AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20260216

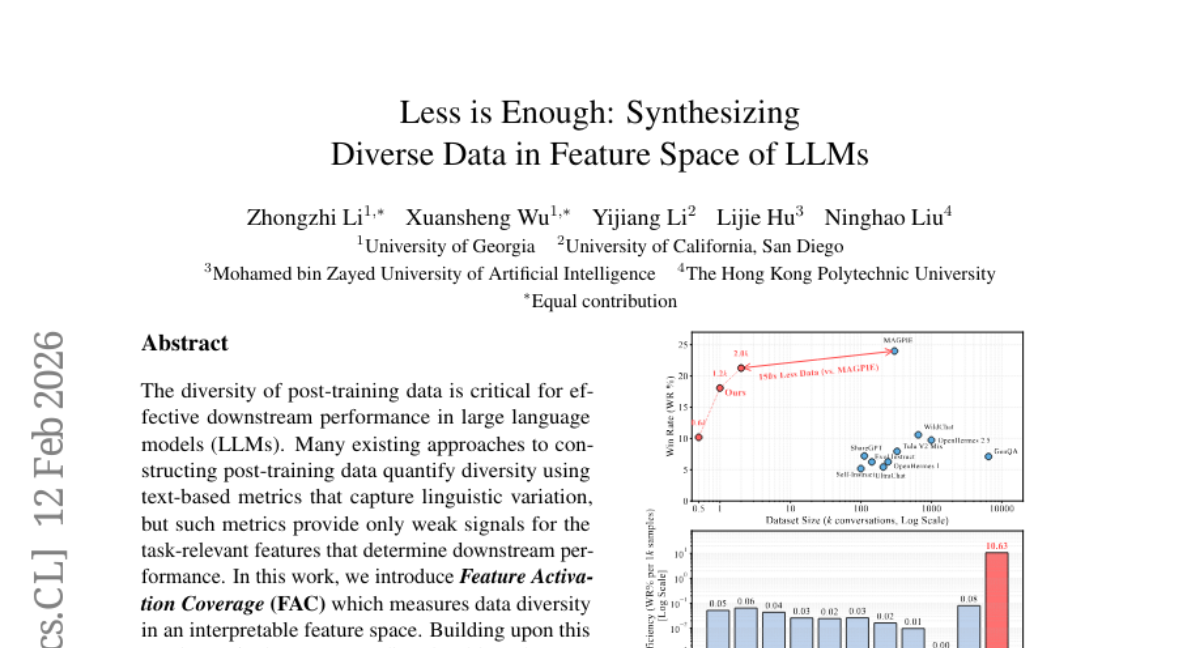
1. Less is Enough: Synthesizing Diverse Data in Feature Space of LLMs
🔑 Keywords: Feature Activation Coverage, data diversity, cross-model knowledge transfer
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Feature Activation Coverage (FAC) to measure data diversity in an interpretable feature space.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A diversity-driven data synthesis framework called FAC Synthesis is proposed, using a sparse autoencoder for feature identification and synthetic sample generation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed approach improves data diversity and downstream performance across various tasks, demonstrating a shared, interpretable feature space that facilitates cross-model knowledge transfer.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.10388
2. MedXIAOHE: A Comprehensive Recipe for Building Medical MLLMs
🔑 Keywords: Medical Vision-Language Model, Entity-Aware Continual Pretraining, Reinforcement Learning, Diagnostic Reasoning, AI in Healthcare
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to enhance clinical understanding and diagnostic reasoning using a model called MedXIAOHE, which is designed for real-world clinical applications.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– MedXIAOHE employs entity-aware continual pretraining to organize diverse medical corpora, reinforcement learning for expert-level reasoning, and tool-augmented agentic training for multi-step diagnostic reasoning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The model achieves state-of-the-art performance across various medical benchmarks, surpassing leading closed-source systems. It offers reliable diagnostic reasoning with verifiable decision traces and adherence to medical instructions, inspiring further research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12705

3. OneVision-Encoder: Codec-Aligned Sparsity as a Foundational Principle for Multimodal Intelligence
🔑 Keywords: Information-theoretic principles, Sparsity-driven encoding, Visual understanding, Video compression, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Improve visual understanding by realigning architectures with information-theoretic principles of video compression, highlighting the importance of sparsity-driven encoding.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed OneVision-Encoder using Codec Patchification to focus computation on regions rich in signal entropy and integrated 3D RoPE for spatial and temporal reasoning over semantic concepts.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrated that efficiency and accuracy are positively correlated, with OV-Encoder outperforming existing models across multiple benchmarks by utilizing fewer resources, underscoring codec-aligned sparsity as a foundational principle for scalable visual generalists.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.08683
4. GeoAgent: Learning to Geolocate Everywhere with Reinforced Geographic Characteristics
🔑 Keywords: GeoAgent, geolocation reasoning, geographic accuracy, geo-similarity reward, consistency reward
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary goal of this research is to enhance geolocation reasoning by using a specialized dataset and reward mechanisms to ensure geographic accuracy and reasoning consistency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of GeoSeek, a new geolocation dataset annotated by geographic experts and professional players.
– Implementation of geo-similarity reward and consistency reward metrics to improve the training process.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– GeoAgent significantly outperforms existing methods and various general VLLMs in geolocation reasoning accuracy and aligns its reasoning more closely with human logic.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12617

5. What does RL improve for Visual Reasoning? A Frankenstein-Style Analysis
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Visual Reasoning, Multimodal Reasoning, Transformer
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To analyze what specific skills reinforcement learning (RL) improves in vision-language models compared to supervised fine-tuning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employed a Frankenstein-style analysis framework including causal probing, parameter comparison, and model merging to isolate and identify improvements in RL.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– RL induces notable inference-time shifts primarily in mid-to-late transformer layers, contributing to vision-to-reasoning alignment and improved reasoning performance. This highlights the limitation of solely relying on benchmark evaluations.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12395

6. RLinf-Co: Reinforcement Learning-Based Sim-Real Co-Training for VLA Models
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Sim-Real Co-training, Vision-Language-Action, Real-World Data Efficiency, Catastrophic Forgetting
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aimed to improve vision-language-action policy performance by utilizing a reinforcement learning-based sim-real co-training framework that leverages both interactive simulation and real-world data.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A two-stage design was implemented: first, warm-starting the policy with supervised fine-tuning on mixed real and simulated demonstrations; then fine-tuning with reinforcement learning in simulation, incorporating an auxiliary supervised loss to anchor the policy on real-world data.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The framework demonstrated significant improvements over conventional methods, increasing real-world success rates and enhancing generalization to unseen task variations, thus offering a scalable path for improving real-robot deployments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12628

7. Towards Universal Video MLLMs with Attribute-Structured and Quality-Verified Instructions
🔑 Keywords: fine-grained audiovisual understanding, structured annotations, Supervised Fine-Tuning, ASID-1M
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The goal is to enhance Universal video understanding by introducing a fine-grained approach to modeling audiovisual content.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study introduces ASID-1M, a large collection of structured, fine-grained annotations, and ASID-Verify, a data curation pipeline ensuring semantic and temporal consistency.
– Utilizes Supervised Fine-Tuning on ASID-1M to train the ASID-Captioner model.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ASID-Captioner demonstrates improved fine-grained caption quality with reduced hallucinations across various audiovisual tasks, achieving state-of-the-art performance among open-source models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.13013

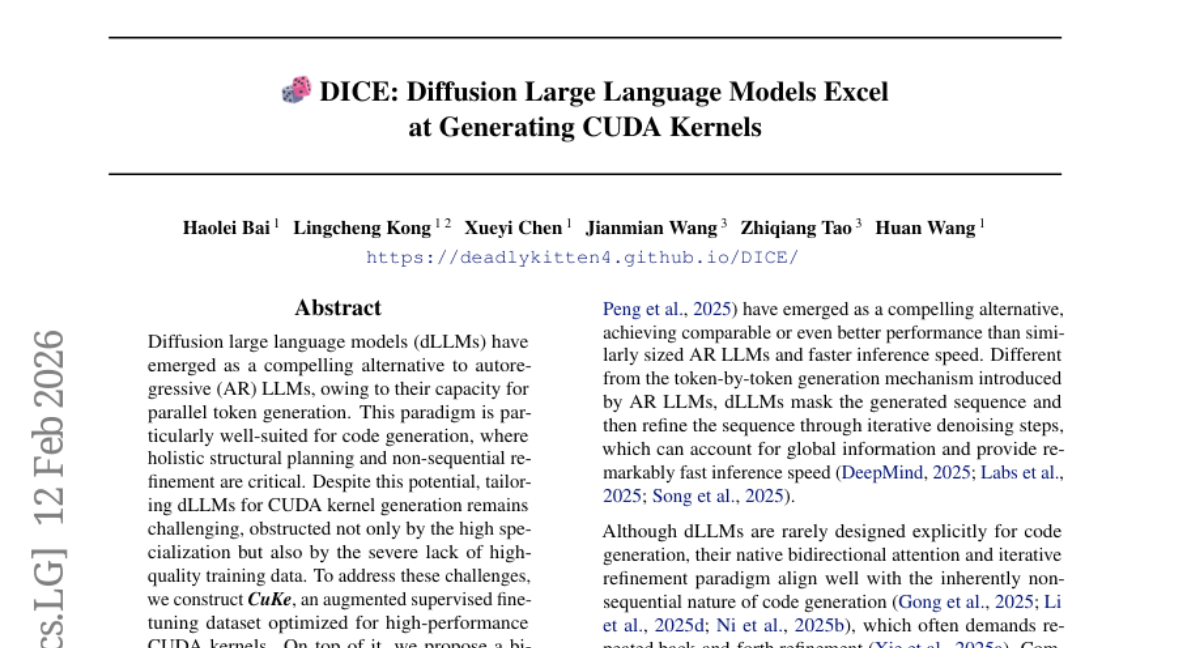
8. DICE: Diffusion Large Language Models Excel at Generating CUDA Kernels
🔑 Keywords: Diffusion Large Language Models, CUDA Kernel Generation, Reinforcement Learning, Parallel Token Generation, CuKe
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance the generation of CUDA kernels using diffusion large language models (dLLMs) through a specialized dataset and a bi-phase reinforcement learning framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Construction of CuKe, a supervised fine-tuning dataset optimized for high-performance CUDA kernel generation.
– Introduction of a BiC-RL framework comprising a CUDA kernel infilling stage and an end-to-end kernel generation stage.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed DICE models, covering three parameter scales (1.7B, 4B, and 8B), outperform existing autoregressive and diffusion models, setting a new benchmark for CUDA kernel generation effectiveness.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11715
9. FLAC: Maximum Entropy RL via Kinetic Energy Regularized Bridge Matching
🔑 Keywords: Field Least-Energy Actor-Critic, Maximum Entropy Reinforcement Learning, kinetic energy, Generalized Schrödinger Bridge, policy optimization
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces Field Least-Energy Actor-Critic (FLAC) to tackle challenges in Maximum Entropy Reinforcement Learning by using kinetic energy as a proxy for regulating policy stochasticity.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors propose a likelihood-free framework under a Generalized Schrödinger Bridge formulation, using kinetic energy minimization to optimize policies without needing explicit action densities and develop an off-policy algorithm with Lagrangian dual mechanism.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Empirical results demonstrate that FLAC delivers superior or comparable performance on high-dimensional benchmarks versus strong baselines, effectively tuning kinetic energy automatically and avoiding explicit density estimation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12829

10. On Robustness and Chain-of-Thought Consistency of RL-Finetuned VLMs
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Vision Language Models, Robustness, Visual Reasoning, Faithfulness
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study investigates the application of Reinforcement Learning (RL) fine-tuning to Vision Language Models (VLMs) to improve their performance on reasoning-intensive tasks, specifically focusing on visual reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research explores the effects of controlled textual perturbations on the robustness and confidence of RL-tuned VLMs, analyzing changes using entropy-based metrics and examining RL fine-tuning dynamics to identify a trade-off between accuracy and faithfulness.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Adversarial augmentation can enhance VLM robustness but does not prevent drift in faithfulness. Incorporating faithfulness-aware rewards can restore alignment between answers and reasoning. However, reliance on accuracy-only evaluations is insufficient, and comprehensive training protocols are needed to balance correctness, robustness, and faithfulness.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12506

11. TADA! Tuning Audio Diffusion Models through Activation Steering
🔑 Keywords: Audio diffusion models, Semantic musical concepts, Attention layers, Contrastive Activation Addition, Sparse Autoencoders
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To understand how specific attention layers in audio diffusion models control distinct musical concepts and enable precise manipulation of audio features.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilization of activation patching to reveal control of distinct semantic musical concepts by specific attention layers.
– Application of Contrastive Activation Addition and Sparse Autoencoders to enable precise control over generated audio.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrated that steering activations of identified attention layers allows for precise alterations of musical elements, such as tempo and mood, highlighting the benefit of the specialization phenomenon.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11910

12. Self-EvolveRec: Self-Evolving Recommender Systems with LLM-based Directional Feedback
🔑 Keywords: Self-EvolveRec, Neural Architecture Search, LLM-driven code evolution, User Simulator, Model Diagnosis Tool
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– Propose the Self-EvolveRec framework to overcome limitations of traditional recommender system design methods by utilizing a directional feedback loop and adaptive evaluation criteria.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Integrate a User Simulator for qualitative critiques and a Model Diagnosis Tool for quantitative verification, along with a Diagnosis Tool – Model Co-Evolution strategy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Self-EvolveRec outperforms existing NAS and LLM-driven code evolution baselines in both recommendation performance and user satisfaction.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12612

13. Favia: Forensic Agent for Vulnerability-fix Identification and Analysis
🔑 Keywords: Favia, vulnerability-fixing commits, LLM agents, semantic reasoning, candidate ranking
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve the identification of vulnerability-fixing commits in large code repositories by leveraging a forensic, agent-based framework called Favia.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Use a combination of scalable candidate ranking and deep semantic reasoning, employing a ReAct-based LLM agent tasked with evaluating commits and localizing vulnerabilities with specialized tools and environmental context.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The framework Favia outperforms existing traditional and LLM-based methods in identifying vulnerability-fixing commits by achieving the strongest precision-recall trade-offs and highest F1-scores, validated on a dataset of over 8 million commits.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12500

14. GeneralVLA: Generalizable Vision-Language-Action Models with Knowledge-Guided Trajectory Planning
🔑 Keywords: GeneralVLA, zero-shot capability, Vision-Language-Action Models, trajectory planning, 3D-aware control policy
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to develop GeneralVLA, a hierarchical vision-language-action model that enables zero-shot robotic manipulation without the need for real-world data collection.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study involves a high-level ASM for affordance segmentation, a mid-level 3DAgent for task understanding and trajectory planning, and a low-level 3D-aware control policy for precise manipulation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– GeneralVLA outperforms state-of-the-art methods by generating effective trajectories for 14 tasks, and the demonstrations can lead to more robust behavior cloning policies than those created with human demonstrations or other existing methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.04315

15. OpenLID-v3: Improving the Precision of Closely Related Language Identification — An Experience Report
🔑 Keywords: Language identification, OpenLID, low-resource languages, multilingual datasets, noise detection
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve language identification accuracy for closely related languages and low-resource variants through enhanced training data, cluster merging, and noise detection mechanisms using an extended version of OpenLID called OpenLID-v3.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The extension of OpenLID involved increasing training data, merging problematic language variant clusters, and introducing a noise label. Evaluations were conducted against GlotLID on multiple benchmarks, focusing on three language groups: Bosnian, Croatian, and Serbian; Romance varieties of Northern Italy and Southern France; and Scandinavian languages.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– OpenLID-v3 demonstrates improved precision using ensemble approaches, though coverage for low-resource languages is substantially reduced. New evaluation datasets were created due to inadequacies in existing ones.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.13139

16.

17. Principled Synthetic Data Enables the First Scaling Laws for LLMs in Recommendation
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, recommender systems, synthetic data, power-law scaling, continual pre-training
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce a novel layered framework for generating high-quality synthetic data to improve the capability and performance of large language models in recommender systems.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The development of a pedagogical curriculum for large language models with high-quality synthetic data that supports predictable scaling laws and addresses the noise and bias in raw user interaction data.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Models trained on this structured synthetic data significantly outperform those trained on real data in ranking tasks, showing robust power-law scaling and predictable perplexity reduction, thus establishing a foundation for improving large language models in recommendation domains.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.07298

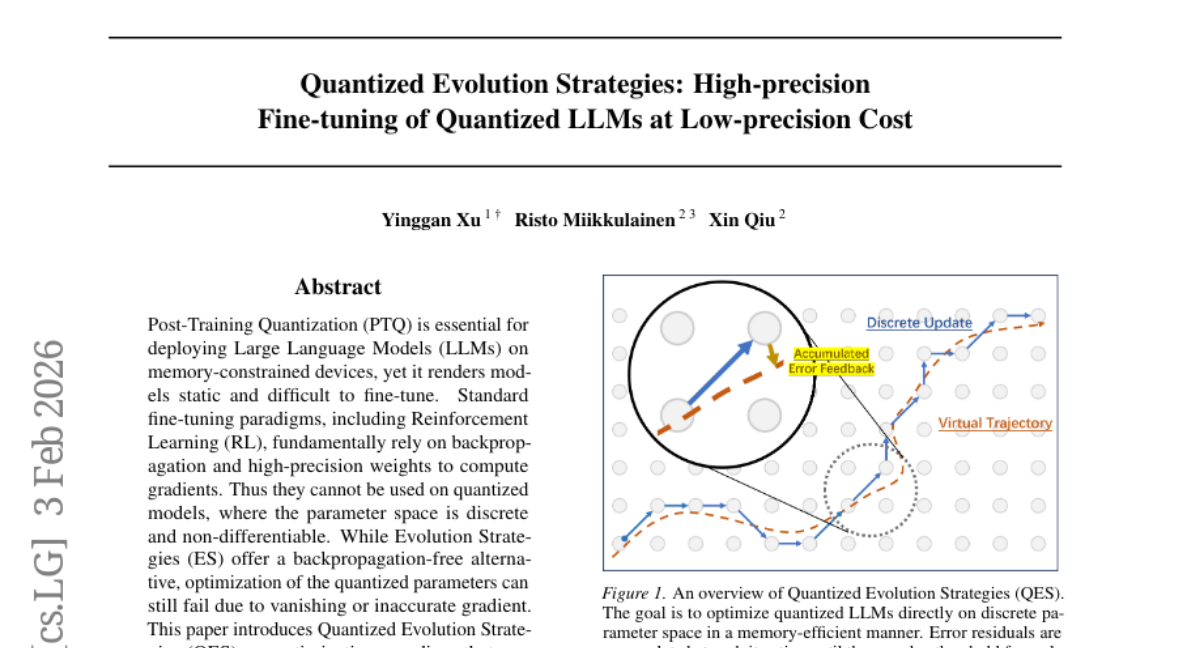
18. Quantized Evolution Strategies: High-precision Fine-tuning of Quantized LLMs at Low-precision Cost
🔑 Keywords: Post-Training Quantization, Large Language Models, Quantized Evolution Strategies, Fine-Tuning
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce Quantized Evolution Strategies (QES) for fine-tuning Large Language Models directly in the quantized parameter space.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– QES integrates accumulated error feedback to maintain high-precision gradient signals.
– It uses stateless seed replay to minimize memory usage to low-precision inference levels.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– QES significantly outperforms existing zeroth-order fine-tuning methods on arithmetic reasoning tasks.
– Enables scaling up of Large Language Models fully within the quantized space.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.03120
19. Light4D: Training-Free Extreme Viewpoint 4D Video Relighting
🔑 Keywords: 4D video synthesis, temporal consistency, Disentangled Flow Guidance, training-free framework, IC-Light
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to enable consistent 4D video synthesis under target illumination, overcoming challenges in maintaining temporal consistency across different viewpoints.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The introduction of Disentangled Flow Guidance for injecting lighting control into the latent space while preserving geometric integrity.
– Development of Temporal Consistent Attention within the IC-Light architecture, along with deterministic regularization, to eliminate flickering and ensure temporal consistency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The Light4D framework shows competitive performance in maintaining temporal consistency and lighting fidelity, managing extreme camera rotations effectively.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11769

20. Learning Image-based Tree Crown Segmentation from Enhanced Lidar-based Pseudo-labels
🔑 Keywords: Tree Crowns, Aerial Imagery, Deep Learning Models, Pseudo-Labels, Segment Anything Model 2
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To develop a method for separating individual tree crowns from aerial imagery using deep learning models and ALS-derived pseudo-labels.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized pseudo-labels from aerial laser scanning and enhanced them with Segment Anything Model 2 for training deep learning models to segment trees in RGB and multispectral images.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The method produces domain-specific training annotations without manual cost and achieves superior segmentation performance compared to existing general domain models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.13022

21. Best of Both Worlds: Multimodal Reasoning and Generation via Unified Discrete Flow Matching
🔑 Keywords: UniDFlow, discrete flow-matching, multimodal tasks, low-rank adapters, zero-shot generalization
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study introduces UniDFlow, a unified framework designed to enhance understanding and generation in multimodal tasks without necessitating retraining.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The approach uses low-rank adapters to decouple the tasks of understanding and generation, employing reference-based alignment for multimodal preference optimization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– UniDFlow achieves state-of-the-art performance across several benchmarks, demonstrating robust zero-shot generalization capabilities in diverse tasks, including inpainting, image generation, and reference-based editing.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12221

22. Code2Worlds: Empowering Coding LLMs for 4D World Generation
🔑 Keywords: Code2Worlds, language-to-simulation code generation, dual-stream architecture, physics-aware closed-loop mechanism, 4D scene generation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to advance 4D dynamic scene generation by addressing challenges in extending language models’ capabilities to simulate dynamic environments grounded in physical laws.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research introduces a novel framework called Code2Worlds, employing a dual-stream architecture and a physics-aware closed-loop mechanism. This includes a PostProcess Agent and VLM-Motion Critic for refining simulation code.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Code2Worlds shows superior performance, with a 41% gain in SGS and 49% higher Richness compared to baselines, demonstrating its ability to generate physics-aware dynamics missing in previous static methods.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11757

23. Xiaomi-Robotics-0: An Open-Sourced Vision-Language-Action Model with Real-Time Execution
🔑 Keywords: Vision-Language-Action, Pre-training, Real-time execution, Bimanual manipulation, Asynchronous execution
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce Xiaomi-Robotics-0, a vision-language-action model that optimizes high-performance manipulation with real-time capabilities.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The model uses large-scale pre-training on cross-embodiment robot trajectories and vision-language data, along with specialized post-training techniques for asynchronous execution to reduce inference latency.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Xiaomi-Robotics-0 outperforms state-of-the-art methods in simulation benchmarks and real-robot tasks, demonstrating high success rates and throughput with consumer-grade hardware.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12684

24. SciAgentGym: Benchmarking Multi-Step Scientific Tool-use in LLM Agents
🔑 Keywords: SciAgentGym, SciAgentBench, SciForge, Scientific tool use, Dependency graph
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to assess and enhance scientific tool-use capabilities by integrating SciAgentGym, SciAgentBench, and SciForge.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The approach includes creating SciAgentGym, an environment with 1,780 domain-specific tools, and SciAgentBench, a tiered evaluation suite, to test agents across various interaction horizons. Additionally, SciForge models tool interactions as a dependency graph for improved training trajectories.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SciAgent-8B, after fine-tuning, shows significant improvement over larger models, indicating potential for next-generation scientific agents, highlighting that current models struggle with extended multi-step scientific workflows.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12984

25. BPDQ: Bit-Plane Decomposition Quantization on a Variable Grid for Large Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Bit-Plane Decomposition, Quantization Grid, Scalar Coefficients, AI-Generated Summary, Hessian-Induced Geometry
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Propose Bit-Plane Decomposition Quantization (BPDQ) for better accuracy in low-bit quantization of large language model inference, particularly under resource constraints.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of a variable quantization grid using bit-planes and scalar coefficients and iterative refinement with approximate second-order information to minimize quantization error.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– BPDQ shows improved feasibility and alignment with optimization objectives, enabling efficient serving with notable accuracy improvements in challenging scenarios.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.04163

26. ABot-M0: VLA Foundation Model for Robotic Manipulation with Action Manifold Learning
🔑 Keywords: Embodied Agents, Action Manifold Learning, Data Curation Pipeline, Knowledge Transfer, VLM Semantics
💡 Category: Robotics and Autonomous Systems
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of ABot-M0 is to create a unified framework for developing embodied agents that addresses challenges in robotics such as inconsistent data and training objectives, and enables efficient and stable action prediction.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– ABot-M0 systematically curates data and optimizes model architecture and training strategies, transforming raw data into unified representations.
– Introduces Action Manifold Learning based on the Action Manifold Hypothesis to predict continuous action sequences using a DiT backbone, enhancing decoding speed and policy stability.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The framework’s pre-training improves knowledge transfer and generalization across various platforms and tasks.
– ABot-M0 supports modular perception to enhance spatial understanding, showing that components operate independently with additive benefits.
– All related code and pipelines will be released to aid reproducibility and future research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11236
27. Intelligent AI Delegation
🔑 Keywords: AI agents, adaptive framework, task decomposition, delegation, trust mechanisms
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to propose an adaptive framework for intelligent AI delegation that is capable of dynamically responding to environmental changes and handling unexpected failures.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers develop a sequence of decisions for task allocation, incorporating authority transfer, responsibility, accountability, and trust mechanisms to enhance delegation between human and AI agents.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed framework is designed to improve task decomposition and delegation methods, applicable to complex networks involving both human and AI delegators and delegatees, and aims to inform the development of protocols in the emerging agentic web.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11865

28. SemanticMoments: Training-Free Motion Similarity via Third Moment Features
🔑 Keywords: Semantic motion, Video representation, Temporal statistics, SimMotion benchmarks, SemanticMoments
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Address the bias towards static appearance in video representation approaches and improve motion-centric video understanding using temporal statistics in semantic feature space.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced SimMotion benchmarks combining synthetic and real-world datasets, and proposed a method called SemanticMoments that calculates temporal statistics over features from pre-trained semantic models without additional training.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– SemanticMoments consistently outperforms existing RGB, flow, and text-supervised methods, demonstrating the efficacy of using temporal statistics in a semantic feature space for scalable and perceptually grounded motion-centric video understanding.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.09146

29. CoPE-VideoLM: Codec Primitives For Efficient Video Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Video Language Models, video codec primitives, temporal dynamics, pre-training strategy
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to enhance Video Language Models (VideoLMs) by addressing the challenges of sparse temporal coverage and computational overhead.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The authors propose the use of video codec primitives (motion vectors and residuals) to reduce redundancy and computational load, alongside lightweight transformer-based encoders that align video primitives with image encoder embeddings through a pre-training strategy.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed approach significantly reduces computation time and token usage while maintaining or surpassing performance across 14 diverse video understanding benchmarks, including tasks such as general question answering and temporal reasoning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.13191

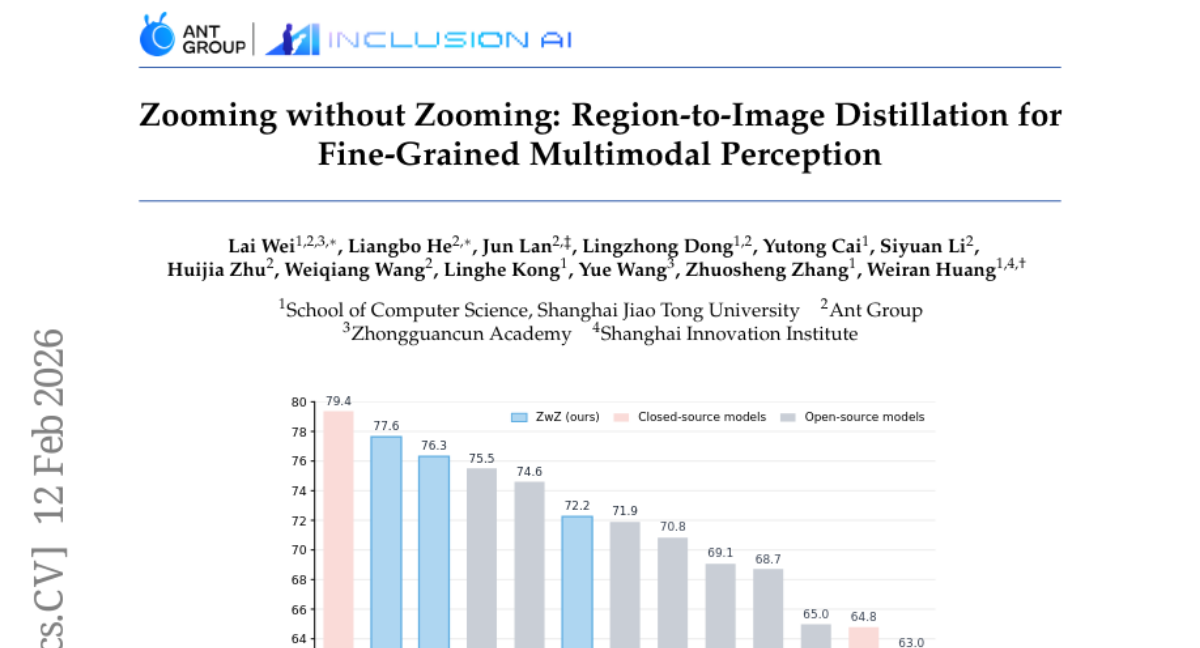
30. Zooming without Zooming: Region-to-Image Distillation for Fine-Grained Multimodal Perception
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal Large Language Models, fine-grained perception, Region-to-Image Distillation, Thinking-with-Images, ZoomBench
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To improve fine-grained perception in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) by internalizing iterative zooming through Region-to-Image Distillation, eliminating the need for repeated tool calls and visual re-encoding.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The approach involves training with micro-cropped regions to generate high-quality visual question answering (VQA) data, then distilling this region-grounded supervision into the full image. A novel benchmark, ZoomBench, is introduced for evaluation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The proposed method achieves leading performance on multiple fine-grained perception benchmarks, enhances general multimodal cognition, and reduces latency by incorporating zooming into a single forward pass, leveraging when “Thinking-with-Images” is necessary.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11858
31. SQuTR: A Robustness Benchmark for Spoken Query to Text Retrieval under Acoustic Noise
🔑 Keywords: Spoken query retrieval, Robustness, Noise, Evaluation dataset
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduction of SQuTR, a robustness benchmark for spoken query retrieval systems, to address limitations in existing evaluation datasets under complex acoustic conditions.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Aggregation of 37,317 unique queries from English and Chinese datasets, synthesis of speech using 200 real voice profiles, and integration of 17 categories of environmental noise under controlled SNR levels in a unified evaluation protocol.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Retrieval performance decreases with increasing noise levels, with large-scale retrieval models particularly struggling under extreme noise, highlighting robustness as a critical challenge.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12783
