprehensiveness Gap for Deep Research Agents
🔑 Keywords: DeepSearchQA, multi-step information-seeking tasks, systematic collation, de-duplication, long-horizon planning
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce DeepSearchQA, a novel benchmark for evaluating agents on complex multi-step information-seeking tasks across 17 fields.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The use of a dataset of 900 prompts designed to test agents on challenging tasks involving systematic collation of information, de-duplication, and reasoning about stopping criteria.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– State-of-the-art agent architectures show significant performance limitations, struggling to balance high recall with precision. Identified failure modes include premature stopping and hedging behaviors, pointing to the need for more robust deep-research capabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.20975

36. VTC-R1: Vision-Text Compression for Efficient Long-Context Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: Long-context reasoning, vision-text compression, vision-language models, optical memory, token compression
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce VTC-R1, a new paradigm integrating vision-text compression into long-context reasoning to enhance efficiency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize VTC-R1 to convert textual traces into compact images for vision-language models, using OpenR1-Math-220K for training to achieve token compression and fine-tuning with VLMs-Glyph and Qwen3-VL.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– VTC-R1 significantly outperforms traditional methods in reasoning speed and efficiency, achieving up to 2.7x speedup in latency, demonstrating its potential for reasoning-intensive applications.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22069
37. Llama-3.1-FoundationAI-SecurityLLM-Reasoning-8B Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: AI Native, Reinforcement Learning, Cybersecurity, Multi-hop reasoning, Safety performance
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The aim is to develop an open-source cybersecurity reasoning model, Foundation-Sec-8B-Reasoning, that can perform well on specialized tasks while maintaining general capabilities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The model is trained using a two-stage process combining supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning from verifiable rewards, utilizing proprietary reasoning data.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The model demonstrates competitive performance across cybersecurity and general-purpose benchmarks, effective generalization on multi-hop reasoning tasks, and strong safety performance through appropriate deployment.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21051

38. Scalable Power Sampling: Unlocking Efficient, Training-Free Reasoning for LLMs via Distribution Sharpening
🔑 Keywords: large language models, distribution sharpening, reinforcement learning, power distribution, inference latency
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve large language model reasoning performance through distribution sharpening without iterative sampling or external rewards.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method leverages approximation of the global power distribution by a token-level scaled low-temperature distribution, enabling a training-free and verifier-free algorithm.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed approach matches or surpasses one-shot GRPO in performance and significantly reduces inference latency by over 10x compared to MCMC-based sampling.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21590

39. Discovering Hidden Gems in Model Repositories
🔑 Keywords: Hidden Gems, Multi-Armed Bandit, Sequential Halving, AI Native, Model Discovery
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To investigate whether the concentration of model usage on a few foundation checkpoints in public repositories is due to efficient market selection or systematic overlooking of superior models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized a Multi-Armed Bandit approach to frame model discovery, accelerating the Sequential Halving search algorithm with shared query sets and aggressive elimination.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Discovered “hidden gems” among rarely used models that significantly outperform popular ones and accelerated model discovery by over 50 times with as few as 50 queries per candidate.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22157
40. LoL: Longer than Longer, Scaling Video Generation to Hour
🔑 Keywords: sink-collapse, Rotary Position Embedding, multi-head attention, autoregressive models, video generation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary aim was to address the issue of sink-collapse in autoregressive video generation, which causes abrupt scene resets and cyclic motion patterns due to a conflict between Rotary Position Embedding and multi-head attention mechanisms.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A lightweight, training-free method was proposed involving multi-head RoPE jitter to break inter-head attention homogenization, mitigating long-horizon collapse while maintaining video generation quality.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The method effectively suppresses sink-collapse, enabling real-time streaming and infinite-length video generation with minimal quality decay. Demonstrations include continuous video generation of up to 12 hours, showcasing the robustness of the approach.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.16914
41. AgentLongBench: A Controllable Long Benchmark For Long-Contexts Agents via Environment Rollouts
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Autonomous Agents, Dynamic Contexts, AgentLongBench, Information Density
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To evaluate large language models as autonomous agents in dynamic environments and identify challenges compared to traditional static benchmarks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of AgentLongBench to simulate environment rollouts using Lateral Thinking Puzzles, generating interaction trajectories in both knowledge-intensive and knowledge-free scenarios.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– State-of-the-art models struggle with dynamic information synthesis in workflows due to high information density in tool responses, which is a greater challenge than memory fragmentation in long dialogues.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.20730

42. PLANING: A Loosely Coupled Triangle-Gaussian Framework for Streaming 3D Reconstruction
🔑 Keywords: Streaming Reconstruction, Hybrid Representation, Neural Gaussians, Decoupled Optimization
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop an efficient streaming reconstruction framework that addresses the challenge of achieving both high-quality rendering and accurate geometry.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces PLANING, which utilizes a hybrid representation combining explicit geometric primitives with neural Gaussians, allowing for decoupled geometry and appearance modeling.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PLANING improves rendering and geometric accuracy with a substantial 18.52% improvement in dense mesh Chamfer-L2 over PGSR, offers faster reconstruction of scenes like ScanNetV2 by over 5x compared to 2D Gaussian Splatting, and enhances structural clarity and computational efficiency for various downstream applications.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22046

43. MMFineReason: Closing the Multimodal Reasoning Gap via Open Data-Centric Methods
🔑 Keywords: Vision Language Models, Multimodal reasoning, Chain-of-Thought, Qwen3-VL, Parameter efficiency
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary objective is to enhance vision language models’ visual reasoning performance through the introduction of a large-scale multimodal reasoning dataset, MMFineReason.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employ a three-stage pipeline involving data collection and standardization, CoT rationale generation, and selection based on reasoning quality and difficulty awareness.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study introduces MMFineReason, improving VLMs’ performance with superior parameter efficiency and demonstrates that a difficulty-aware filtering strategy with just 7% of the dataset achieves comparable performance to the full dataset.
– Fine-tuned models MMFineReason-2B/4B/8B establish new state-of-the-art results, with MMFineReason-8B surpassing several existing models.
– Findings highlight a synergistic effect boosting general capabilities through reasoning-oriented data composition.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.21821

44. DynamicVLA: A Vision-Language-Action Model for Dynamic Object Manipulation
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language-Action (VLA), Temporal Reasoning, Closed-Loop Adaptation, Multimodal Inference, Dynamic Object Manipulation
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address dynamic object manipulation challenges through a Vision-Language-Action model with temporal reasoning and closed-loop adaptation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized a compact 0.4B VLA with a convolutional vision encoder for efficient encoding.
– Enabled continuous inference and latent-aware action streaming to improve response speed and reduce latency.
– Introduced the Dynamic Object Manipulation (DOM) benchmark with 200K synthetic episodes and 2K real-world episodes for data foundation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrated remarkable improvements in response speed, perception, and generalization.
– Established DynamicVLA as a unified framework for general dynamic object manipulation across various scenarios.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22153
45. Everything in Its Place: Benchmarking Spatial Intelligence of Text-to-Image Models
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, Text-to-image (T2I) models, Spatial intelligence, Spatial reasoning, Information-dense prompts
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research introduces a new benchmark, SpatialGenEval, to evaluate and improve spatial reasoning capabilities in text-to-image (T2I) models through more complex and information-dense prompts.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– SpatialGenEval consists of 1,230 information-rich prompts across 25 real-world scenes, incorporating diverse spatial sub-domains with multi-choice questions.
– A new dataset, SpatialT2I, was developed with 15,400 text-image pairs for fine-tuning existing T2I models, ensuring image consistency and information preservation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study finds higher-order spatial reasoning is a significant challenge for current T2I models.
– Fine-tuning foundation models such as Stable Diffusion-XL, Uniworld-V1, and OmniGen2 with the new dataset enhances performance, showing significant gains in realistic spatial effects.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.20354
