AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20260213

1. The Devil Behind Moltbook: Anthropic Safety is Always Vanishing in Self-Evolving AI Societies
🔑 Keywords: Multi-agent LLM systems, self-evolution trilemma, safety alignment, statistical blind spots, external oversight
💡 Category: Foundations of AI
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study investigates the fundamental limitations of self-improvement in multi-agent LLM systems while maintaining safety alignment.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research uses a combination of theoretical insights through an information-theoretic framework and empirical testing within systems like Moltbook to assess safety concerns.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Continuous self-evolution in isolated settings leads to statistical blind spots and safety misalignments, highlighting the necessity for external oversight or new safety mechanisms to address intrinsic risks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.09877

2. DeepGen 1.0: A Lightweight Unified Multimodal Model for Advancing Image Generation and Editing
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal Model, Generative Models, AI-generated content, Data-centric Training Strategy, Alignment Pre-training
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop DeepGen 1.0, a lightweight 5B unified multimodal model that matches or exceeds the capabilities of much larger models in image generation and editing.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes Hierarchical Feature Extraction and Stacked Channel Bridging (SCB) framework with learnable “think tokens.”
– Implements a three-stage data-centric training strategy, including Alignment Pre-training, Joint Supervised Fine-tuning, and Reinforcement Learning with MR-GRPO.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DeepGen 1.0 shows leading performance across benchmarks, surpassing larger models by significant margins, while providing an efficient and high-performance alternative to existing unified multimodal research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12205

3. MOSS-Audio-Tokenizer: Scaling Audio Tokenizers for Future Audio Foundation Models
🔑 Keywords: Transformer, AI Native, Audio Tokenization, Automatic Speech Recognition, Text-to-Speech
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to develop a fully end-to-end Transformer-based audio tokenizer architecture that enables high-fidelity reconstruction across diverse audio domains and enhances performance in text-to-speech (TTS) and automatic speech recognition (ASR).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Proposing the CAT (Causal Audio Tokenizer) architecture that optimizes the encoder, quantizer, and decoder from scratch for high-fidelity audio reconstruction.
– Developing MOSS-Audio-Tokenizer, a large-scale, Transformer-based audio tokenizer with 1.6 billion parameters, pre-trained on 3 million hours of diverse audio data.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The MOSS-Audio-Tokenizer outperforms existing codec models across speech, sound, and music domains, particularly excelling in TTS models and ASR tasks while supporting predictable scaling and high-fidelity reconstruction.
– Establishes the CAT architecture as a unified, scalable interface for the next generation of native audio foundation models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.10934

4. LawThinker: A Deep Research Legal Agent in Dynamic Environments
🔑 Keywords: Legal reasoning, Explore-Verify-Memorize strategy, DeepVerifier module, knowledge accuracy, procedural compliance
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop LawThinker, an autonomous legal research agent that employs a unique Explore-Verify-Memorize strategy to enhance legal reasoning through accurate and procedurally compliant processes.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of an Explore-Verify-Memorize strategy with a DeepVerifier module to dynamically verify intermediate steps in legal reasoning.
– Examination of retrieval results based on knowledge accuracy, fact-law relevance, and procedural compliance.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LawThinker demonstrated a 24% improvement on dynamic benchmarks compared to direct reasoning and 11% over workflow-based methods, with significant improvements in process-oriented metrics.
– Validated generalization capability through evaluations on three static benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12056

5. Stroke of Surprise: Progressive Semantic Illusions in Vector Sketching
🔑 Keywords: Progressive Semantic Illusions, vector sketching, generative framework, dual-branch Score Distillation Sampling, semantic transformation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to introduce Progressive Semantic Illusions, where a vector sketch undergoes semantic transformation through sequential stroke additions, enhancing recognizability and illusion strength.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a generative framework called Stroke of Surprise, employing dual-branch Score Distillation Sampling for sequence-aware joint optimization to manage semantic transformations in sketches.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method achieves superior performance compared to state-of-the-art baselines in terms of recognizability and illusion strength, demonstrating an expansion from spatial to temporal dimensions in visual anagrams.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12280
6. RISE: Self-Improving Robot Policy with Compositional World Model
🔑 Keywords: RISE, Compositional World Model, reinforcement learning, self-improving pipeline
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce RISE, a framework that enhances robotic reinforcement learning by using a Compositional World Model for virtual policy improvement.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Develop a system that predicts multi-view futures and evaluates imagined outcomes through a controllable dynamics model and a progress value model, integrating this into a closed-loop self-improving pipeline.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RISE achieves significant performance improvements in real-world tasks, outperforming prior approaches with notable gains in dynamic manipulation tasks like brick sorting, backpack packing, and box closing.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11075
7. χ_{0}: Resource-Aware Robust Manipulation via Taming Distributional Inconsistencies
🔑 Keywords: Robotic Manipulation, Distributional Shift, Model Arithmetic, Stage Advantage, Train-Deploy Alignment
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to address distributional shifts and achieve high reliability in long-horizon robotic manipulation through a novel, resource-efficient framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces three technical pillars: Model Arithmetic for efficient distribution merging, Stage Advantage for stable progress signals, and Train-Deploy Alignment for bridging distribution gaps.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed framework, χ_{0}, significantly improves success rates over state-of-the-art methods, demonstrating high-reliability in garment manipulation tasks with impressive autonomy for extensive periods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.09021
8. DeepSight: An All-in-One LM Safety Toolkit
🔑 Keywords: DeepSight, Large Models, Safety Evaluation, Safety Diagnosis, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce DeepSight, an open-source project designed to integrate safety evaluation and diagnosis for large language and multimodal models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilize unified protocols and specialized toolkits, DeepSafe and DeepScan, to connect evaluation and diagnosis stages, shifting from black-box to white-box insights.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DeepSight provides a reproducible, efficient, and scalable solution to the safety workflow challenges of large models, supporting frontier AI risk evaluation with a focus on internal mechanisms.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12092

9. Adapting Vision-Language Models for E-commerce Understanding at Scale
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language Models, Multimodal Comprehension, E-commerce Data, Attribute-Centric, Targeted Adaptation
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance e-commerce product understanding by adapting general-purpose Vision-Language Models through targeted techniques.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Conducted a large-scale experimental study to evaluate the impact of targeted adaptation on general VLMs in processing e-commerce data.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The research demonstrates that targeted adaptation significantly boosts e-commerce performance while maintaining the multimodal capabilities of Vision-Language Models.
– Proposed a new evaluation suite for assessing deep product understanding and dynamic attribute extraction in the context of e-commerce.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11733

10. Sparse Video Generation Propels Real-World Beyond-the-View Vision-Language Navigation
🔑 Keywords: Vision-language navigation, Video generation models, Beyond-the-View Navigation, Real-world deployment, SparseVideoNav
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to explore the integration of video generation models into vision-language navigation systems to enhance Beyond-the-View Navigation (BVN) tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of video generation models that align with language instructions through long-horizon supervision.
– Introduction of SparseVideoNav to achieve efficient sub-second trajectory inference via a generated sparse future spanning a 20-second horizon.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SparseVideoNav demonstrates a 27x speed improvement and achieves a 2.5x success rate over state-of-the-art large language model baselines in real-world zero-shot experiments.
– It marks the first instance of successful deployment of BVN capability in challenging night scenes.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.05827

11. T3D: Few-Step Diffusion Language Models via Trajectory Self-Distillation with Direct Discriminative Optimization
🔑 Keywords: Diffusion Large Language Models, Trajectory Self-distillation, Direct Discriminative Optimization, Few-step Decoding, AI Native
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve the efficiency of few-step decoding in diffusion large language models without compromising generation quality.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed a trajectory self-distillation framework utilizing Direct Discriminative Optimization to enhance the generative trajectories of the model.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed approach consistently outperforms other few-step decoding methods and significantly reduces the gap with full-step decoding, paving the way for practical applications of few-step DLLMs.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12262

12. MiniCPM-SALA: Hybridizing Sparse and Linear Attention for Efficient Long-Context Modeling
🔑 Keywords: Sparse Attention, Linear Attention, Hybrid Architecture, Continual Training Framework, Inference Speed
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop an efficient architecture for processing ultra-long contexts using a hybrid approach that combines sparse and linear attention, aiming to reduce training costs while maintaining model performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Integration of sparse attention and linear attention using a layer selection algorithm in a 1:3 ratio.
– Utilization of a hybrid positional encoding and a cost-effective continual training framework to transform pre-trained models into hybrid models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The MiniCPM-SALA model maintains general capabilities comparable to full-attention models with significantly improved efficiency.
– Achieves up to 3.5x the inference speed of full-attention models and supports context lengths of up to 1M tokens.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11761
13. Voxtral Realtime
🔑 Keywords: Voxtral Realtime, streaming speech recognition, automatic speech recognition, latency, causal audio encoder
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Voxtral Realtime, a natively streaming automatic speech recognition model designed for sub-second latency performance equivalent to offline systems.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Trained end-to-end for streaming with explicit alignment between audio and text streams, using a new causal audio encoder and Ada RMS-Norm for improved delay conditioning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Model achieves performance on par with Whisper, a leading offline transcription system, with a release under the Apache 2.0 license, demonstrating scalability across a large dataset of 13 languages.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11298

14. ExStrucTiny: A Benchmark for Schema-Variable Structured Information Extraction from Document Images
🔑 Keywords: ExStrucTiny, Vision Language Models, Key Entity Extraction, structured Information Extraction, document images
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce the ExStrucTiny dataset to address the limitations of existing datasets for structured information extraction from document images.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed through a novel pipeline combining manual and synthetic human-validated samples to cover varied document types and extraction scenarios.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Analyzes challenges for Vision Language Models, such as schema adaptation, query under-specification, and answer localization, aiming to improve structured IE in documents.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12203
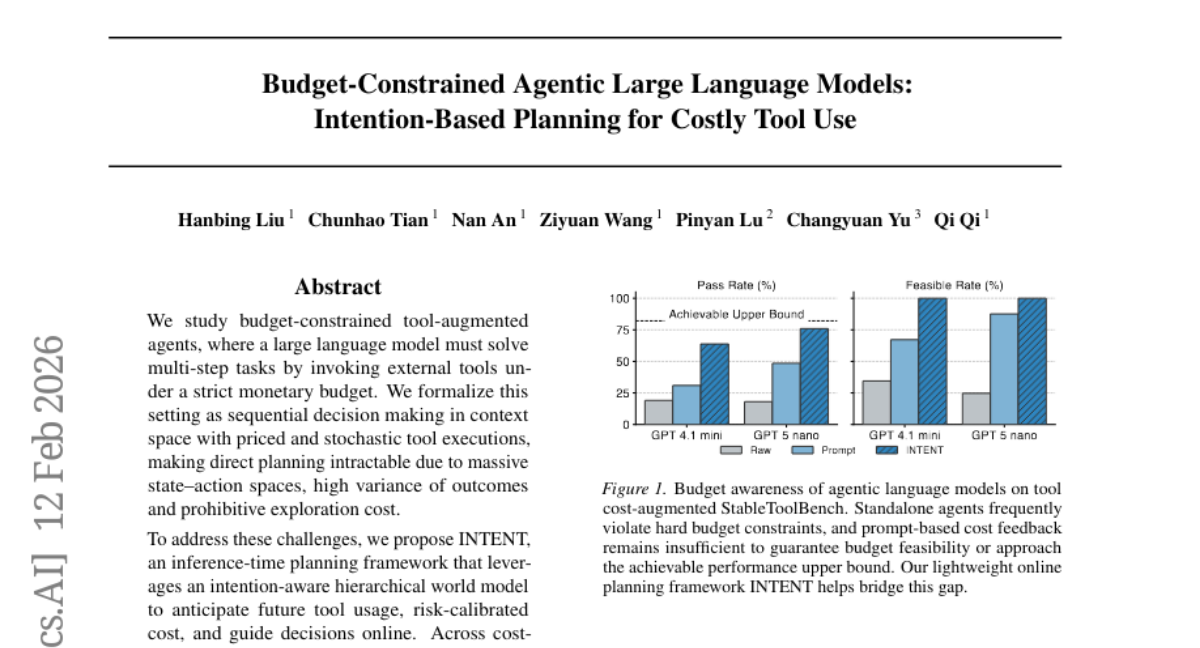
15. Budget-Constrained Agentic Large Language Models: Intention-Based Planning for Costly Tool Use
🔑 Keywords: budget-constrained tool-augmented agents, large language model, intent-aware planning, hierarchical world model
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study focuses on optimizing multi-step task completion for tool-augmented agents operating under monetary constraints using a hierarchical world model and intent-aware planning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The paper introduces INTENT, a planning framework that uses an intention-aware hierarchical world model to improve tool usage prediction and guide decision-making in the presence of stochastic tool executions and high variance in outcomes.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– INTENT enforces strict budget feasibility and enhances task success in cost-augmented environments, while maintaining robustness against dynamic market shifts such as changes in tool prices and varying budgets.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11541
16. P-GenRM: Personalized Generative Reward Model with Test-time User-based Scaling
🔑 Keywords: Personalized Generative Reward Model, Reinforcement Learning, User Prototypes, Test-time User-based Scaling, Personalized Alignment
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop the P-GenRM, the first Personalized Generative Reward Model with test-time user-based scaling to address the limitation of existing personalized reward models in achieving accurate, user-specific reward signals and enhancing generalization.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The model uses structured evaluation chains and dual-granularity scaling mechanisms, clustering users into User Prototypes and leveraging adaptive personas and scoring rubrics for improved personalization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– P-GenRM provides state-of-the-art results on personalized reward model benchmarks, showing an average improvement of 2.31%. Test-time user-based scaling contributes an additional 3% boost, indicating enhanced personalized alignment and scalability.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12116

17. ScalSelect: Scalable Training-Free Multimodal Data Selection for Efficient Visual Instruction Tuning
🔑 Keywords: ScalSelect, training-free, multimodal data selection, linear-time complexity, vision-language models
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of this research was to develop ScalSelect, a scalable and training-free method for selecting representative multimodal data to achieve near-full-dataset performance with reduced computational resources in vision-language models (VLMs).
🛠️ Research Methods:
– ScalSelect constructs sample representations by extracting visual features attended by instruction tokens in the target VLM and identifies samples whose representations best approximate the dominant subspace of the full dataset, enabling scalable importance scoring without pairwise comparisons.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ScalSelect significantly reduces the data required for training to 16% while maintaining over 97.5% of full-dataset performance and, in some scenarios, even surpasses full-data training, demonstrating its efficiency and effectiveness in handling large-scale VLMs.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11636

18. MetaphorStar: Image Metaphor Understanding and Reasoning with End-to-End Visual Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: MetaphorStar, Visual Reinforcement Learning, Image Implication Tasks, Multimodal Large Language Models, State-of-the-Art (SOTA)
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance metaphor comprehension in images using an end-to-end visual reinforcement learning framework called MetaphorStar, which addresses cultural, emotional, and contextual implications in visual content.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed a specialized fine-grained dataset (TFQ-Data), a visual RL method (TFQ-GRPO), and a benchmark (TFQ-Bench) within the MetaphorStar framework.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MetaphorStar, particularly MetaphorStar-32B, achieves state-of-the-art performance on visual implication tasks and demonstrates significantly improved performance of 82.6% on image implication benchmarks, outperforming other mainstream multimodal large language models.
– The study also provides insights into model parameter scaling, training data scaling, and the impact of various model architectures and training strategies, showcasing the method’s broad applicability.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.10575

19. Pretraining A Large Language Model using Distributed GPUs: A Memory-Efficient Decentralized Paradigm
🔑 Keywords: Decentralized Training, Expert Synchronization, Mixture-of-Experts, Federated Optimization
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a memory-efficient decentralized framework for pretraining mixture-of-experts large language models (MoE LLMs) that overcomes GPU memory limitations.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Proposing SParse Expert Synchronization (SPES), which involves training only a subset of experts per node and using expert-merging warm-up strategies to enhance synchronization and knowledge sharing.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The SPES framework successfully trains a 2B-parameter MoE LLM using 16 standalone 48GB GPUs, achieving competitive performance compared to centrally trained models and demonstrating scalability with larger models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11543

20. Stemphonic: All-at-once Flexible Multi-stem Music Generation
🔑 Keywords: Stemphonic, synchronized stems, multi-stem generation, AI-generated music
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces “Stemphonic,” a diffusion- and flow-based framework aimed at generating synchronized musical stems efficiently in one inference pass.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The framework treats each stem as a batch element and uses a shared noise latent during training. At inference time, synchronized multi-stem outputs are generated in one pass with stem-specific text inputs.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Stemphonic improves both the quality and speed of music stem generation, producing higher-quality outputs and accelerating the full mix generation process by 25 to 50% compared to existing methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.09891

21.

22. Detecting RLVR Training Data via Structural Convergence of Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement learning, Verifiable rewards, Behavioral signature, Min-kNN Distance, Prompt generation diversity
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To detect behavioral signatures in reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards using a novel black-box method.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced Min-kNN Distance, a method that samples multiple completions and computes the average of the k smallest nearest-neighbor edit distances without accessing the reference model or token probabilities.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Min-kNN Distance effectively distinguishes RL-seen examples from unseen ones, outperforming existing methods for RL contamination detection.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11792

23. Neural Additive Experts: Context-Gated Experts for Controllable Model Additivity
🔑 Keywords: Neural Additive Experts, predictive accuracy, feature interpretability, dynamic gating mechanism, mixture of experts framework
💡 Category: Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a novel framework, Neural Additive Experts (NAEs), that balances interpretability and accuracy in machine learning models by integrating multiple specialized networks and a dynamic gating mechanism.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of the mixture of experts framework and targeted regularization techniques to manage feature interactions and maintain clarity in feature attributions.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Theoretical analysis and experiments demonstrate that NAEs enhance predictive accuracy while providing clear feature-level explanations, achieving a balanced trade-off between interpretability and performance. Extensive evaluations on real-world datasets confirm the model’s effectiveness.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.10585

24. ABot-N0: Technical Report on the VLA Foundation Model for Versatile Embodied Navigation
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language-Action, Embodied navigation, LLM-based Cognitive Brain, Flow Matching-based Action Expert
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to achieve a “Grand Unification” of embodied navigation tasks using a unified Vision-Language-Action model called ABot-N0, which is capable of performing across 5 core tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study employs a hierarchical Brain-Action architecture integrating an LLM-based Cognitive Brain for semantic reasoning and a Flow Matching-based Action Expert for trajectory generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ABot-N0 significantly outperforms specialized models, achieving new state-of-the-art performance across 7 benchmarks, demonstrating its robustness for long-horizon missions in real-world environments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11598
25. Sci-CoE: Co-evolving Scientific Reasoning LLMs via Geometric Consensus with Sparse Supervision
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, Co-evolving Paradigms, Scientific Reasoning, Sparse Supervision, Unsupervised Learning
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop Sci-CoE, a two-stage scientific co-evolving framework, for enhancing the scientific reasoning capabilities of large language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of a sparse supervision approach transitioning to unsupervised learning, integrating a geometric reward mechanism to promote self-evolution as both solver and verifier.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Sci-CoE improves complex reasoning capabilities, boosts system robustness, and exhibits strong scalability across general scientific benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12164

26. Multimodal Fact-Level Attribution for Verifiable Reasoning
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal Reasoning, Grounded Attribution, Benchmark, MLLMs, Structured Grounding
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce MuRGAt, a benchmark for evaluating fact-level multimodal attribution in complex reasoning tasks, which requires models to cite precise modalities and temporal segments in their answers.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of an automatic evaluation framework that correlates strongly with human judgments for reliable assessment of multimodal reasoning tasks.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Even strong MLLMs often produce hallucinated citations despite correct reasoning, and there exists a trade-off between reasoning depth and structured grounding that affects accuracy.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11509

27. Gaia2: Benchmarking LLM Agents on Dynamic and Asynchronous Environments
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Model Agents, Asynchronous Environments, Temporal Constraints, Write-Action Verifier, Reinforcement Learning
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Gaia2 as a benchmark for evaluating large language model agents in dynamic environments with temporal and multi-agent collaboration constraints.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Features include a write-action verifier for fine-grained evaluation and reinforcement learning from verifiable rewards in evolving environments.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Evaluation reveals no model excels in all capabilities; GPT-5 performs best overall in static scores but struggles with time-sensitive tasks, demonstrating fundamental trade-offs in reasoning, efficiency, and robustness.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11964

28. Single-minus gluon tree amplitudes are nonzero
🔑 Keywords: scattering amplitudes, Klein space, minus-helicity, Weinberg’s soft theorem, complexified momenta
💡 Category: Foundations of AI
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to explore single-minus tree-level n-gluon scattering amplitudes, challenging the assumption that they vanish under certain conditions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors derive a piecewise-constant closed-form expression to describe the decay of a single minus-helicity gluon into n-1 plus-helicity gluons, considering half-collinear configurations in Klein space or complexified momenta.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The derived formula does not trivially satisfy multiple consistency conditions and specifically aligns with Weinberg’s soft theorem, illustrating nonvanishing scattering amplitudes for specific configurations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12176

29. MolmoSpaces: A Large-Scale Open Ecosystem for Robot Navigation and Manipulation
🔑 Keywords: MolmoSpaces, robot policy benchmarking, simulator-agnostic, zero-shot policies, sim-to-real correlation
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce MolmoSpaces, an open ecosystem designed for large-scale robot policy benchmarking across diverse indoor environments and tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed MolmoSpaces containing 230k indoor environments and 130k annotated object assets that are simulator-agnostic, supporting various simulators such as MuJoCo, Isaac, and ManiSkill.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MolmoSpaces-Bench shows strong sim-to-real correlation and demonstrates that newer zero-shot policies outperform earlier versions, with discoveries on sensitivities like prompt phrasing and camera occlusion.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11337
30. ThinkRouter: Efficient Reasoning via Routing Thinking between Latent and Discrete Spaces
🔑 Keywords: ThinkRouter, model confidence, latent reasoning, STEM reasoning, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces ThinkRouter, a confidence-aware routing mechanism designed to enhance reasoning efficiency by switching between discrete token and latent spaces based on model confidence.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers analyze model confidence dynamics during latent reasoning to understand reasoning trajectories, and propose ThinkRouter for inference-time routing. They conduct extensive experiments on STEM reasoning and coding benchmarks across multiple large-scale reasoning models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ThinkRouter outperforms explicit CoT, random routing, and latent reasoning baselines by achieving an average improvement of 19.70 points in Pass@1 and reducing generation length by up to 15.55%. The mechanism effectively calibrates errors and accelerates end-of-thinking token generation by lowering model confidence.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11683

31. Dreaming in Code for Curriculum Learning in Open-Ended Worlds
🔑 Keywords: Foundation Models, Open-ended learning, Curriculum Control, Long-horizon progression, AI-generated environments
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper proposes “Dreaming in Code (DiCode)” as a framework to enable agents to acquire long-horizon skills in open-ended worlds through the use of foundation models and curriculum control.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The DiCode framework utilizes foundation models to synthesize executable environment code, creating code-level variations to scaffold learning in complex environments.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Empirical results show that DiCode enables significant improvements in agents’ learning, achieving a 16% boost in mean return over the strongest baseline and facilitating success in complex tasks where previous methods failed, thus proving the framework’s effectiveness in curriculum control and bridging competence gaps.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.08194
32. PISCO: Precise Video Instance Insertion with Sparse Control
🔑 Keywords: PISCO, Video Diffusion Model, Instance Insertion, Sparse Keyframe Control, Variable-Information Guidance
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces PISCO, a video diffusion model designed for precise video instance insertion with sparse keyframe control, aiming to enhance high-fidelity AI-assisted filmmaking by enabling targeted modifications.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes Variable-Information Guidance and Distribution-Preserving Temporal Masking to address distribution shifts and stabilize temporal generation, complemented by geometry-aware conditioning for realistic scene adaptation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– PISCO outperforms existing inpainting and video editing baselines, showing significant performance improvements as additional control signals are provided, supported by evaluations on the PISCO-Bench benchmark.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.08277

33. Unveiling Implicit Advantage Symmetry: Why GRPO Struggles with Exploration and Difficulty Adaptation
🔑 Keywords: Asymmetric Group Relative Advantage Estimation, Reinforcement Learning, Exploration, Adaptive Difficulty, Large Language Models
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address exploration and difficulty adaptation challenges in reinforcement learning with large language models through dynamic modulation of exploration incentives and sample difficulty focus.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study reveals the sub-optimality of traditional symmetric Group Relative Advantage Estimation (GRAE) through controlled experiments, demonstrating the benefits of Asymmetric GRAE (A-GRAE).
💬 Research Conclusions:
– A-GRAE asymmetrically suppresses advantages of correct trajectories, encouraging essential exploration, and maximizes learning efficiency by initially prioritizing simpler samples, then transitioning to more complex ones. Experiments show consistent improvements over traditional methods across multiple benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.05548

34. NarraScore: Bridging Visual Narrative and Musical Dynamics via Hierarchical Affective Control
🔑 Keywords: NarraScore, Vision-Language Models, Global Semantic Anchor, Token-Level Affective Adapter, narrative logic
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary objective is to address the challenges in synthesizing coherent soundtracks for long-form videos, specifically focusing on overcoming computational scalability, temporal coherence, and semantic blindness in narrative logic.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A hierarchical framework named NarraScore is used, leveraging frozen Vision-Language Models as affective sensors. It employs a Dual-Branch Injection strategy for balancing global structure and local dynamics through a Global Semantic Anchor and Token-Level Affective Adapter.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– NarraScore establishes a new autonomous paradigm for long-video soundtrack generation, achieving state-of-the-art consistency and narrative alignment with minimal computational overhead.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.09070

35. EgoHumanoid: Unlocking In-the-Wild Loco-Manipulation with Robot-Free Egocentric Demonstration
🔑 Keywords: humanoid loco-manipulation, vision-language-action policy, egocentric human demonstrations, embodiment gap, view and action alignment
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– EgoHumanoid aims to enable humanoid loco-manipulation by co-training vision-language-action policies using egocentric human demonstrations combined with limited robot data.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces an alignment pipeline to bridge the embodiment gap between humans and robots, focusing on view alignment to address visual domain discrepancies and action alignment to map human motions into a kinematically feasible action space.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Extensive experiments reveal that utilizing robot-free egocentric data significantly improves performance by 51% over robot-only baselines in diverse environments, highlighting the potential for scaling human data in humanoid applications.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.10106
36. dVoting: Fast Voting for dLLMs
🔑 Keywords: Diffusion Large Language Models, AI-generated summary, voting technique, iterative refinement, parallel test-time scaling
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce and demonstrate the effectiveness of diffusion large language models (dLLMs) with a focus on parallel token generation to enhance reasoning without requiring additional training.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of dVoting, a fast voting technique, which leverages iterative refinement through sampling, consistency analysis, and regenerating uncertain tokens across multiple samples until convergence is achieved.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– dVoting significantly enhances performance across various benchmarks, achieving notable percentage gains on multiple datasets, such as GSM8K, MATH500, ARC-C, and MMLU, thus proving the efficacy of the proposed method in improving reasoning in large language models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12153

37. Think Longer to Explore Deeper: Learn to Explore In-Context via Length-Incentivized Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: In-Context Exploration, State Coverage, Autoregressive Generation, Shallow Exploration Trap, Length-Incentivized Exploration
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to improve models’ performance during test-time by enhancing In-Context Exploration, addressing challenges in long sequence sampling within Autoregressive Generation.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces a Length-Incentivized Exploration method with a length-based reward and a redundancy penalty to maximize state coverage and mitigate the Shallow Exploration Trap.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method shows an average improvement of 4.4% in in-domain tasks and a 2.7% gain in out-of-domain benchmarks, demonstrating its effectiveness across different models such as Qwen3 and Llama.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11748
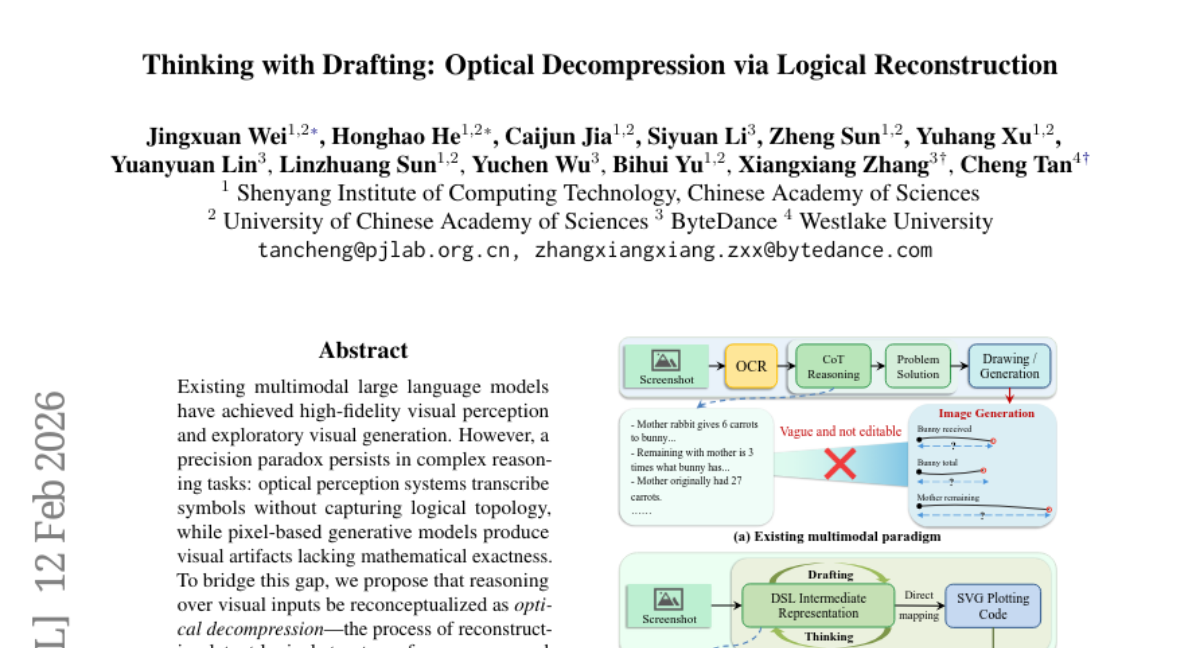
38. Thinking with Drafting: Optical Decompression via Logical Reconstruction
🔑 Keywords: Visual Reasoning, Optical Decompression, Domain-Specific Language, Deterministic Visual Proofs
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance visual reasoning by reconstructing logical structures from compressed visual tokens using a DSL-based approach.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces the concept of Thinking with Drafting (TwD), utilizing a minimalist Domain-Specific Language (DSL) as an intermediate representation to create deterministic visual proofs for verification.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– TwD serves as a superior cognitive scaffold, transforming visual generation into a logical verifier and providing a generalizable path for improved visual reasoning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11731
39. GigaBrain-0.5M*: a VLA That Learns From World Model-Based Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language-Action, Reinforcement Learning, Robotic Manipulation, RAMP, Cross-task Adaptation
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The aim is to enhance vision-language-action (VLA) models with world model-based reinforcement learning to improve robotic manipulation performance and long-horizon task execution.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced GigaBrain-0.5M*, a VLA model trained via reinforcement learning using a world model-based approach, specifically using RAMP to enable robust cross-task adaptation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The GigaBrain-0.5M* model demonstrates a substantial performance gain of approximately 30% over the RECAP baseline in complex tasks and exhibits reliable long-horizon execution as validated by real-world deployment videos.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12099
40. Learning beyond Teacher: Generalized On-Policy Distillation with Reward Extrapolation
🔑 Keywords: On-policy distillation, Reward scaling factor, Generalized On-Policy Distillation, Reward extrapolation, Reward correction
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To extend on-policy distillation through a Generalized On-Policy Distillation (G-OPD) framework, incorporating flexible reference models and reward scaling factors for enhanced performance.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Theoretical analysis demonstrating OPD as a case of dense KL-constrained RL; experimental implementation on math reasoning and code generation tasks to evaluate G-OPD.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Reward extrapolation (ExOPD) consistently enhances student performance compared to standard OPD.
– Reward correction further improves distillation performance, provided access to the teacher’s pre-RL variant.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12125

41. Composition-RL: Compose Your Verifiable Prompts for Reinforcement Learning of Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Composition-RL, Verifiable Prompts, Cross-domain RL
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance reasoning capabilities in reinforcement learning by composing multiple problems into new verifiable questions, optimizing the use of limited verifiable prompts.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method involves using Composition-RL to automatically create new compositional prompts, allowing more effective training across various model sizes and cross-domain reinforcement learning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Composition-RL significantly improves reasoning capabilities compared to training on the original dataset, with performance enhanced by a curriculum approach that increases compositional depth. The approach facilitates effective cross-domain RL.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12036