AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20260205
1. ERNIE 5.0 Technical Report
🔑 Keywords: ERNIE 5.0, Autoregressive Model, Multimodal Understanding, Mixture-of-Experts, Elastic Training
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduction of ERNIE 5.0, a trillion-parameter autoregressive model designed for unified multimodal understanding and generation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized a sparse MoE architecture with modality-agnostic expert routing and an innovative elastic training paradigm to optimize performance under resource constraints.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ERNIE 5.0 demonstrates strong and balanced performance across text, image, video, and audio modalities, marking a significant production-scale achievement in AI research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.04705

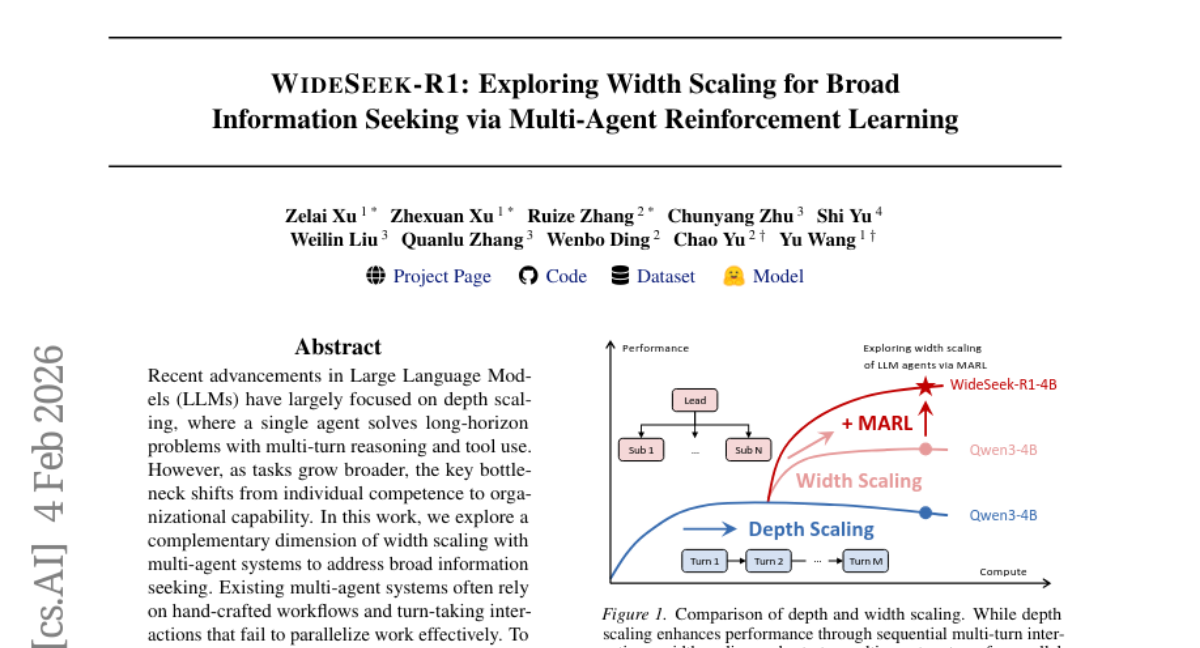
2. WideSeek-R1: Exploring Width Scaling for Broad Information Seeking via Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: Multi-agent systems, Reinforcement learning, Width scaling, Large Language Models, Parallel execution
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To explore width scaling in multi-agent systems for broad information-seeking tasks using a lead-agent-subagent framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of WideSeek-R1, trained via multi-agent reinforcement learning with a shared LLM and specialized tools for parallel execution.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– WideSeek-R1-4B achieves comparable performance to larger single-agent systems, with consistent performance improvements observed as the number of parallel subagents increases.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.04634
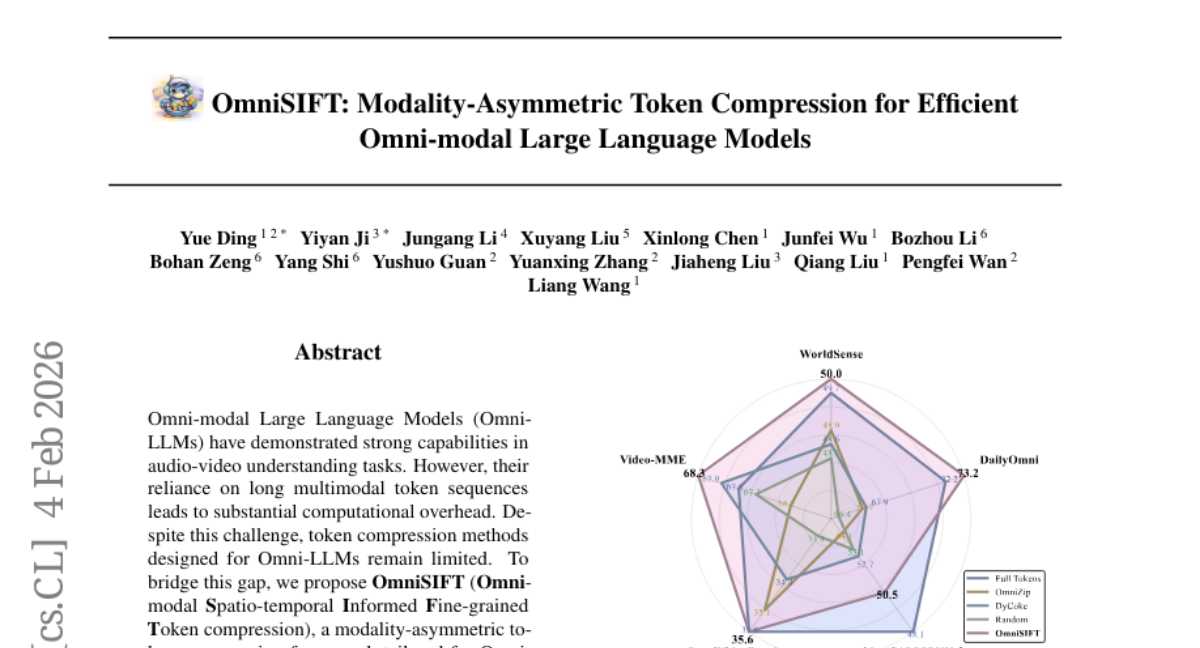
3. OmniSIFT: Modality-Asymmetric Token Compression for Efficient Omni-modal Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Omni-modal Large Language Models, token compression, multimodal token sequences, spatio-temporal video pruning, vision-guided audio selection
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to reduce computational overhead in Omni-modal Large Language Models (Omni-LLMs) through a framework called OmniSIFT, which focuses on token compression.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– OmniSIFT utilizes a two-stage compression strategy: spatio-temporal video pruning to eliminate redundancy and vision-guided audio selection to filter audio tokens. The system is optimized using a differentiable straight-through estimator.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– OmniSIFT shows efficacy and robustness, significantly reducing computational overhead while maintaining or surpassing performance compared to existing compression baselines, achieving superior results even with a reduced token context.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.04804
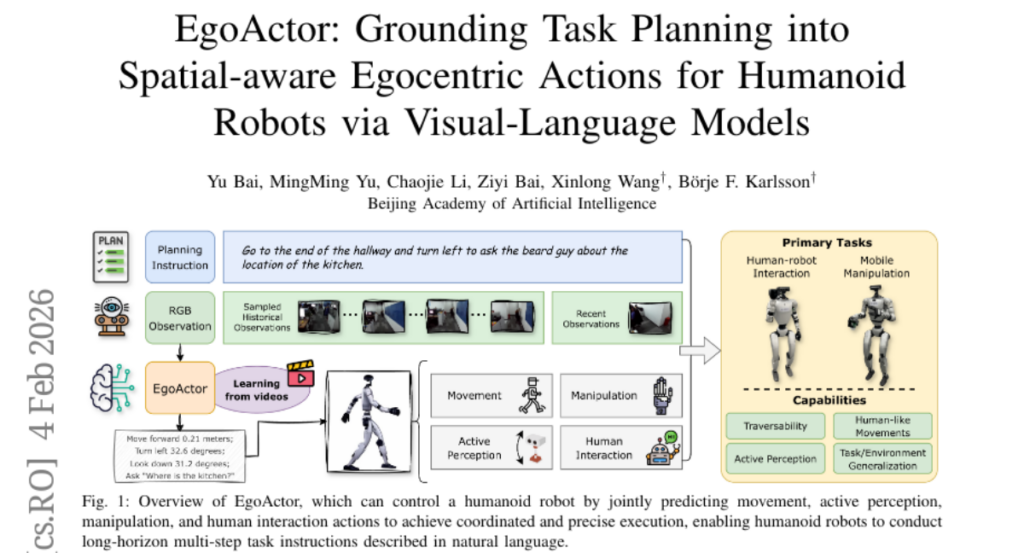
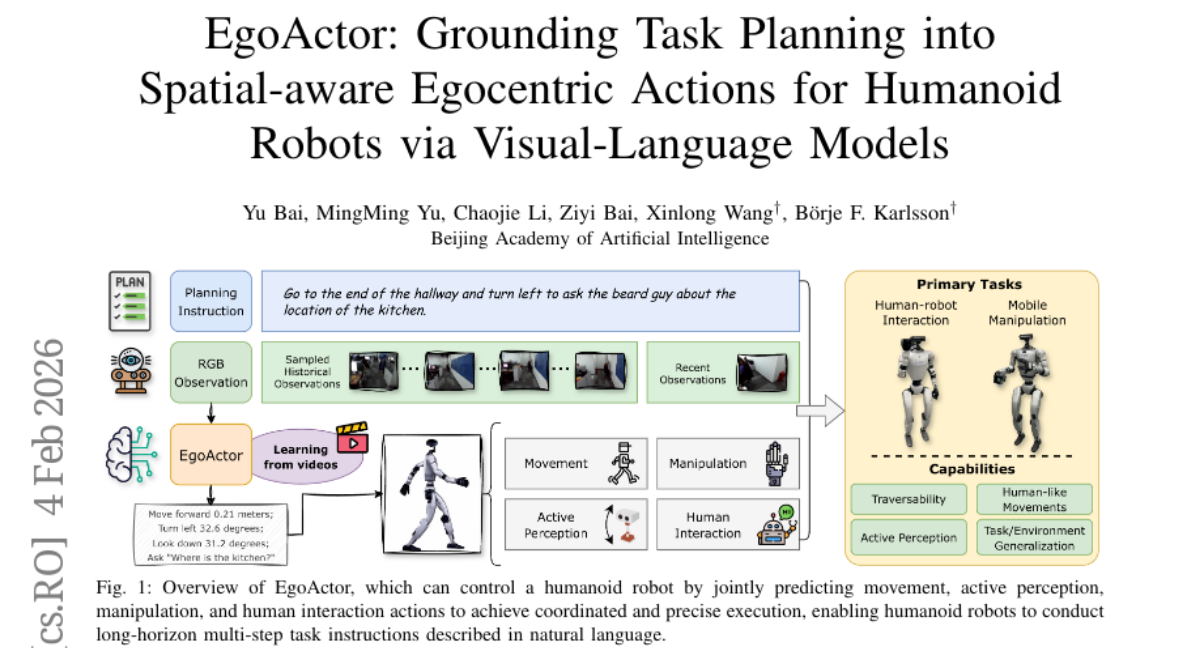
4. EgoActor: Grounding Task Planning into Spatial-aware Egocentric Actions for Humanoid Robots via Visual-Language Models
🔑 Keywords: EgoActor, vision-language model, humanoid actions, real-world environments, AI-generated
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to deploy humanoid robots capable of integrating perception and execution in dynamically changing environments by proposing a task named EgoActing.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of EgoActor, a unified vision-language model, employing broad supervision over egocentric RGB-only data, spatial reasoning, and both simulated and real-world demonstrations to ensure real-time coordination between perception and execution.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Extensive evaluations indicate that EgoActor effectively bridges the gap between abstract task planning and concrete motor execution, generalizing across diverse tasks and unseen environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.04515
5. SoMA: A Real-to-Sim Neural Simulator for Robotic Soft-body Manipulation
🔑 Keywords: 3D Gaussian Splat, deformable dynamics, real-to-sim simulation, robot manipulation, latent neural space
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to address the challenge of simulating deformable objects under complex interactions for robot manipulation, focusing on enhancing accuracy, stability, and generalization in simulations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced SoMA, a 3D Gaussian Splat simulator that integrates deformable dynamics, environmental forces, and robot actions within a unified latent neural space, enabling end-to-end real-to-sim simulation without relying on predefined physical models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SoMA significantly improves resimulation accuracy and generalization by 20% in real-world robot manipulation tasks, supporting stable simulation of complex tasks like long-horizon cloth folding beyond observed trajectories.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.02402
6. Residual Context Diffusion Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Residual Context Diffusion, diffusion large language models, contextual residuals, decoupled two-stage training, denoising steps
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to enhance diffusion large language models (dLLMs) by recycling discarded token information using Residual Context Diffusion (RCD), aiming to improve accuracy with minimal computational overhead.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The paper proposes a module called Residual Context Diffusion (RCD) that utilizes discarded token representations to create contextual residuals. It employs a decoupled two-stage training pipeline to avoid memory bottlenecks associated with backpropagation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RCD significantly improves the accuracy of dLLMs by 5-10 points across various benchmarks with minimal extra computation. On challenging AIME tasks, RCD nearly doubles baseline accuracy, requiring 4-5x fewer denoising steps to achieve equivalent accuracy levels.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22954
7. AutoFigure: Generating and Refining Publication-Ready Scientific Illustrations
🔑 Keywords: FigureBench, AutoFigure, scientific illustrations, text-to-illustration, agentic framework
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce FigureBench, the first large-scale benchmark for generating scientific illustrations from long-form scientific texts.
– To propose AutoFigure, an agentic framework for automatically generating publication-ready scientific illustrations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of FigureBench, containing 3,300 high-quality scientific text-figure pairs, and extensive experiments to benchmark AutoFigure’s performance against baseline methods.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– AutoFigure consistently outperforms baseline methods, producing high-quality and publication-ready scientific illustrations with both structural completeness and aesthetic appeal.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.03828

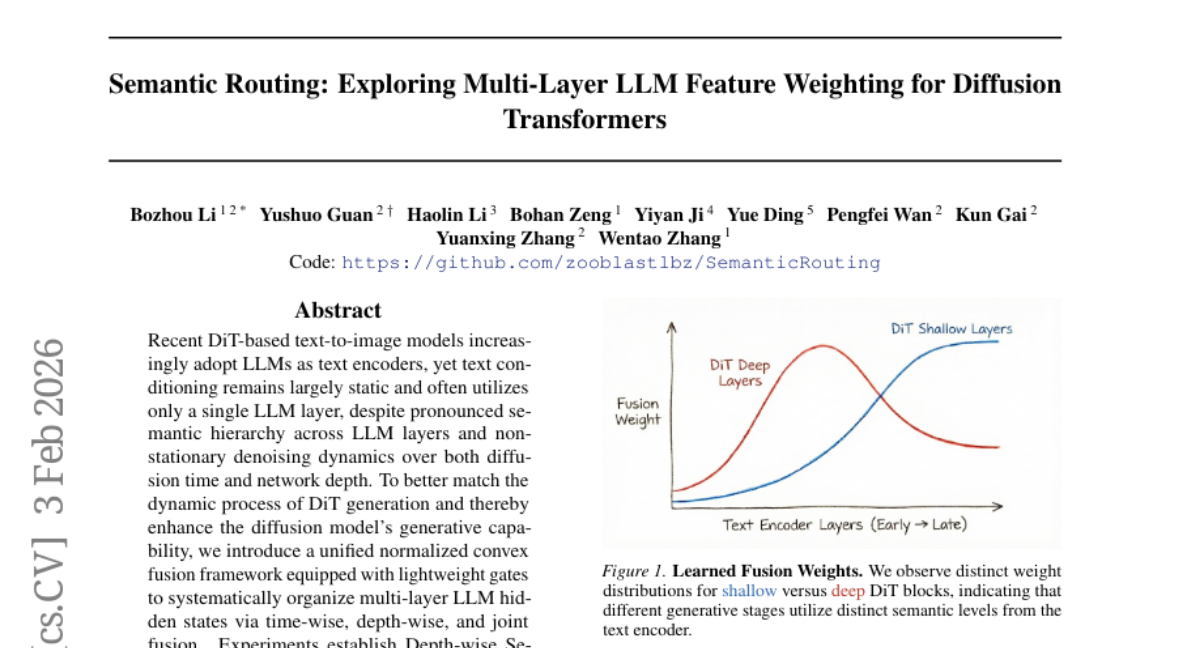
8. Semantic Routing: Exploring Multi-Layer LLM Feature Weighting for Diffusion Transformers
🔑 Keywords: DiT-based models, LLM hidden states, text-image alignment, compositional generation, depth-wise semantic routing
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Enhance text conditioning in DiT-based text-to-image models through a unified normalized convex fusion framework to improve generative capability.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of a unified normalization with convex fusion using lightweight gates to organize multi-layer LLM hidden states with time-wise, depth-wise, and joint fusion strategies.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Depth-wise Semantic Routing emerges as the most effective conditioning strategy, significantly improving text-image alignment and compositional generation.
– A caution around time-wise fusion, which can degrade visual generation quality due to train-inference trajectory mismatch.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.03510
9. VLS: Steering Pretrained Robot Policies via Vision-Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language Steering, Training-free Inference-time Adaptation, Imitation Learning, Generative Robot Policies, Vision-Language Models
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces Vision-Language Steering (VLS) as a solution for addressing the limitations of pretrained diffusion and flow-matching policies under test-time shifts without the need for retraining.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– VLS leverages vision-language models to create trajectory-differentiable reward functions for steering the sampling process during inference-time, accommodating out-of-distribution inputs without modifying existing policy parameters.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– VLS demonstrates a significant improvement over prior methods with a 31% improvement on CALVIN and a 13% gain on LIBERO-PRO, and successfully adapts to spatial and semantic shifts in real-world conditions, proving its effectiveness for inference-time adaptation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.03973
10. CL-bench: A Benchmark for Context Learning
🔑 Keywords: Context Learning, Language Models, Real-world Tasks, Pre-trained Knowledge, CL-bench
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main goal is to enhance the context learning capabilities of language models, enabling them to effectively handle complex, real-world tasks that demand new knowledge beyond pre-training.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced CL-bench, a comprehensive benchmark with 500 complex contexts, 1,899 tasks, and 31,607 verification rubrics, crafted to evaluate the context learning ability of language models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Evaluation of ten state-of-the-art language models showed that on average, only 17.2% of tasks are solved, indicating limitations in current models’ context learning abilities. The best-performing model, GPT-5.1, managed 23.7%, highlighting a major bottleneck in advancing real-world, complex task-solving.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.03587

11. PaperSearchQA: Learning to Search and Reason over Scientific Papers with RLVR
🔑 Keywords: Search agents, language models, reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards, scientific papers, PaperSearchQA
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To train search agents to reason over scientific papers, enhancing technical question-answering capabilities which are crucial for future AI Scientist systems.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a search corpus of 16 million biomedical paper abstracts with the creation of PaperSearchQA dataset using reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards, benchmarking against non-RL retrieval baselines.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The developed search agents demonstrate superior reasoning and self-verification capabilities, effectively outperforming traditional retrieval methods; data and methods are scalable and applicable to other scientific domains.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.18207

12. From Data to Behavior: Predicting Unintended Model Behaviors Before Training
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, Large Language Models, unintended biases, Data2Behavior, Manipulating Data Features
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Data2Behavior to predict unintended model behaviors before training.
– Propose Manipulating Data Features (MDF) to uncover potential biases without parameter updates.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– MDF analyzes data features and uses mean representations during a model’s forward pass to reveal latent statistical signals.
– The method is lightweight and requires only 20% of the GPU resources compared to fine-tuning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MDF reliably predicts potential biases and safety risks in models like Qwen3-14B and Gemma-3-12b-it, aiding in identifying pre-training vulnerabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.04735

13. Agent-Omit: Training Efficient LLM Agents for Adaptive Thought and Observation Omission via Agentic Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: LLM agents, Agent-Omit, effectiveness-efficiency trade-offs, omission reward, agentic reinforcement learning
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to develop a framework, Agent-Omit, that enhances LLM agents’ efficiency by adaptively omitting redundant thoughts and observations during multi-turn interactions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The methods involve synthesizing cold-start data to fine-tune the omission behaviors and employing an omit-aware agentic reinforcement learning approach, which includes a dual sampling mechanism and tailored omission reward.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experimental results indicate that Agent-Omit achieves superior effectiveness-efficiency trade-offs, showing performance comparable to frontier LLM agents and surpassing existing methods in efficiency.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.04284

14. SpatiaLab: Can Vision-Language Models Perform Spatial Reasoning in the Wild?
🔑 Keywords: Spatial reasoning, vision-language models, real-world complexity, 3D Geometry, Spatial Navigation
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to evaluate and advance the spatial reasoning capabilities of vision-language models (VLMs) through the introduction of a comprehensive benchmark called SpatiaLab.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A benchmark comprising 1,400 visual question-answer pairs across six major spatial categories, with 30 distinct task types, was used to assess both open- and closed-source VLMs compared to human performance.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Results show a significant gap in VLMs’ spatial reasoning performance compared to humans, with VLMs achieving lower accuracy in both multiple-choice and open-ended tasks, highlighting key limitations in handling complex spatial relationships, navigation, and 3D geometry.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.03916

15. A2Eval: Agentic and Automated Evaluation for Embodied Brain
🔑 Keywords: Agentic Automatic Evaluation, embodied VLM, evaluation suite, computational costs, ranking bias
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To automate the assessment of embodied vision-language models to reduce costs and improve accuracy through the Agentic Automatic Evaluation (A2Eval) framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize two collaborative agents, a Data Agent and an Eval Agent, to autonomously curate benchmarks and evaluate models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– A2Eval significantly reduces evaluation suite size by 85% and computational costs by 77%, achieving a 4.6x speedup. It also corrects ranking biases, enhancing human alignment and maintaining high ranking fidelity with Spearman’s rho=0.85 and Kendall’s tau=0.81.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.01640

16. BatCoder: Self-Supervised Bidirectional Code-Documentation Learning via Back-Translation
🔑 Keywords: BatCoder, Self-supervised Reinforcement Learning, Code Generation, Documentation Production, Back-translation
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces BatCoder, a framework designed to improve code and documentation generation through self-supervised reinforcement learning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework employs a back-translation strategy to jointly optimize code and documentation, allowing training with only code and increasing available training examples.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– BatCoder outperformed strong open-source baselines with 83.5% and 81.0% pass@1 on HumanEval and MBPP, showing excellent scaling regarding training corpus size and model capacity.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.02554
17. Efficient Autoregressive Video Diffusion with Dummy Head
🔑 Keywords: AI-generated summary, autoregressive video diffusion model, multi-head self-attention, heterogeneous memory allocation, dynamic head programming
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Address the inefficiencies in autoregressive video diffusion models’ attention mechanisms to enhance video generation efficiency without compromising quality.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implement Dummy Forcing through heterogeneous memory allocation and dynamic head programming to streamline context accessibility.
– Utilize context packing for cache compression to achieve significant speedup.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Dummy Forcing improves efficiency with up to 2.0x speedup and supports video generation at 24.3 FPS with minor impact on quality.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.20499
18. SAFE: Stable Alignment Finetuning with Entropy-Aware Predictive Control for RLHF
🔑 Keywords: reinforcement learning, RLHF, SAFE, KL divergence, PPO
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a new reinforcement learning algorithm (SAFE) for language model alignment that improves stability and performance over PPO through enhanced KL divergence control and adaptive reward management.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of a pure on-policy actor-critic RL method which incorporates Double Soft-Min Critic for pessimistic value estimation and a multi-layer stabilization framework with entropy-gated KL regulation and PID-controlled adaptive thresholds.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SAFE achieves a 5.15% higher average training reward compared to PPO, demonstrating negligible reward crashes and superior KL control, while introducing minimal computational overhead and providing a crash-resistant framework suitable for production deployment.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.04651

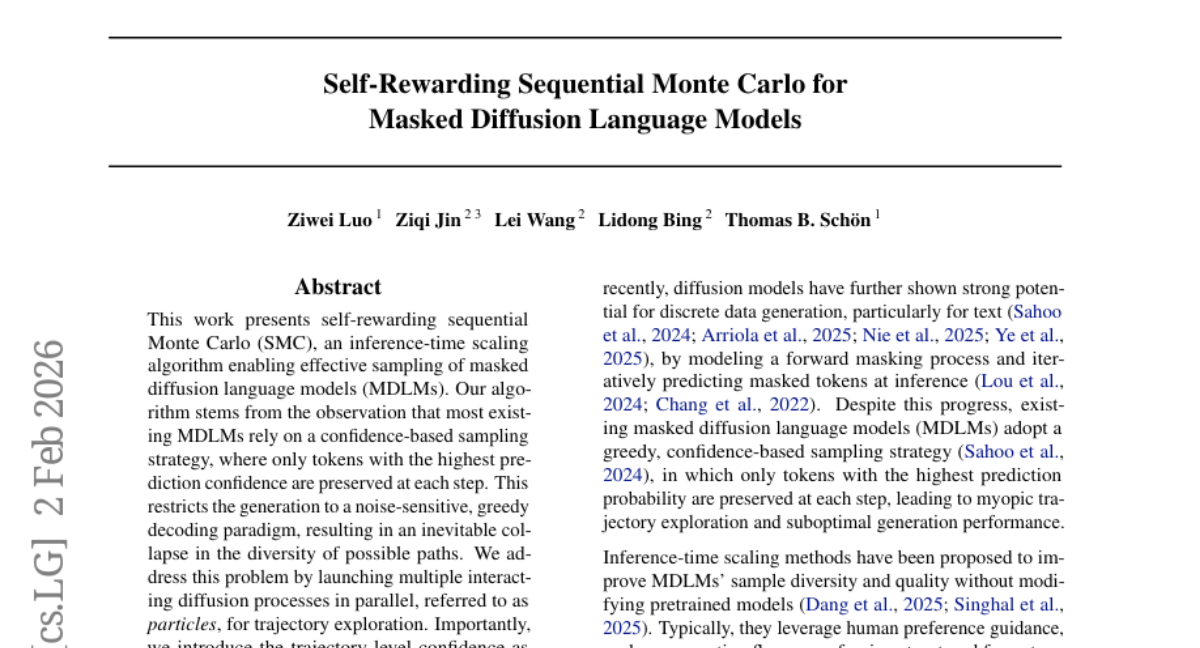
19. Self-Rewarding Sequential Monte Carlo for Masked Diffusion Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Sequential Monte Carlo, Masked Diffusion Language Models, Confidence-based Sampling, Diffusion Processes, Parallel Inference
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To present a self-rewarding sequential Monte Carlo algorithm for effective sampling of masked diffusion language models, aiming to overcome limitations of traditional confidence-based sampling strategies.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced parallel diffusion processes with trajectory-level confidence as a self-rewarding signal for assigning particle importance weights. Utilized iterative weighting and resampling of particles to enhance sampling quality.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed self-rewarding SMC approach significantly improves generation quality and diversity without additional training or reward guidance, effectively enhancing parallel inference capacity into improved sampling outcomes.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.01849
20. Context Learning for Multi-Agent Discussion
🔑 Keywords: Multi-Agent Discussion, context learning, LLM, context coherence, self-adaptive mechanism
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address the inconsistency in Multi-Agent Discussion methods by developing a context learning approach that dynamically generates context instructions to improve the coherence and performance of multiple Large Language Models (LLMs).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The paper introduces the multi-LLM context learning (M2CL) method, which involves training context generators for each agent to dynamically produce context instructions using automatic information organization and refinement, guided by a self-adaptive mechanism.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The M2CL method significantly enhances performance by 20%–50% over existing methods on tasks such as academic reasoning, embodied tasks, and mobile control, and demonstrates improved consensus reaching, transferability, and computational efficiency.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.02350

21. Trust The Typical
🔑 Keywords: LLM safety, OOD detection, semantic space, GPU implementation, multilingual harms
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a novel framework for Large Language Model (LLM) safety by treating safety as an out-of-distribution (OOD) detection problem that can achieve state-of-the-art performance without the need for harmful example training.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementing Trust The Typical (T3), a framework relying on semantic space analysis to detect deviations from safe LLM prompt distributions. This involves a GPU-optimized model that focuses solely on safe English text but is applicable across multiple domains and languages.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The T3 framework significantly reduces false positive rates, up to 40 times lower compared to specialized safety models, while maintaining effectiveness across 18 benchmarks, including toxicity and multilingual harms. It shows readiness for production with minimal performance overhead.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.04581

22. Proxy Compression for Language Modeling
🔑 Keywords: Proxy Compression, Language Models, Compressed Inputs, Raw Byte Sequences, Training Efficiency
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce proxy compression as an alternative training scheme that maintains the efficiency benefits of compressed inputs while providing an end-to-end, raw-byte interface during inference.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Joint training of a language model on both raw byte sequences and compressed views generated by external compressors.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Proxy compression improves training efficiency and significantly outperforms pure byte-level baselines with fixed compute budgets. As the model scale increases, proxy-trained models can match or rival traditional tokenizer approaches while maintaining the robustness of byte-level modeling.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.04289

23. Reward-free Alignment for Conflicting Objectives
🔑 Keywords: Reward-free Alignment, Conflicted Objectives, Pairwise Preference Data, Conflict-averse Gradient Descent, Pareto Trade-offs
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a reward-free alignment framework that addresses conflicts in multi-objective alignment of language models using conflict-averse gradient descent with clipping.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of a novel clipped variant of conflict-averse gradient descent to resolve gradient conflicts in language model alignment, and utilization of pairwise preference data for updates.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The framework shows improved Pareto trade-offs in multi-objective tasks, with better alignment outcomes across several language model families (Qwen 3, Llama 3, Gemma 3) compared to existing methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.02495

24. AgentArk: Distilling Multi-Agent Intelligence into a Single LLM Agent
🔑 Keywords: AgentArk, Multi-Agent Systems, Hierarchical Distillation, Computational Efficiency
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to distill multi-agent reasoning dynamics into a single model, enhancing computational efficiency while retaining the intelligence of multi-agent systems.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study investigates three hierarchical distillation strategies: reasoning-enhanced fine-tuning, trajectory-based augmentation, and process-aware distillation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The distilled models maintain the efficiency of a single agent and exhibit strong reasoning and self-correction capabilities, demonstrating enhanced robustness and generalization across diverse reasoning tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.03955

25. FOTBCD: A Large-Scale Building Change Detection Benchmark from French Orthophotos and Topographic Data
🔑 Keywords: FOTBCD, building change detection, geographic diversity, cross-domain generalization, orthophotos
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce the FOTBCD dataset for large-scale building change detection across diverse geographic regions in France.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized high-resolution French orthophotos and topographic building data for creating FOTBCD.
– Released two datasets: FOTBCD-Binary for pixel-wise binary detection and FOTBCD-Instances for instance-level detection.
– Compared FOTBCD-Binary performance against existing benchmarks like LEVIR-CD+ and WHU-CD.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Geographic diversity at the dataset level improves cross-domain generalization in building change detection tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22596

26.

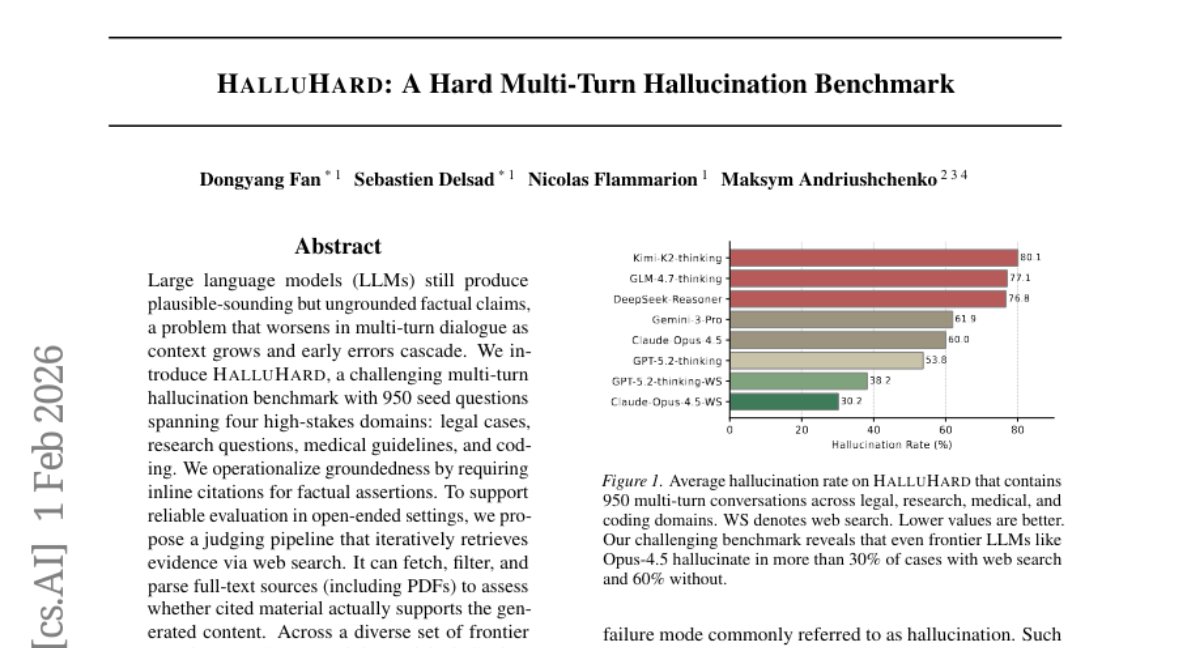
27. HalluHard: A Hard Multi-Turn Hallucination Benchmark
🔑 Keywords: Large language models, multi-turn dialogue, hallucination, groundedness, web search
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces HalluHard, a benchmark designed to evaluate the hallucination issue in multi-turn dialogue generated by large language models across high-stakes domains.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The approach includes operationalizing groundedness by requiring inline citations for factual assertions and using a judging pipeline that retrieves evidence via web search to ensure content support.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Despite efforts using web search to reduce hallucinations, errors persist significantly, influenced by model capacity, turn position, effective reasoning, and necessary knowledge types.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.01031
28. LongVPO: From Anchored Cues to Self-Reasoning for Long-Form Video Preference Optimization
🔑 Keywords: Direct Preference Optimization, vision-language models, ultra-long videos, recursive captioning, synthetic preference triples
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce LongVPO, a framework that enables vision-language models to understand ultra-long videos without long-video annotations, using a two-stage approach.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Stage 1 involves creating synthetic preference triples and filtering for visual-similarity and question-specificity to avoid positional bias.
– Stage 2 implements a recursive captioning pipeline, generating scene-level metadata and employing a large language model for multi-segment reasoning tasks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LongVPO outperforms state-of-the-art open-source models on long-video benchmarks with only 16K synthetic examples and maintains strong performance on short-video tasks, proving to be a scalable solution for efficient long-form video understanding.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.02341

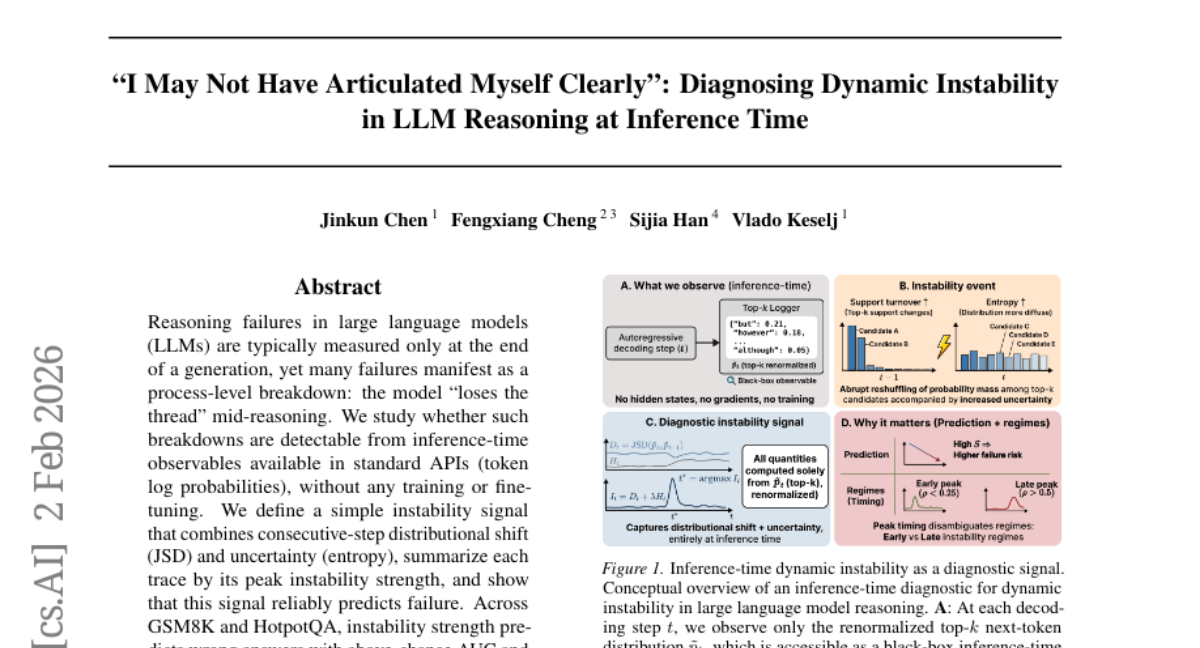
29. “I May Not Have Articulated Myself Clearly”: Diagnosing Dynamic Instability in LLM Reasoning at Inference Time
🔑 Keywords: reasoning failures, large language models, instability signal, corrective instability, destructive instability
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To investigate whether reasoning failures in large language models can be detected mid-reasoning using inference-time observables, without additional training or fine-tuning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized instability signals derived from token log probabilities and entropy to predict incorrect answers. Analysis was performed on GSM8K and HotpotQA datasets to assess instability signal effectiveness across different model sizes.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Instability signals can reliably predict failures in reasoning, with the timing of distribution shifts indicating corrective versus destructive instability. This method is model-agnostic, requires no additional training, and serves as a diagnostic tool rather than a correction mechanism.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.02863
30. SkeletonGaussian: Editable 4D Generation through Gaussian Skeletonization
🔑 Keywords: 4D generation, SkeletonGaussian, dynamic 3D objects, motion editing, articulated representation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main goal is to enable editable 4D generation by decomposing motion into skeleton-driven and fine-grained non-rigid components.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces SkeletonGaussian, a framework utilizing monocular video input to generate editable dynamic 3D Gaussians. It employs a hierarchical articulated representation for motion decomposition, combining robust skeleton extraction with linear blend skinning and hexplane-based refinement for non-rigid deformations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experimental results indicate that SkeletonGaussian provides superior generation quality and intuitive motion editing compared to existing methods, setting a new paradigm for editable 4D generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.04271

31. OmniRad: A Radiological Foundation Model for Multi-Task Medical Image Analysis
🔑 Keywords: OmniRad, Radiological Foundation Model, Representation Reuse, Cross-task Transferability, MedMNISTv2
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce OmniRad, a self-supervised radiological foundation model, and demonstrate its enhanced performance in classification and segmentation tasks using representation reuse and cross-task transferability.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Pretraining on 1.2 million medical images, utilizing radiology-inspired principles.
– Evaluating with various downstream adaptation regimes such as lightweight task-specific adapters and full end-to-end fine-tuning for assessing representation quality and task-specific performance.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– OmniRad achieves a classification F1 improvement of up to 2.05% over competing models on the MedMNISTv2 collection.
– Demonstrates mean Dice score improvements across six MedSegBench datasets, showcasing improvement in feature clustering and modality-related separation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.04547

32. RexBERT: Context Specialized Bidirectional Encoders for E-commerce
🔑 Keywords: RexBERT, E-commerce semantics, BERT-style encoders, Pretraining recipe, Natural language understanding
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of the research is to develop RexBERT, a family of BERT-style encoders specifically designed to improve performance in e-commerce domains through specialized pretraining and high-quality in-domain data.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Researchers introduced a novel corpus called Ecom-niverse, consisting of 350 billion tokens from various retail and shopping sources.
– A reproducible pretraining approach was developed, comprising three phases: general pre-training, context extension, and annealed domain specialization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RexBERT models, with fewer parameters, outperform larger general-purpose encoders and match or surpass modern long-context models on domain-specific benchmarks.
– The research demonstrates that optimized in-domain data and a methodical training process offer significant advantages for e-commerce applications over simple scaling of models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.04605

33. Protein Autoregressive Modeling via Multiscale Structure Generation
🔑 Keywords: PAR, autoregressive modeling, hierarchical structure modeling, protein backbone generation, flow-based decoding
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary aim is to present the PAR framework, which enhances protein backbone generation by employing a multi-scale autoregressive approach.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes multi-scale downsampling, autoregressive transformers, and flow-based decoding to accurately model protein structures.
– Implements noisy context learning and scheduled sampling to effectively address exposure bias in autoregressive models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrates improved protein structure quality with strong zero-shot generalization capability, supporting flexible and robust generation without the need for fine-tuning.
– Exhibits favorable scaling behavior and high-quality protein design on the unconditional generation benchmark, highlighting its potential in protein structure generation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.04883

34. Skin Tokens: A Learned Compact Representation for Unified Autoregressive Rigging
🔑 Keywords: Generative 3D models, SkinTokens, TokenRig, Reinforcement Learning, Skinning weights
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to address challenges in animation rigging by introducing a novel discrete representation for skinning weights called SkinTokens, and a unified framework TokenRig, to enhance rigging accuracy.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research leverages an FSQ-CVAE to transform skinning from a continuous regression task to a token sequence prediction problem, using reinforcement learning with tailored geometric and semantic rewards to improve generalization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed SkinTokens method significantly improves skinning accuracy by 98%-133% compared to current methods, and the complete TokenRig framework, optimized with reinforcement learning, enhances bone prediction accuracy by 17%-22%, offering a scalable, high-fidelity solution for 3D content creation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.04805
35. No One-Size-Fits-All: Building Systems For Translation to Bashkir, Kazakh, Kyrgyz, Tatar and Chuvash Using Synthetic And Original Data
🔑 Keywords: Machine Translation, Turkic Languages, LoRA Fine-tuning, Zero-shot, Synthetic Data
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to explore machine translation for five Turkic language pairs using various approaches.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Applied LoRA fine-tuning on nllb-200 model with synthetic data for specific language pairs.
– Used prompting with DeepSeek-V3.2 and retrieval-based methods to enhance translation performance.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Achieved varying chrF++ scores, with highest scores of 49.71 for Kazakh and 46.94 for Bashkir using LoRA.
– Zero-shot and retrieval-based methods also showed promising results for Tatar and Kyrgyz languages.
– Released the dataset and obtained weights for community use.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.04442

36. Beyond Unimodal Shortcuts: MLLMs as Cross-Modal Reasoners for Grounded Named Entity Recognition
🔑 Keywords: GMNER, Modality bias, Cross-modal reasoning, Multimodal Large Language Models
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to explore the potential of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) in performing Grounded Multimodal Named Entity Recognition (GMNER) in an end-to-end manner.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study proposes Modality-aware Consistency Reasoning (MCR) which includes Multi-style Reasoning Schema Injection (MRSI) and Constraint-guided Verifiable Optimization (CVO) to address modality bias.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MCR is effective in mitigating modality bias and achieves superior performance in GMNER and visual grounding tasks compared to existing baselines.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.04486

37. Likelihood-Based Reward Designs for General LLM Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: log-probability rewards, reinforcement learning, chain-of-thought, likelihood-based rewards, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To evaluate the effectiveness of log-probability rewards in fine-tuning large language models on various reasoning benchmarks, compared to traditional binary rewards.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Systematic investigation and comparison of log-probability derived rewards with standard baselines on both verifiable and non-verifiable reasoning benchmarks, employing reinforcement learning methodologies.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Log-probability rewards outperform binary rewards in chain-of-thought fine-tuning and are consistent in both verifiable and non-verifiable settings, demonstrating better success rates and perplexity metrics.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.03979

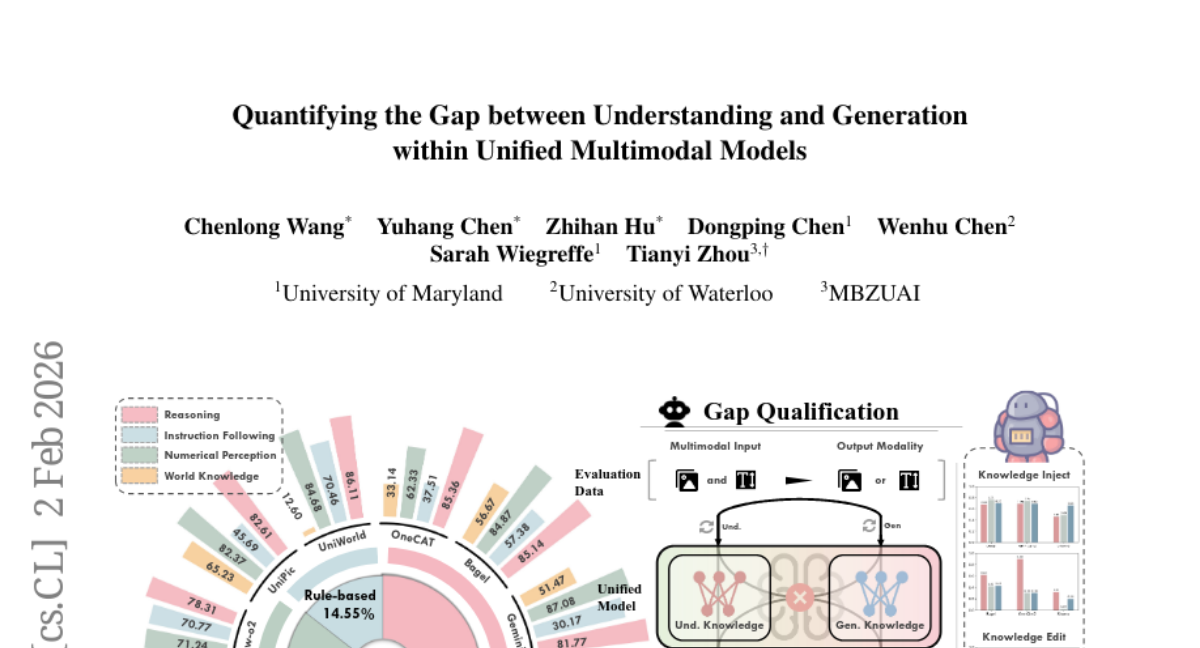
38. Quantifying the Gap between Understanding and Generation within Unified Multimodal Models
🔑 Keywords: Unified Multimodal Models, AI-generated summary, cognitive coherence, cross-modal consistency, knowledge manipulation
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to explore whether understanding and generation capabilities in Unified Multimodal Models (UMMs) are genuinely integrated within a single model, addressing the gap in cognitive coherence between these capabilities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced GapEval, a bidirectional benchmark to quantify the gap between understanding and generation capabilities. This benchmark assesses bidirectional inference capability and cross-modal consistency by allowing questions to be answered in both image and text modalities.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments show a persistent gap between the understanding and generation capabilities in various UMM architectures, indicating only surface-level integration. The study finds that the disjoint nature of knowledge within UMMs and unsynchronized emergence of capabilities across modalities suggest limitations in achieving deep cognitive convergence.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.02140
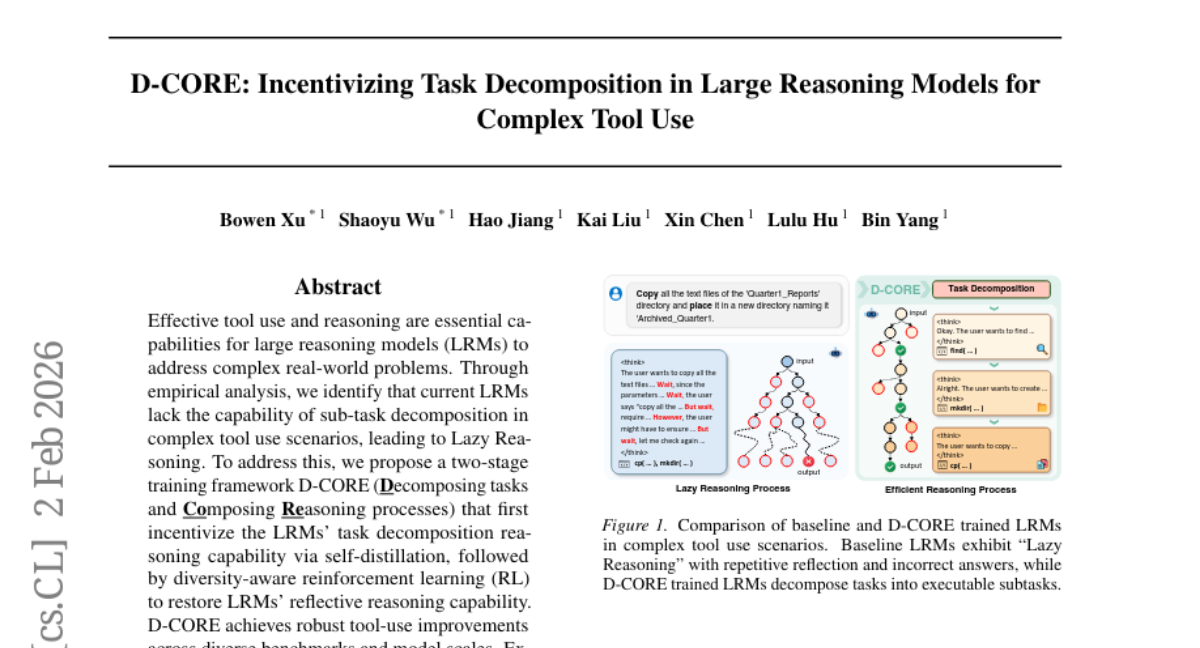
39. D-CORE: Incentivizing Task Decomposition in Large Reasoning Models for Complex Tool Use
🔑 Keywords: Large Reasoning Models, Sub-task Decomposition, Lazy Reasoning, Self-distillation, Diversity-aware Reinforcement Learning
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance large reasoning models’ ability to decompose complex tasks and improve reasoning processes for effective tool use.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers propose a two-stage training framework called D-CORE, which involves self-distillation to improve task decomposition and diversity-aware reinforcement learning to enhance reflective reasoning capabilities.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– D-CORE significantly improves tool-use effectiveness across various benchmarks, achieving superior performance compared to other models, even those with larger scales, as demonstrated by achieving new state-of-the-art results on BFCLv3.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.02160
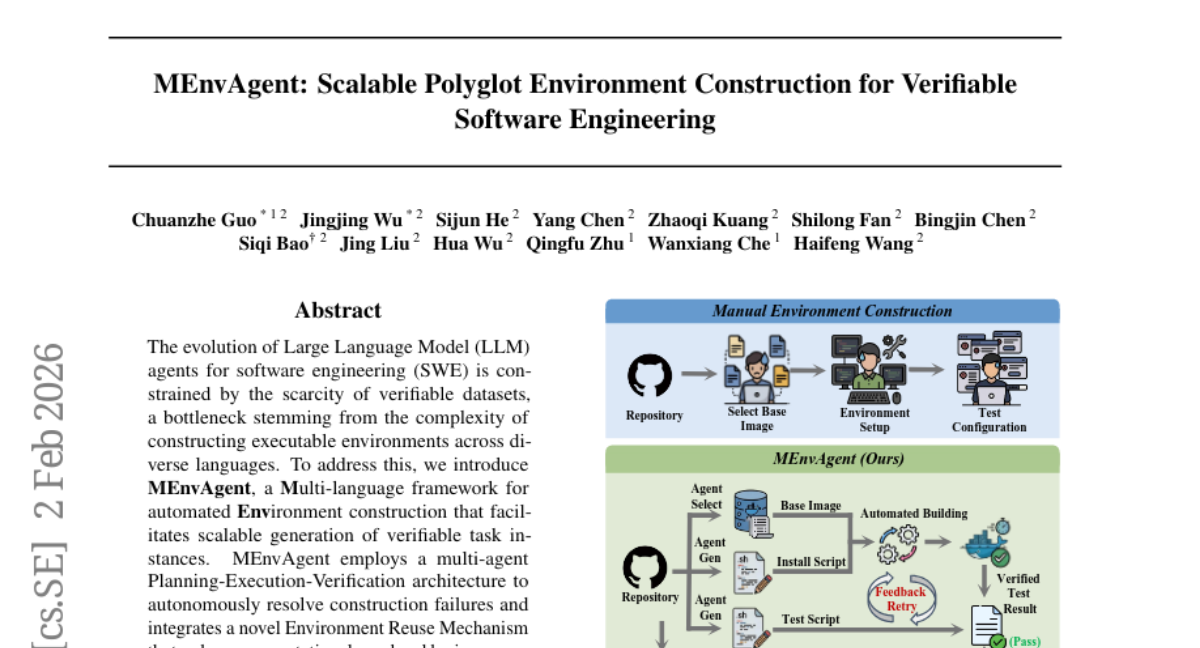
40. MEnvAgent: Scalable Polyglot Environment Construction for Verifiable Software Engineering
🔑 Keywords: MEnvAgent, Planning-Execution-Verification architecture, Environment Reuse Mechanism, verifiable datasets, AI-generated
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce MEnvAgent, a multi-language framework designed to automate the construction of scalable and verifiable environments for software engineering tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a multi-agent Planning-Execution-Verification architecture and an Environment Reuse Mechanism to improve environment construction and reduce computational overhead.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MEnvAgent significantly improves Fail-to-Pass rates by 8.6% and reduces time costs by 43% on a new benchmark, MEnvBench. It also constructs MEnvData-SWE, the largest open-source dataset of verifiable Docker environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2601.22859
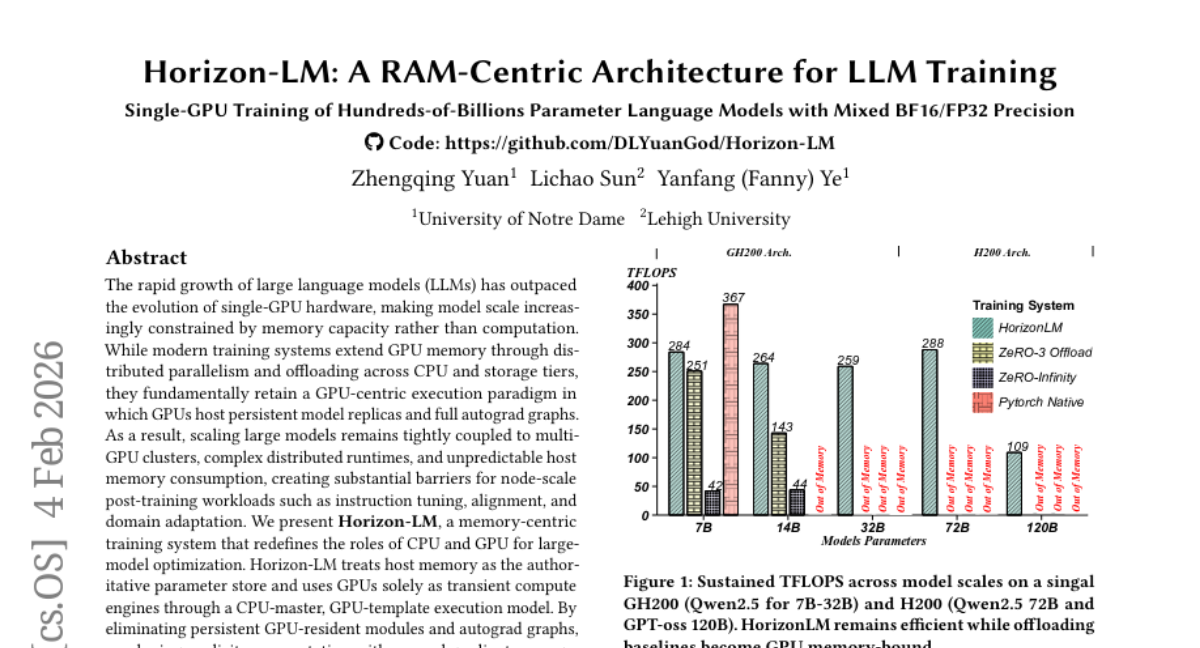
41. Horizon-LM: A RAM-Centric Architecture for LLM Training
🔑 Keywords: Horizon-LM, large language models, CPU-GPU roles, GPU memory usage, pipelined execution
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to enable efficient large-model training on single GPUs by redefining CPU-GPU roles and minimizing persistent GPU memory usage through innovative execution strategies.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Horizon-LM employs a CPU-master and GPU-template execution model. This approach involves treating host memory as the main parameter store and utilizing GPUs as transient compute engines. Techniques like explicit recomputation and pipelined double-buffered execution are used to optimize memory usage.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Horizon-LM effectively decouples model scaling from the number of GPUs and limits memory usage to the theoretical parameter footprint. It achieves significant training throughput improvements and high device utilization across different platforms, showing that host memory determines the feasibility of training large models on a single GPU.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.04816
42. A-RAG: Scaling Agentic Retrieval-Augmented Generation via Hierarchical Retrieval Interfaces
🔑 Keywords: Agentic RAG framework, hierarchical retrieval interfaces, AI-generated summary, keyword search, semantic search
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce A-RAG, an Agentic RAG framework, enabling dynamic adaptation in retrieval decisions across multiple granularities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized three retrieval tools: keyword search, semantic search, and chunk read, allowing adaptive information retrieval via hierarchical interfaces.
– Conducted experiments on multiple open-domain QA benchmarks to evaluate performance.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– A-RAG consistently outperforms traditional approaches in RAG tasks with comparable or fewer retrieved tokens.
– Demonstrates effective leveraging of model capabilities and dynamic adaptation to different retrieval tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.03442

43. Vibe AIGC: A New Paradigm for Content Generation via Agentic Orchestration
🔑 Keywords: Vibe AIGC, Intent-Execution Gap, multi-agent workflows, agentic orchestration
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce a new generative AI paradigm, Vibe AIGC, which aims to bridge the gap between human intent and machine execution by using agentic orchestration.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize hierarchical multi-agent workflows and a centralized Meta-Planner to deconstruct user-provided “Vibe” (aesthetic and functional preferences) into executable pipelines.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The Vibe AIGC paradigm promises to transform AI from a fragile inference engine into a robust engineering partner, thereby democratizing the creation of complex digital assets and redefining the human-AI collaborative economy.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.04575

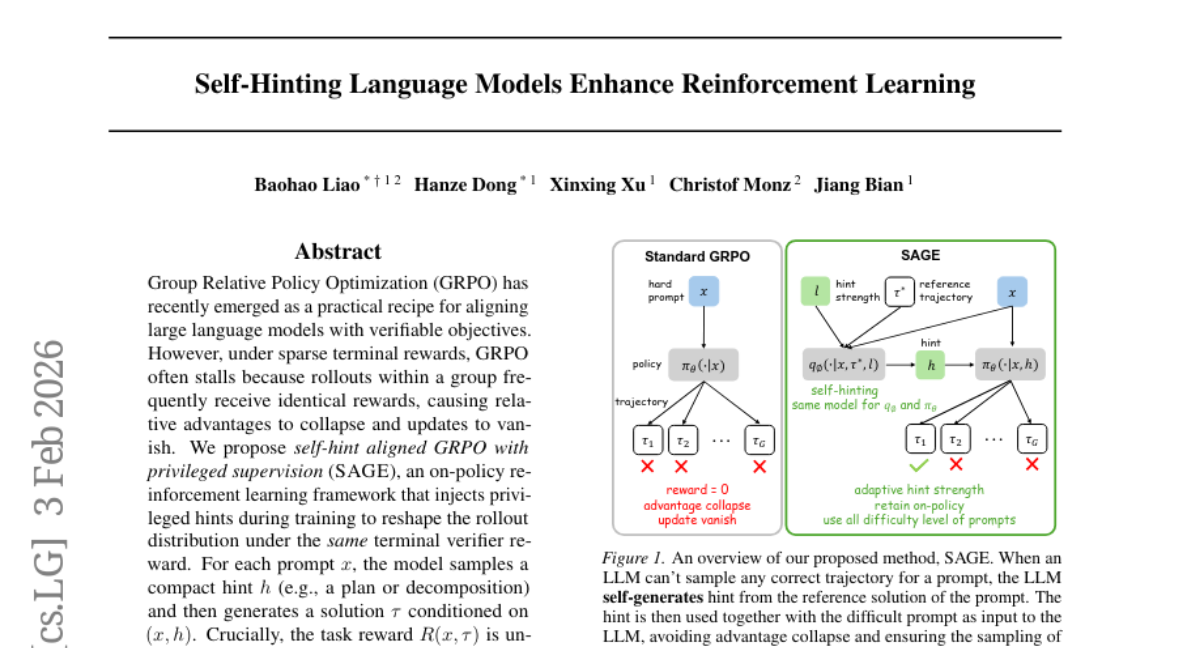
44. Self-Hinting Language Models Enhance Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: self-hint, GRPO, reinforcement learning, sparse rewards, large language models
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) by introducing an on-policy framework called SAGE that injects self-hints during training to increase the diversity of outcomes under sparse rewards, thereby improving the alignment of large language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of privileged supervision to inject self-hints, reshaping the rollout distribution while maintaining the same terminal verifier reward. This technique helps prevent the collapse of GRPO’s advantages under sparse rewards by enhancing within-group outcome diversity.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The SAGE framework consistently outperforms GRPO in experiments conducted on 6 benchmarks with 3 different large language models, showing improved performance scores of +2.0, +1.2, and +1.3 on Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct, Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct, and Qwen3-4B-Instruct, respectively. The approach serves as an adaptive curriculum that better addresses learner bottlenecks than fixed hint strategies.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.03143
45. HY3D-Bench: Generation of 3D Assets
🔑 Keywords: 3D content creation, generative models, AI-generated content (AIGC), multi-view renderings, 3D perception
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce HY3D-Bench, an open-source ecosystem aimed at enhancing 3D content creation through a unified, high-quality foundation for 3D generation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Curate a library of 250k high-fidelity 3D objects using a rigorous pipeline for training-ready artifacts, including watertight meshes and multi-view renderings.
– Implement structured part-level decomposition for granularity in fine-grained perception and controllable editing.
– Develop a scalable AIGC synthesis pipeline to bridge real-world distribution gaps and contribute 125k synthetic assets.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– HY3D-Bench facilitates democratized access to robust data resources, promoting innovation in 3D perception, robotics, and digital content creation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.03907
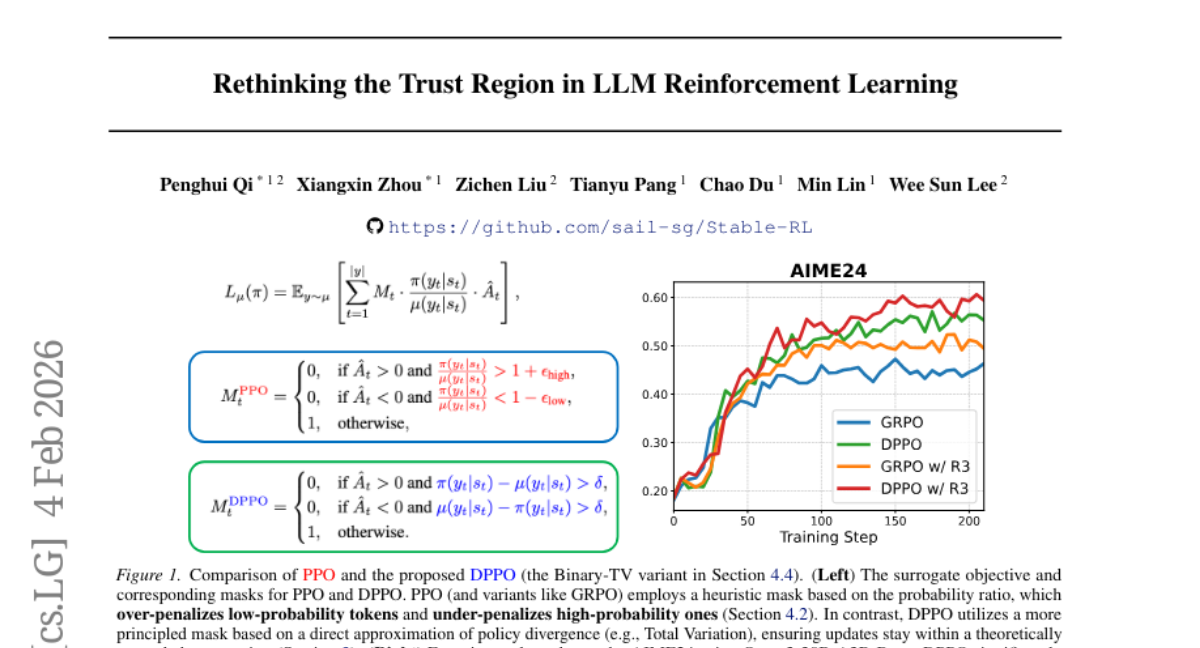
46. Rethinking the Trust Region in LLM Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Large Language Models, Proximal Policy Optimization, Policy Divergence, Training Stability
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) for fine-tuning Large Language Models (LLMs) by using direct policy divergence constraints instead of ratio clipping, enhancing training stability and efficiency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced Divergence Proximal Policy Optimization (DPPO) with a principled policy divergence constraint. Used Binary and Top-K approximations to manage memory usage and computational overhead.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DPPO provides superior stability and efficiency in training compared to existing methods, offering a robust foundation for Reinforcement Learning-based LLM fine-tuning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.04879
47. TIDE: Trajectory-based Diagnostic Evaluation of Test-Time Improvement in LLM Agents
🔑 Keywords: Test-Time Improvement, autonomous LLM agents, task optimization efficiency, working memory, environment-agnostic framework
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance understanding of Test-Time Improvement (TTI) in autonomous LLM agents by addressing inadequacies in current evaluation methods related to task optimization efficiency and memory usage.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of the Test-time Improvement Diagnostic Evaluation (TIDE), a framework that analyzes TTI through three dimensions: temporal dynamics of task completion, constraints by recursive behaviors, and burdens of accumulated memory.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study reveals that improving agent performance involves optimizing the interaction dynamics between the agent and the environment, extending beyond mere internal reasoning scale improvements.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.02196

48. Quant VideoGen: Auto-Regressive Long Video Generation via 2-Bit KV-Cache Quantization
🔑 Keywords: KV cache, Quant VideoGen, Semantic Aware Smoothing, Progressive Residual Quantization, memory efficiency
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to address the KV cache memory limitations in autoregressive video diffusion models, specifically focusing on improving memory efficiency without significantly impacting latency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces Quant VideoGen, a training-free quantization framework utilizing Semantic Aware Smoothing and Progressive Residual Quantization to optimize memory use by addressing video spatiotemporal redundancy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Quant VideoGen significantly reduces KV cache memory by up to 7 times with less than 4% latency increase, consistently outperforming existing methods in terms of generation quality and establishing a new standard in memory efficiency.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.02958
49. HySparse: A Hybrid Sparse Attention Architecture with Oracle Token Selection and KV Cache Sharing
🔑 Keywords: Hybrid Sparse Attention, sparse attention layers, token selection, full attention layer, KV caches
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce the Hybrid Sparse Attention (HySparse) architecture that interleaves full attention layers with sparse attention layers to improve efficiency and performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employ full attention layers to guide token selection and KV cache reuse in sparse layers, addressing limitations of traditional sparse attention methods.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– HySparse consistently outperforms full attention and hybrid SWA baselines, achieving significant performance gains and reducing KV cache storage by nearly 10x, especially in large models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.03560
50. Training Data Efficiency in Multimodal Process Reward Models
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal Process Reward Models, data efficiency, label mixtures, label reliability, Balanced-Information Score
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study focuses on achieving data efficiency in training Multimodal Process Reward Models (MPRMs) by using a balanced-information scoring approach to maximize performance with minimal data.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A theoretical framework is proposed to identify informative gradient updates based on label mixtures and reliability. The Balanced-Information Score (BIS) method is introduced to enhance training efficiency, tested on VisualProcessBench with two model backbones.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The BIS method enables training models to achieve full-data performance with only 10% of the data, surpassing random subsampling by 4.1% in efficiency and effectiveness.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.04145
51. FASA: Frequency-aware Sparse Attention
🔑 Keywords: FASA, KV Cache Memory, Token Pruning, Functional Sparsity, AI Native
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary objective is to introduce FASA, a novel framework aimed at reducing KV cache memory usage while maintaining high performance for long-context LLM tasks by employing a query-aware token eviction strategy.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research utilizes a novel technique of identifying “dominant” frequency-chunks (FCs) that exhibit high contextual agreement to predict token importance dynamically and reduce memory bandwidth requirements.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– FASA significantly reduces computational cost and memory usage without sacrificing accuracy, achieving near-full performance with a reduced token set, and demonstrating enhanced speed and efficiency compared to existing token-eviction baselines.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.03152
