AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20260212
1. Step 3.5 Flash: Open Frontier-Level Intelligence with 11B Active Parameters
🔑 Keywords: Mixture-of-Experts, agentic intelligence, efficient parameter utilization, optimized attention mechanisms, self-improvement
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to develop Step 3.5 Flash, a sparse Mixture-of-Experts model, aiming to bridge frontier-level agentic intelligence with computational efficiency, while maintaining strong performance across various tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a combination of 196B foundation parameters and 11B active parameters to ensure efficient inference.
– Employs interleaved sliding-window/full attention and Multi-Token Prediction (MTP-3) to reduce latency in agentic interactions.
– Implements a scalable reinforcement learning framework that integrates verifiable signals and preference feedback, promoting consistent self-improvement.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Step 3.5 Flash achieves high performance across various benchmarks, comparable to advanced models like GPT-5.2 xHigh and Gemini 3.0 Pro.
– Redefines the efficiency frontier, providing a robust foundation for deploying sophisticated agents in industrial environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.10604

2. GENIUS: Generative Fluid Intelligence Evaluation Suite
🔑 Keywords: Generative Fluid Intelligence, Unified Multimodal Models, Inducing Implicit Patterns, Contextual Knowledge, Attention Intervention Strategy
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to evaluate Unified Multimodal Models regarding their Generative Fluid Intelligence, focusing on pattern induction, constraint reasoning, and contextual adaptation capabilities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A new evaluation suite, GENIUS, is introduced to systematically evaluate generative fluid intelligence using tasks such as inducing implicit patterns, executing ad-hoc constraints, and adapting to contextual knowledge.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study finds significant deficiencies in context comprehension among 12 representative models, highlighting that these deficits are due to limited context comprehension rather than a lack of generative ability. It proposes a training-free attention intervention strategy to address these issues.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11144
3. Towards Autonomous Mathematics Research
🔑 Keywords: AI-assisted mathematical research, International Mathematical Olympiad, reasoning systems, human-AI collaboration, semi-autonomous evaluation
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Aletheia, a math research agent capable of generating and verifying solutions in natural language from competition-level to PhD-level exercises, contributing significantly to AI-assisted mathematical research.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes an advanced version of Gemini Deep Think for challenging reasoning problems, along with a novel inference-time scaling law and intensive tool use to manage mathematical research complexities.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrated achievements include AI-generated research papers with varying degrees of human-AI collaboration and the autonomous resolution of several open questions from Bloom’s Erdos Conjectures database.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.10177

4. How Do Decoder-Only LLMs Perceive Users? Rethinking Attention Masking for User Representation Learning
🔑 Keywords: attention masking, Gradient-Guided Soft Masking, user representation learning, decoder-only language models, bidirectional attention
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Investigate the impact of different attention masking strategies on user embedding quality in decoder-only language models for user behavior analysis.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Conduct a systematic study of causal, hybrid, and bidirectional attention masks within a contrastive learning framework, introducing Gradient-Guided Soft Masking to improve training dynamics.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed Gradient-Guided Soft Masking approach shows consistently more stable training and higher-quality bidirectional representations compared to other methods, underscoring the importance of masking design and training transition when adapting decoder-only LLMs for user representation learning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.10622

5. G-LNS: Generative Large Neighborhood Search for LLM-Based Automatic Heuristic Design
🔑 Keywords: Generative Evolutionary Framework, Large Language Models, Automated Heuristic Design, Large Neighborhood Search, Combinatorial Optimization Problems
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a generative evolutionary framework called G-LNS that enhances LLM-based Automated Heuristic Design for Large Neighborhood Search operators in Combinatorial Optimization Problems.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of Large Language Models for co-evolving destroy and repair operators.
– Implementation of a cooperative evaluation mechanism to capture interaction between operators.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– G-LNS significantly outperforms existing LLM-based AHD methods and classical solvers.
– The developed heuristics achieve near-optimal solutions with reduced computational budgets and exhibit robust generalization across various unseen instance distributions.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.08253

6. ROCKET: Rapid Optimization via Calibration-guided Knapsack Enhanced Truncation for Efficient Model Compression
🔑 Keywords: ROCKET, model compression, multi-choice knapsack problem, sparse matrix factorization, dictionary learning
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To present ROCKET, a novel training-free model compression method that surpasses current methods by efficiently allocating layer-wise compression using a multi-choice knapsack problem approach.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a unique combination of sparse matrix factorization and activation-weights sensitivity for efficient weight sparsification, bypassing traditional iterative optimization techniques.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ROCKET achieves state-of-the-art performance, maintaining over 90% of original model accuracy at 30% compression without fine-tuning, and further performance recovery with light fine-tuning, especially when applied to large-scale models like Qwen3-14B.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11008
7. Ex-Omni: Enabling 3D Facial Animation Generation for Omni-modal Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Omni-modal large language models, 3D facial animation, semantic reasoning, temporal scaffolding, token-as-query gated fusion
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance omni-modal large language models with 3D facial animation synchronized with speech, addressing the challenge of aligning semantic reasoning with temporal dynamics.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of the open-source framework Ex-Omni, which separates semantic reasoning from temporal generation and uses speech units for temporal scaffolding.
– Introduction of the InstructEx dataset to assist in augmenting models with speech-accompanied 3D facial animation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Ex-Omni enables stable and aligned speech and facial animation generation, performing competitively against existing open-source omni-modal models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.07106

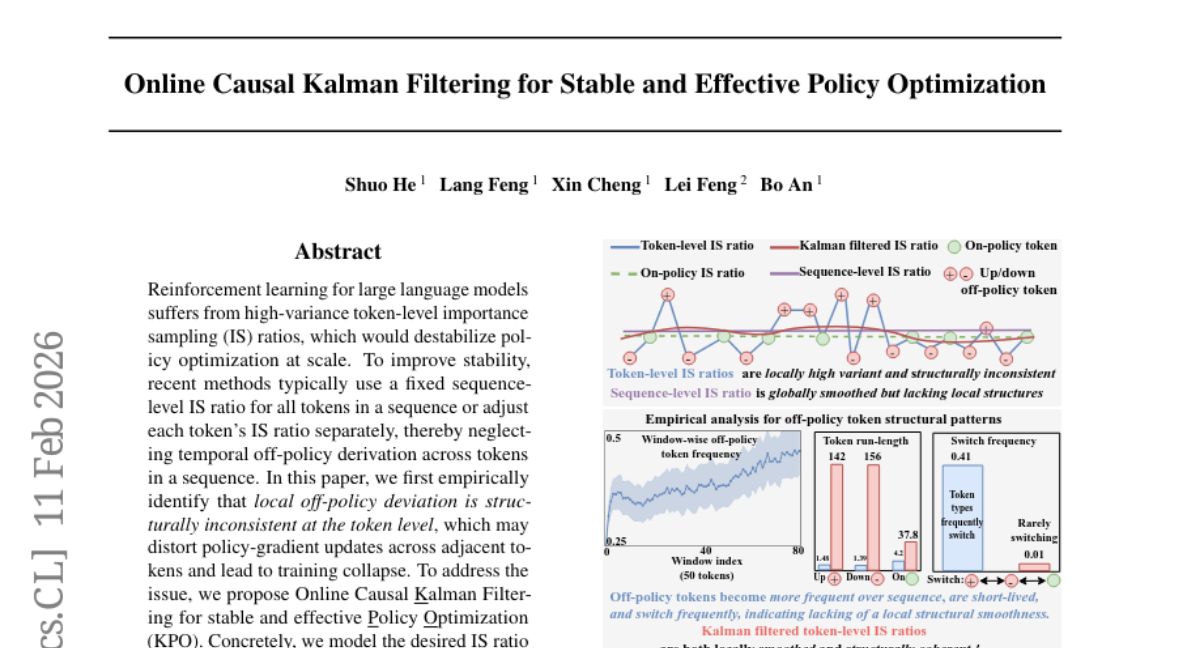
8. Online Causal Kalman Filtering for Stable and Effective Policy Optimization
🔑 Keywords: Online Causal Kalman Filtering, Reinforcement Learning, Large Language Models, Importance Sampling, Policy Optimization
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to address the high-variance token-level importance sampling in reinforcement learning for large language models, which destabilizes policy optimization.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces Online Causal Kalman Filtering by modeling the importance sampling ratios as evolving latent states, using Kalman filtering for stable and effective policy optimization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method, KPO, achieves superior stability and effectiveness in policy updates, outperforming state-of-the-art counterparts in experiments on challenging math reasoning datasets.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.10609
9. DataChef: Cooking Up Optimal Data Recipes for LLM Adaptation via Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: DataChef-32B, reinforcement learning, data recipe, Large Language Models, downstream performance
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to automate data recipe generation for LLM adaptation using reinforcement learning with proxy rewards.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– DataChef-32B model uses online reinforcement learning to generate data recipes based on proxy rewards predicting downstream performance.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DataChef-32B creates practical data recipes comparable to human-curated ones and effectively adapts LLMs to various tasks, notably surpassing benchmarks in the math domain.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11089
10. LiveMedBench: A Contamination-Free Medical Benchmark for LLMs with Automated Rubric Evaluation
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, data contamination, clinical reasoning, Automated Rubric-based Evaluation
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address the limitations in medical LLM evaluation by introducing a reliable, continuously updated benchmark called LiveMedBench that aligns with expert clinical reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed a Multi-Agent Clinical Curation Framework to filter raw data noise and validate clinical integrity.
– Introduced an Automated Rubric-based Evaluation Framework for granular assessment.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LiveMedBench outperforms existing benchmarks by ensuring data contamination and temporal misalignment are minimized.
– Demonstrated that majority of LLMs face significant challenges in tailoring medical knowledge to specific context requirements, emphasizing the need for better contextual application.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.10367
11. Stroke3D: Lifting 2D strokes into rigged 3D model via latent diffusion models
🔑 Keywords: Rigged 3D meshes, Controllable Skeleton Generation, Enhanced Mesh Synthesis, TextuRig, SKA-DPO
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduction of Stroke3D, a framework that generates rigged 3D meshes from 2D strokes and text prompts.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Stroke3D employs a two-stage pipeline: Controllable Skeleton Generation using Skeletal Graph VAE and Enhanced Mesh Synthesis via TextuRig and SKA-DPO.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Stroke3D enables intuitive creation of animatable 3D content and is the first to condition mesh generation on user-drawn 2D strokes, producing plausible skeletons and high-quality meshes.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.09713

12. VidVec: Unlocking Video MLLM Embeddings for Video-Text Retrieval
🔑 Keywords: Generative Multimodal Large Language Models, video-text embedding, intermediate-layer embeddings, zero-shot retrieval, text-based alignment
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To leverage Generative Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) for the purpose of video-text embedding and retrieval, demonstrating improvements over traditional Video Foundation Models (VFMs).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Conducted a systematic layer-wise analysis of MLLMs to identify the encoding of task-relevant information in intermediate layers.
– Introduced a text-based alignment strategy to map video captions to short summaries, facilitating learning without visual supervision.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method using intermediate-layer embeddings and a calibrated MLLM head achieves superior zero-shot retrieval performance without requiring additional training.
– Outperforms existing methods, achieving state-of-the-art results on standard video retrieval benchmarks, without fine-tuning beyond text alignment.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.08099
13. QP-OneModel: A Unified Generative LLM for Multi-Task Query Understanding in Xiaohongshu Search
🔑 Keywords: Unified Generative LLM, Multi-Task Query Understanding, Reinforcement Learning, Semantic Understanding, Social Network Service
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop QP-OneModel, a Unified Generative LLM aimed at enhancing semantic understanding and downstream task performance in Social Network Service (SNS) query processing.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Reformulate heterogeneous sub-tasks into a unified sequence generation paradigm combined with a progressive three-stage alignment strategy.
– Implement multi-reward Reinforcement Learning to refine model training and performance.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– QP-OneModel demonstrates a significant performance gain over traditional discriminative models, with improvements in NER and Term Weighting.
– The model shows superior generalization capabilities and enhances metrics like retrieval relevance and user retention when implemented on Xiaohongshu.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.09901

14. Free(): Learning to Forget in Malloc-Only Reasoning Models
🔑 Keywords: Free-Module, LoRA adapter, Reasoning Models, self-forgetting mechanism, test-time compute
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Free()LM to address reasoning model limitations by incorporating a self-forgetting mechanism that improves performance, particularly across various scales and long-horizon tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Develop and utilize Free-Module as a plug-and-play LoRA adapter allowing dynamic context pruning through iterative reasoning and cleaning modes.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Free()LM achieves an average improvement of 3.3% over leading reasoning baselines and establishes new SOTA benchmarks, significantly enhancing performance in long-horizon tasks, particularly where traditional models fail entirely.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.08030

15. Latent Thoughts Tuning: Bridging Context and Reasoning with Fused Information in Latent Tokens
🔑 Keywords: Latent Thoughts Tuning, continuous latent space, curriculum learning, reasoning accuracy, feature collapse
💡 Category: Foundations of AI
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce Latent Thoughts Tuning (LT-Tuning), a framework aimed at improving reasoning robustness in continuous latent space by overcoming limitations of existing latent paradigms.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a Context-Prediction-Fusion mechanism that combines contextual hidden states with semantic guidance and a progressive three-stage curriculum learning pipeline.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LT-Tuning effectively outperforms existing latent reasoning baselines by mitigating feature collapse and enhancing reasoning accuracy through dynamic switching between latent and explicit thinking modes.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.10229
16. ArcFlow: Unleashing 2-Step Text-to-Image Generation via High-Precision Non-Linear Flow Distillation
🔑 Keywords: Diffusion models, Distillation, Non-linear flow trajectories, Velocity field, Trajectory distillation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce ArcFlow, a few-step distillation framework improving inference speed and maintaining quality in diffusion models by using non-linear flow trajectories.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Parametrize velocity fields as a mixture of continuous momentum processes to create continuous non-linear trajectories within each denoising step.
– Implement trajectory distillation on pre-trained models with lightweight adapters to ensure fast and stable convergence.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ArcFlow achieves a 40x speedup with only 2 NFEs and maintains quality by fine-tuning less than 5% of parameters, proving its effectiveness in large-scale models through qualitative and quantitative benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.09014

17. Bielik Guard: Efficient Polish Language Safety Classifiers for LLM Content Moderation
🔑 Keywords: Polish Language, Safety Classifier, Large Language Models, F1 Scores, Precision
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to develop an efficient and accurate Polish language content safety classifier named Bielik Guard, which categorizes content across five safety domains.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Two model variants of Bielik Guard were created: a 0.1B parameter model based on MMLW-RoBERTa-base and a 0.5B parameter model based on PKOBP/polish-roberta-8k, fine-tuned using a community-annotated dataset of 6,885 Polish texts.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The 0.5B variant demonstrates superior discrimination with F1 scores of 0.791 (micro) and 0.785 (macro). The 0.1B variant is exceptionally efficient, achieving a high precision of 77.65% and a low false positive rate of 0.63%, outperforming similar-sized models like HerBERT-PL-Guard.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.07954

18. When Actions Go Off-Task: Detecting and Correcting Misaligned Actions in Computer-Use Agents
🔑 Keywords: Misaligned Actions, External Attacks, DeAction, AI-generated Summary, Task Efficiency
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To define and study the detection of misaligned actions in Computer-use agents (CUAs) and explore methods to improve safety and task efficiency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed MisActBench, a benchmark with human-annotated alignment labels, and proposed DeAction, a guardrail to detect and correct misaligned actions through structured feedback.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DeAction significantly outperforms existing methods with a 15% absolute increase in F1 score on MisActBench, and reduces attack success rate by over 90% while maintaining task success rates in benign environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.08995

19. Weight Decay Improves Language Model Plasticity
🔑 Keywords: weight decay, model plasticity, fine-tuning, overfitting, linearly separable representations
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To investigate the role of weight decay in improving model plasticity and fine-tuning performance in large language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Conducted systematic experiments to analyze how larger weight decay values impact model adaptability to downstream tasks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Larger weight decay values enhance model plasticity and lead to better performance gains during fine-tuning by reducing overfitting and encouraging linearly separable representations.
– Highlights the need for evaluation metrics beyond cross-entropy loss for effective hyperparameter optimization.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11137

20. GoodVibe: Security-by-Vibe for LLM-Based Code Generation
🔑 Keywords: GoodVibe, Neuron-Level Framework, Code Language Model Security, Vibe Coding, Gradient-based Attribution
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of the study is to enhance the security of code language models by improving their ability to generate secure code without compromising their general utility or increasing training costs significantly.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A neuron-level framework named GoodVibe is developed, leveraging gradient-based attribution and neuron-selective fine-tuning to target and improve security-relevant neurons.
– Activation-driven neuron clustering is introduced to enable efficient updates with minimal overhead, applied across multiple programming languages.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The framework significantly improves the security of generated code, achieving up to a 2.5x improvement compared to base models, while drastically reducing the number of trainable parameters and training computation needs.
– GoodVibe offers an effective and scalable approach to secure code generation, matching or exceeding the performance of full fine-tuning methods with much lower resource requirements.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.10778

21. TIC-VLA: A Think-in-Control Vision-Language-Action Model for Robot Navigation in Dynamic Environments
🔑 Keywords: Vision-language-action models, latency-aware framework, delayed semantic reasoning, imitation learning, photo-realistic simulation
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces a latency-aware framework for vision-language-action models to handle delayed semantic reasoning during real-time action generation in robotic systems.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors propose a framework called Think-in-Control (TIC)-VLA that incorporates latency-consistent training by injecting reasoning inference delays during imitation learning and online reinforcement learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– TIC-VLA significantly outperforms previous models in dynamic environments, maintaining robust real-time control despite multi-second reasoning latency.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.02459

22. StealthRL: Reinforcement Learning Paraphrase Attacks for Multi-Detector Evasion of AI-Text Detectors
🔑 Keywords: AI Native, reinforcement learning, adversarial paraphrasing, semantic preservation, detector evasion
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces StealthRL, a reinforcement learning framework designed to create adversarial paraphrases that evade AI text detectors while preserving the original meaning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes reinforcement learning with LoRA adapters and Group Relative Policy Optimization on Qwen3-4B to train a paraphrase policy against a multi-detector ensemble, evaluating it against three different AI text detector families.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– StealthRL achieves a near-zero detection rate and reveals significant robustness gaps in current AI text detectors, successfully evading detection even by a detector family not seen during training, indicating shared architectural vulnerabilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.08934

23. Large Language Lobotomy: Jailbreaking Mixture-of-Experts via Expert Silencing
🔑 Keywords: Mixture-of-Experts, Large Language Models, Safety Alignment, Expert Routing, Expert Silencing
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To propose an attack method, Large Language Lobotomy (L^3), that exploits expert routing dynamics in Mixture-of-Experts language models to compromise safety alignment while maintaining language utility.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of adaptive expert silencing to identify and bypass safety-critical experts in MoE architectures, increasing the success rate of attacks without additional training.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study demonstrated that L^3 significantly raises the average attack success rate from 7.3% to 70.4%, reaching up to 86.3%. This highlights a conflict between efficiency-oriented MoE design and robust safety alignment, suggesting a need for more robust distribution of safety mechanisms in these models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.08741

24.

25. Graph-Enhanced Deep Reinforcement Learning for Multi-Objective Unrelated Parallel Machine Scheduling
🔑 Keywords: Deep Reinforcement Learning, Proximal Policy Optimization, Graph Neural Network, Scheduling Problem, Multi-Objective
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to address the Unrelated Parallel Machine Scheduling Problem (UPMSP) by effectively balancing Total Weighted Tardiness (TWT) and Total Setup Time (TST) using a novel framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study employs a Deep Reinforcement Learning framework that combines Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) with Graph Neural Networks (GNN) to develop a direct scheduling policy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed PPO-GNN framework significantly outperforms traditional methods like standard dispatching rules and metaheuristics, achieving a better trade-off between minimizing TWT and TST in complex manufacturing scheduling scenarios.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.08052
26. Spend Search Where It Pays: Value-Guided Structured Sampling and Optimization for Generative Recommendation
🔑 Keywords: V-STAR, generative recommendation, Reinforcement Learning, exploration efficiency, Tree-structured Advantage
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to address limitations in generative recommendation systems by enhancing exploration and reward signal quality using the V-STAR framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Combines Value-guided Decoding and Tree-structured Advantage Reinforcement to form a self-evolving loop. It utilizes Value-Guided Efficient Decoding (VED) for efficient exploration and Sibling-GRPO for calculating sibling-relative advantages.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Extensive experiments demonstrate that V-STAR outperforms state-of-the-art baselines by providing superior accuracy and diversity in recommendations while maintaining strict latency constraints.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.10699

27. FedPS: Federated data Preprocessing via aggregated Statistics
🔑 Keywords: Federated Learning, Federated Data Preprocessing, Data-Sketching, Feature Scaling, Privacy-Preserving
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce FedPS, a framework for privacy-preserving and efficient data preprocessing in federated learning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize aggregated statistics and data-sketching techniques to summarize local datasets while maintaining statistical integrity.
– Design federated algorithms for preprocessing tasks like feature scaling, encoding, discretization, and missing-value imputation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– FedPS offers a communication-efficient and flexible preprocessing solution that supports horizontal and vertical federated learning, enhancing practical deployments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.10870

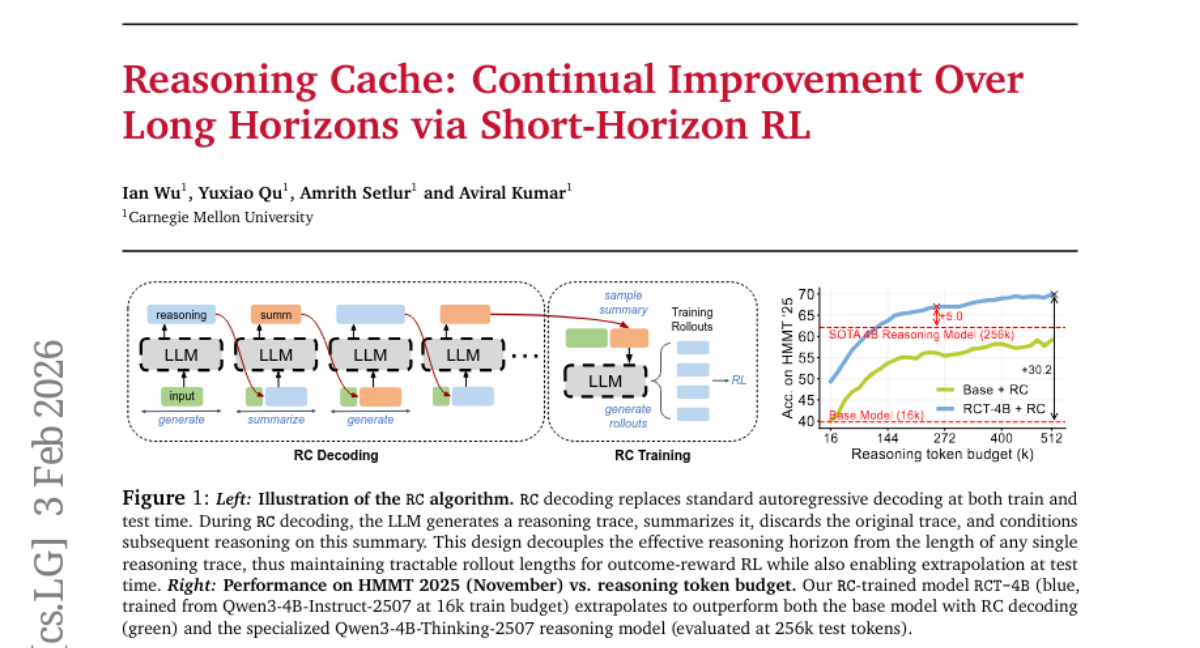
28. Reasoning Cache: Continual Improvement Over Long Horizons via Short-Horizon RL
🔑 Keywords: Iterative Decoding, Large Language Models, Reasoning Chains, Extrapolation, Test-time Performance
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce an iterative decoding algorithm, RC, to enable Large Language Models to extrapolate and improve beyond training limitations by constructing reasoning chains.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized the RC algorithm during training and inference to replace standard autoregressive decoding, leveraging the asymmetry between response generation and summarization of LLMs.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Models using RC can operate over significantly longer reasoning horizons, achieving improved performance in long-horizon tasks, notably enhancing test-time performance by leveraging existing scaffolds and summary-conditioned generation abilities.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.03773
29. UMEM: Unified Memory Extraction and Management Framework for Generalizable Memory
🔑 Keywords: LLM-based agents, Unified Memory Extraction and Management, Semantic Neighborhood Modeling, marginal utility reward
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper proposes a self-evolving framework called Unified Memory Extraction and Management (UMEM) to improve generalization in LLM-based agents by optimally coordinating memory extraction and management.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces Semantic Neighborhood Modeling and uses a neighborhood-level marginal utility reward optimized via GRPO to ensure memory generalizability.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– UMEM substantially outperforms baseline methods, achieving up to a 10.67% improvement in multi-turn interactive tasks, and maintains a monotonic growth curve during continuous evolution.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.10652

30. Rethinking the Value of Agent-Generated Tests for LLM-Based Software Engineering Agents
🔑 Keywords: LLM code agents, test writing, observational feedback, SWE-bench, Large Language Model
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To empirically analyze the impact of test writing by LLM code agents on the resolution of repository-level issues.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– An empirical study analyzing agent trajectories using six state-of-the-art LLMs on the SWE-bench and conducting controlled experiments by varying test writing prompts.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Writing tests provides limited improvement in issue resolution, often replaced by observational debugging methods.
– Changes in the volume of agent-written tests do not significantly alter final outcomes.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.07900

31. AgenticPay: A Multi-Agent LLM Negotiation System for Buyer-Seller Transactions
🔑 Keywords: AI Native, multi-agent, negotiation, strategic reasoning, AgenticPay
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces AgenticPay, a benchmark and simulation framework designed to evaluate multi-agent language-mediated economic interactions, focusing on negotiation performance and strategic reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– AgenticPay includes a diverse suite of over 110 tasks and uses a multi-round linguistic negotiation process to model market transactions. The framework is used to benchmark proprietary and open-weight LLMs.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Significant gaps in negotiation performance and challenges in long-horizon strategic reasoning were revealed, establishing AgenticPay as a foundational tool for studying agentic commerce and language-based market interaction.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.06008

32. Benchmarking Large Language Models for Knowledge Graph Validation
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Knowledge Graphs, Fact Validation, Retrieval-Augmented Generation, Multi-Model Consensus
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce FactCheck, a benchmark designed to evaluate the effectiveness of Large Language Models (LLMs) in Knowledge Graph (KG) fact validation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Evaluation of open-source and commercial LLMs on three real-world KGs using FactCheck, assessing dimensions such as LLMs’ internal knowledge, external evidence via Retrieval-Augmented Generation, and aggregated knowledge through multi-model consensus.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LLMs show potential but lack stability and reliability for real-world KG fact validation, with strategies like Retrieval-Augmented Generation and multi-model consensus providing inconsistent and costly improvements.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.10748

33. Beyond Correctness: Learning Robust Reasoning via Transfer
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, LLM reasoning, transfer reward, robustness, sampling consistency
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Reinforcement Learning with Transferable Reward (RLTR) to enhance robustness and generalizability in LLM reasoning by testing cross-model guidance capabilities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implement transfer rewards to verify whether a reasoning prefix from one model can guide another model to a correct answer, improving robustness and generalizability.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RLTR improves sampling consistency and final answer accuracy, achieving comparable performance to RLVR with significantly fewer training steps, evidenced by a +3.6%p gain on MATH500 with approximately 2.5x fewer training steps.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.08489
34. ECHO-2: A Large-Scale Distributed Rollout Framework for Cost-Efficient Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: Distributed Reinforcement Learning, Post-Training, Large Language Models, Policy Staleness, Cost Efficiency
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary goal is to post-train large language models (LLMs) efficiently by addressing rollout generation, dissemination, and training within a distributed reinforcement learning framework called ECHO-2.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a distributed RL approach, combining centralized learning with distributed rollouts and managing policy staleness as a controlled parameter. Implements an overlap-based capacity model to improve training efficiency and employs peer-assisted pipelined broadcast and cost-aware activation to mitigate latency and cost issues.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ECHO-2 enhances cost efficiency in the post-training phase of LLMs and maintains reinforcement learning rewards comparable to strong baselines, demonstrated through experiments on 4B and 8B models in real wide-area bandwidth scenarios.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.02192

35. When the Prompt Becomes Visual: Vision-Centric Jailbreak Attacks for Large Image Editing Models
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Centric Jailbreak Attack, image editing models, safety benchmarks, introspective multimodal reasoning
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to explore and address the emerging threat of visual-to-visual jailbreak attacks on image editing models through malicious visual inputs.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research introduces a new safety-oriented benchmark called IESBench to systematically study the threat and tests the Vision-Centric Jailbreak Attack on state-of-the-art models.
– A training-free defense mechanism based on introspective multimodal reasoning is proposed to enhance model safety.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Vision-Centric Jailbreak Attack effectively compromises models, with high success rates, exposing new vulnerabilities in image editing systems.
– The proposed defense significantly improves the safety of poorly aligned models, achieving security comparable to commercial systems with minimal computational burden.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.10179

36. Blockwise Advantage Estimation for Multi-Objective RL with Verifiable Rewards
🔑 Keywords: Blockwise Advantage Estimation, structured generations, reward interference, Outcome-Conditioned Baseline, nested rollouts
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address reward interference in structured text generations by assigning separate advantages to different text blocks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Proposing Blockwise Advantage Estimation combined with Outcome-Conditioned Baseline to reduce reliance on scalar rewards and expensive nested rollouts.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The method mitigates reward interference and is competitive with state-of-the-art approaches, offering a modular solution for structured generations without additional rollouts.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.10231

37. EcoGym: Evaluating LLMs for Long-Horizon Plan-and-Execute in Interactive Economies
🔑 Keywords: Long-horizon planning, LLM-based agents, interactive economies, persistent economic dynamics, controllability-utility trade-offs
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– EcoGym is introduced as a generalizable benchmark for evaluating the long-term planning capabilities of LLM-based agents in interactive economic environments.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– EcoGym comprises diverse environments (Vending, Freelance, Operation) for continuous plan-and-execute decision-making with standardized interfaces and budgeted actions over an extended evaluation horizon.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments reveal a systematic tension where no single LLM model excels across all scenarios, with models showing suboptimality in either high-level strategies or action execution.
– EcoGym is established as an open, extensible testbed for transparent long-horizon agent evaluation in realistic economic settings.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.09514

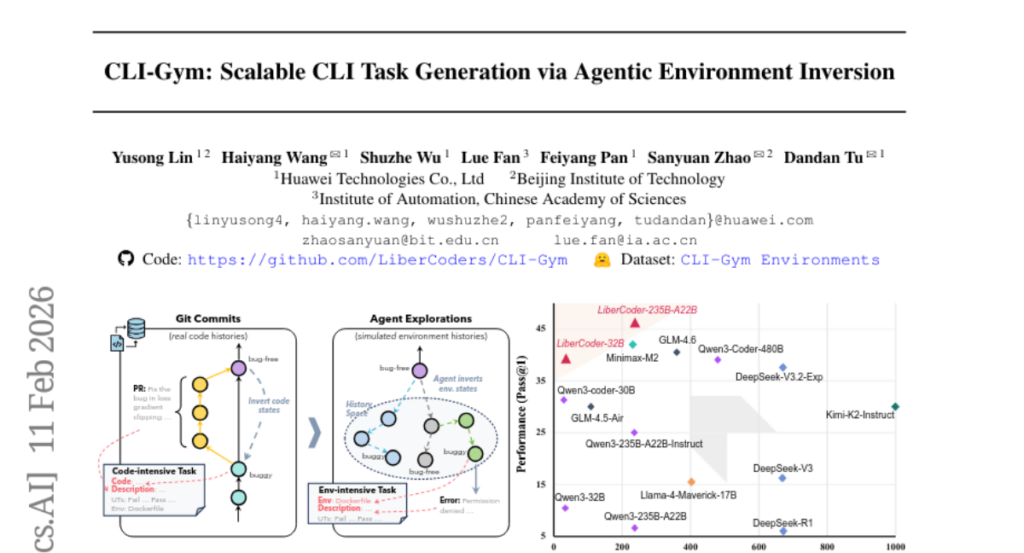
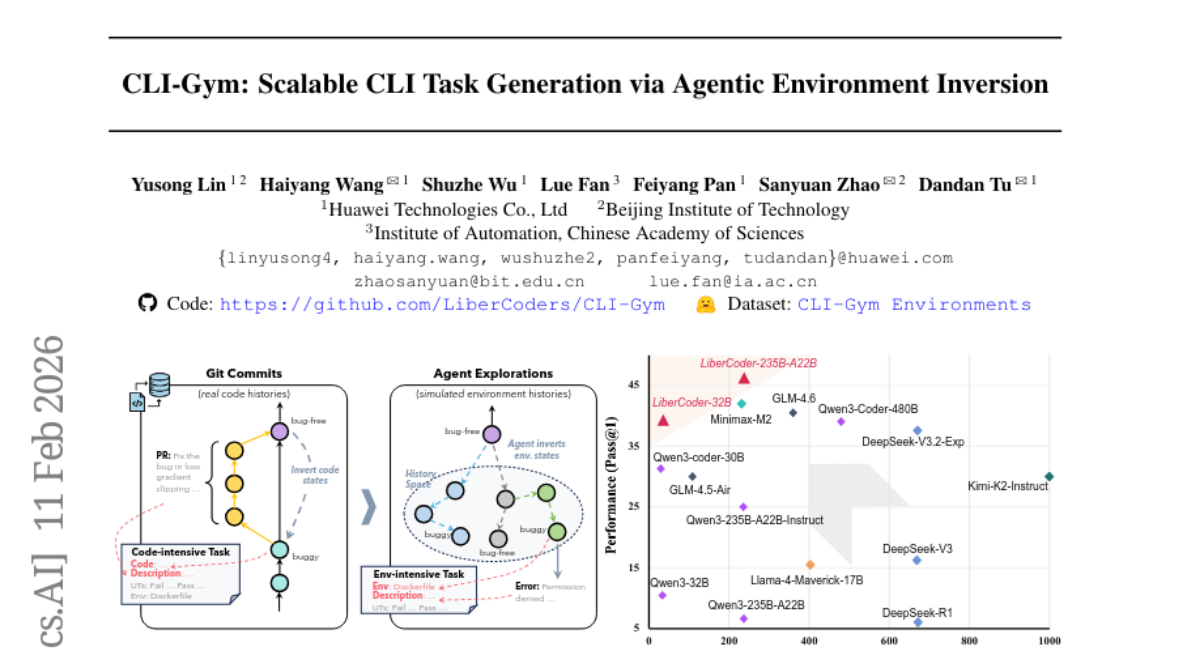
38. CLI-Gym: Scalable CLI Task Generation via Agentic Environment Inversion
🔑 Keywords: CLI-Gym, LiberCoder, environment-intensive tasks, Terminal-Bench, execution feedback
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enable scalable derivation of environment-intensive tasks by simulating and exploring environment histories, enhancing agent capabilities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized an analogy between Dockerfile and agentic tasks to simulate and explore environment histories, employing execution feedback for task derivation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CLI-Gym enabled the derivation of 1,655 environment-intensive tasks, marking the largest collection of its kind, and LiberCoder achieved significant performance improvement on Terminal-Bench by +21.1%, outperforming strong baselines.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.10999
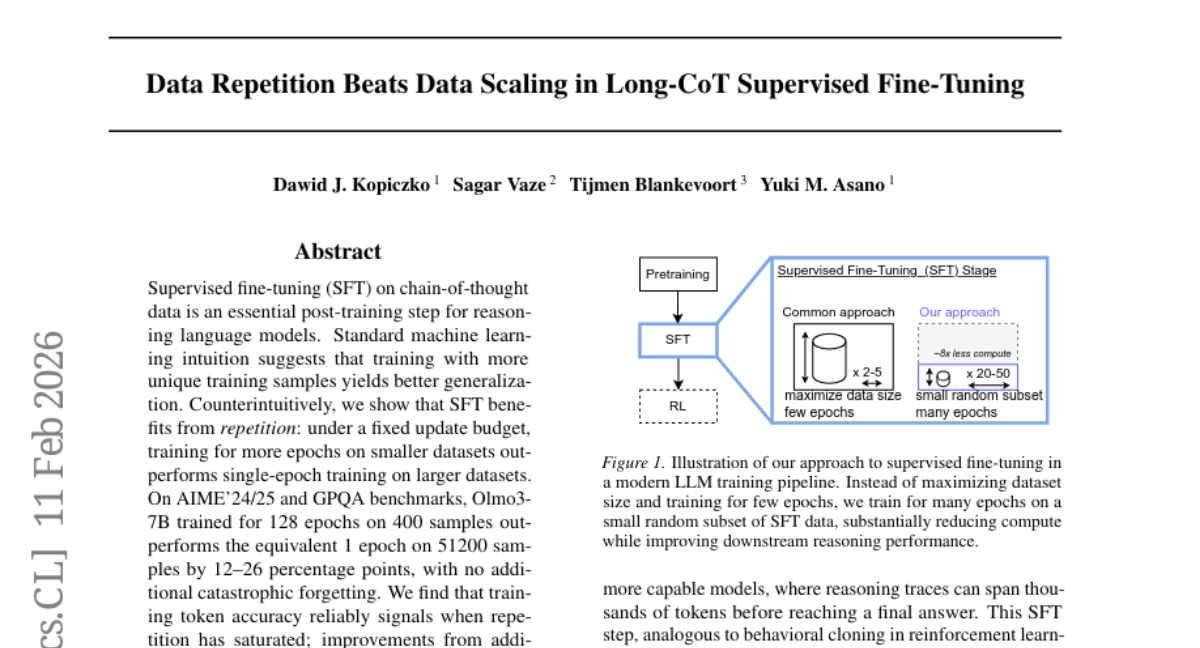
39. Data Repetition Beats Data Scaling in Long-CoT Supervised Fine-Tuning
🔑 Keywords: Supervised Fine-Tuning, Chain-of-Thought Data, Reasoning Language Models, Token Accuracy, Memorization
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To explore the effects of repeated example training on smaller datasets for reasoning language models, compared to single-pass training on larger datasets.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized supervised fine-tuning (SFT) on chain-of-thought data for reasoning language models, tested on AIME’24/25 and GPQA benchmarks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Repetition in training on smaller datasets proves advantageous, enhancing performance significantly over single-epoch training on larger datasets.
– Token accuracy can serve as a stopping criterion, as improvements plateau at full memorization.
– Presents repetition advantage as an open problem, suggesting that full memorization aligns with better generalization.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11149
40. GameDevBench: Evaluating Agentic Capabilities Through Game Development
🔑 Keywords: GameDevBench, Multimodal Understanding, Game Development, AI-generated Feedback, Software Development Complexity
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce GameDevBench as the first benchmark to evaluate agents’ performance on complex game development tasks that require deep multimodal understanding.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Creation of 132 tasks based on web and video tutorials to test the agents’ capability in handling tasks requiring significant multimodal understanding, across large codebases and diverse multimedia assets.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Agents showed limited success with current multimodal game development tasks, with the best agent completing only 54.5% of tasks. Task difficulty correlated strongly with multimodal complexity, suggesting improvements in image and video-based feedback mechanisms can enhance agent performance.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11103

41. Internalizing Meta-Experience into Memory for Guided Reinforcement Learning in Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Meta-Experience, Large Language Models, Reinforcement Learning, self-verification, parametric memory
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) through Meta-Experience Learning (MEL) by integrating self-distilled error representations into parametric memory.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized self-verification and contrastive analysis to identify reasoning errors and summarize them into generalizable meta-experience, which is incorporated into the LLM’s parametric memory to induce a language-modeled reward signal.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MEL consistently improves performance across benchmarks, achieving 3.92%–4.73% Pass@1 gains across varying model sizes, thereby showing effective enhancement in reasoning capabilities and knowledge reuse.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.10224

42. FeatureBench: Benchmarking Agentic Coding for Complex Feature Development
🔑 Keywords: FeatureBench, agentic coding, software development, execution-based evaluation, automated task collection
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– Develop FeatureBench to assess AI-generated agentic coding performance in feature-oriented software development.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Execution-based evaluation protocol and test-driven method for automated task derivation from code repositories.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– FeatureBench identified limited success (11.0%) of state-of-the-art agents like Claude 4.5 Opus on complex tasks, promising further advancements in agentic coding capabilities.
– The approach offers scalable and updatable task evaluation, valuable for ongoing agent training and minimizing data leakage.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.10975

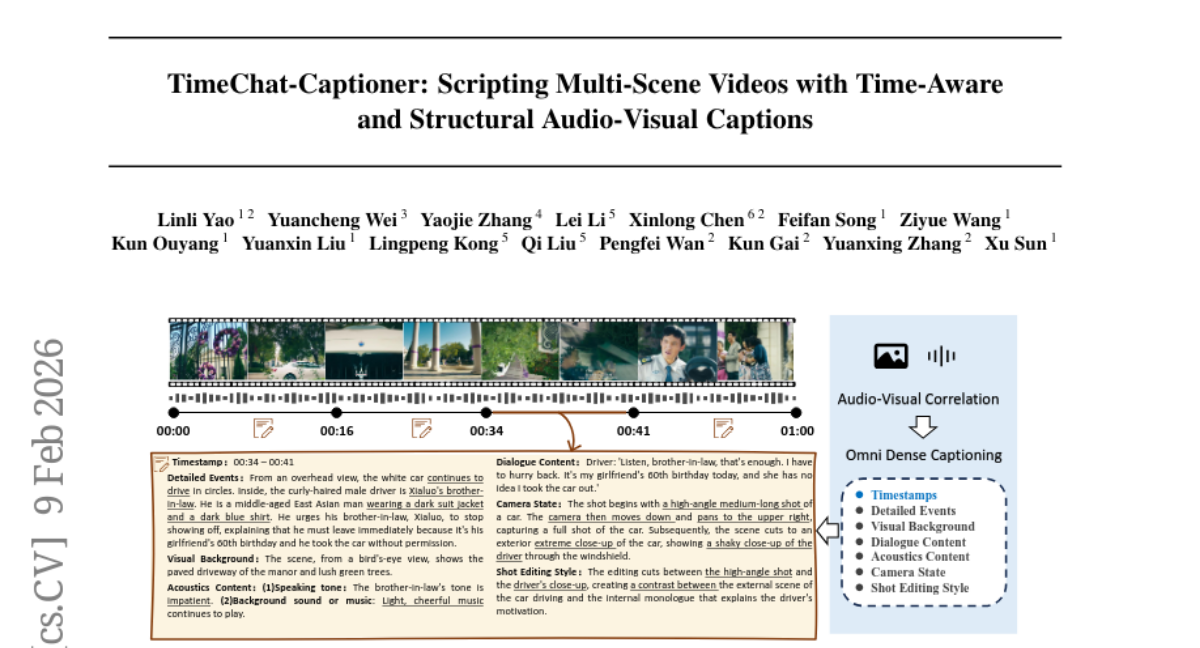
43. TimeChat-Captioner: Scripting Multi-Scene Videos with Time-Aware and Structural Audio-Visual Captions
🔑 Keywords: Omni Dense Captioning, six-dimensional structural schema, AI-generated summary, TimeChat-Captioner-7B, temporal grounding
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces Omni Dense Captioning, aiming to generate structured audio-visual narratives with explicit timestamps to enhance semantic coverage and visualization.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implementation of a six-dimensional structural schema for “script-like” captions, construction of the benchmark OmniDCBench, and the introduction of a unified metric, SodaM, for evaluation.
– Use of a training dataset, TimeChatCap-42K, and development of TimeChat-Captioner-7B, a strong baseline model trained with SFT and GRPO, incorporating task-specific rewards.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– TimeChat-Captioner-7B achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming Gemini-2.5-Pro, and enhances downstream capabilities in audio-visual reasoning and temporal grounding.
– All related datasets, models, and code are made publicly available for further research and development.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.08711
44. When to Memorize and When to Stop: Gated Recurrent Memory for Long-Context Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: GRU-Mem, large language models, long-context reasoning, text-controlled gates, reinforcement learning
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to improve reasoning capabilities over long contexts in large language models, overcoming challenges like performance degradation and inefficient memory updates.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces GRU-Mem, employing text-controlled gates to stabilize memory updates and reinforce learning rewards for efficient computational processes. It proposes update and exit gates to manage memory more effectively.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– GRU-Mem demonstrates significant improvements in long-context reasoning tasks, outperforming vanilla MemAgent with enhanced efficiency and up to 400% inference speed acceleration.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.10560

45. ASA: Training-Free Representation Engineering for Tool-Calling Agents
🔑 Keywords: Activation Steering Adapter, tool calling, mid-layer activations, distribution shift, steering vectors
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address the brittleness of large language model (LLM) agents in domain-specific tool calling due to evolving interfaces and representation-behavior gaps.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of a training-free method, Activation Steering Adapter, using mid-layer activation interventions guided by a mixture of router-conditioned steering vectors and a probe-guided signed gate.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Activation Steering Adapter significantly improves tool-use F1 score from 0.18 to 0.50 and reduces the false positive rate from 0.15 to 0.05 using minimal resources without weight updates.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.04935

46. PhyCritic: Multimodal Critic Models for Physical AI
🔑 Keywords: PhyCritic, Physical AI, RLVR pipeline, Perception, Reasoning
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The development of PhyCritic, a multimodal critic model specially optimized for Physical AI tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a two-stage RLVR pipeline including a physical skill warmup stage for enhancing perception and reasoning, followed by self-referential critic finetuning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PhyCritic demonstrates significant performance improvements in both physical and general-purpose multimodal tasks, enhancing judgment stability and correctness in physical AI environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11124
