AI Native Daily Paper Digest – 20260217
1. DeepImageSearch: Benchmarking Multimodal Agents for Context-Aware Image Retrieval in Visual Histories
🔑 Keywords: DeepImageSearch, agentic paradigm, multimodal retrieval systems, contextual cues, DISBench
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce DeepImageSearch, reformulating image retrieval as an autonomous exploration task utilizing an agentic approach for multi-step reasoning over visual histories.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed a benchmark named DISBench using interconnected visual data for challenging image retrieval tasks.
– Employed a human-model collaborative pipeline with vision-language models to mine latent spatiotemporal associations, and devised a baseline using a modular agent framework with dual-memory for long-horizon navigation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Demonstrated the need to incorporate agentic reasoning into next-generation retrieval systems, as DISBench poses significant challenges to current state-of-the-art models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.10809

2. REDSearcher: A Scalable and Cost-Efficient Framework for Long-Horizon Search Agents
🔑 Keywords: REDSearcher, task synthesis, tool-augmented queries, midtraining, reinforcement learning
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To optimize search agents for long-horizon search tasks through a unified framework, addressing the challenges of task synthesis and high-cost rollouts.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduces a dual-constrained optimization for task synthesis using graph topology and evidence dispersion.
– Implements tool-augmented queries to encourage proactive tool usage.
– Enhances core atomic capabilities during midtraining to reduce costs.
– Employs a local simulated environment for efficient algorithmic iteration in reinforcement learning experiments.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The REDSearcher framework achieves state-of-the-art performance in both text-only and multimodal search agent benchmarks, and will release high-quality search trajectories and resources to facilitate future research.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.14234

3. Query as Anchor: Scenario-Adaptive User Representation via Large Language Model
🔑 Keywords: Query-as-Anchor, Large Language Models, User Representation, AI-generated Summary, KV-cache-accelerated Inference
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to introduce a framework, Query-as-Anchor, that shifts user modeling from static encoding to dynamic, query-aware synthesis using large language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study employs hierarchical coarse-to-fine encoders in dual-tower LLMs via joint contrastive-autoregressive optimization and introduces Cluster-based Soft Prompt Tuning for model alignment.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The framework demonstrates consistent state-of-the-art performance across 10 Alipay industrial benchmarks, shows strong scalability, efficient deployment, and effectiveness in large-scale online A/B testing.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.14492

4. Data Darwinism Part I: Unlocking the Value of Scientific Data for Pre-training
🔑 Keywords: Data Darwinism, ten-level taxonomy, data-model co-evolution, Generative Refinement, Cognitive Completion
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The primary objective is to establish a ten-level taxonomy framework called Data Darwinism that improves foundation model performance on scientific text.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study involves creating Darwin-Science, a 900B-token corpus, and testing various levels of data processing (L0-L5) using advanced LLMs, implementing techniques like Generative Refinement and Cognitive Completion for enhanced data-model co-evolution.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The study confirms that advanced processing through higher levels of their taxonomy (up to L5) significantly boosts model performance, evidenced by a +5.60 and +8.40 point improvement on domain-aligned tasks, showcasing the effectiveness of Data Darwinism.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.07824

5. UniWeTok: An Unified Binary Tokenizer with Codebook Size 2^{128} for Unified Multimodal Large Language Model
🔑 Keywords: Unified Multimodal Large Language Models, visual tokenizers, binary codebook, SigLu activation function, image generation
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– UniWeTok introduces a unified discrete tokenizer designed to enhance performance in image generation and multimodal tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A massive binary codebook with Pre-Post Distillation and Generative-Aware Prior is used for training.
– A convolution-attention hybrid architecture with SigLu activation function is employed.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– UniWeTok achieves state-of-the-art performance in image generation with lower computational requirements and demonstrates competitive capabilities in multimodal understanding and editing tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.14178

6. InnoEval: On Research Idea Evaluation as a Knowledge-Grounded, Multi-Perspective Reasoning Problem
🔑 Keywords: Large Language Models, idea evaluation, multi-perspective reasoning, deep innovation evaluation framework, heterogeneous deep knowledge search
💡 Category: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To address the limitations in existing idea evaluation methods and introduce the InnoEval framework that emulates human-level idea assessment through knowledge-grounded, multi-perspective reasoning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a heterogeneous deep knowledge search engine to retrieve and ground evidence from diverse sources.
– Employs an innovation review board with reviewers from different academic backgrounds for multi-dimensional decoupled evaluation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Experiments show that InnoEval outperforms baselines in various evaluation tasks, with its judgments and consensus closely aligning with human expert assessments.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.14367
7. Embed-RL: Reinforcement Learning for Reasoning-Driven Multimodal Embeddings
🔑 Keywords: Reasoning-driven UME, Chain-of-Thought, Embedder-Guided Reinforcement Learning, Multimodal Large Language Models, Traceability CoT
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to enhance cross-modal semantic consistency and retrieval performance by integrating Embedder-Guided Reinforcement Learning with a reasoning-driven universal multimodal embedding framework.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduction of an EG-RL framework allowing the Embedder to provide supervision to the Reasoner.
– Development of Traceability Chain-of-Thought (T-CoT) to focus on retrieval-relevant elements with multimodal cues.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The framework outperforms existing models on benchmarks such as MMEB-V2 and UVRB, showcasing improved cross-modal semantic consistency and generalization across complex scenarios.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.13823

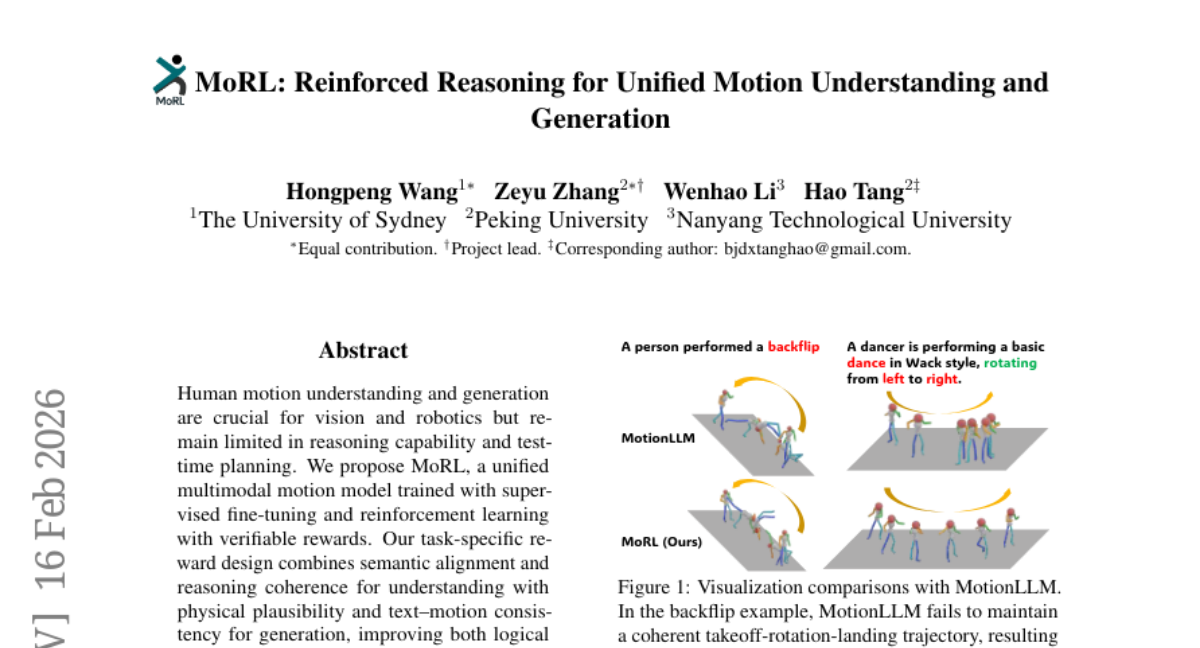
8. MoRL: Reinforced Reasoning for Unified Motion Understanding and Generation
🔑 Keywords: multimodal motion model, supervised fine-tuning, reinforcement learning, semantic alignment, physical plausibility
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– To enhance human motion understanding and generation by integrating semantic alignment and reasoning coherence with physical plausibility and text-motion consistency.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Employed a unified multimodal motion model named MoRL, trained using supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards.
– Introduced a reasoning method, Chain-of-Motion, and developed two large-scale CoT datasets for improved test-time reasoning and planning.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– MoRL showed significant improvements over state-of-the-art baselines in logical reasoning and perceptual realism on HumanML3D and KIT-ML datasets.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.14534
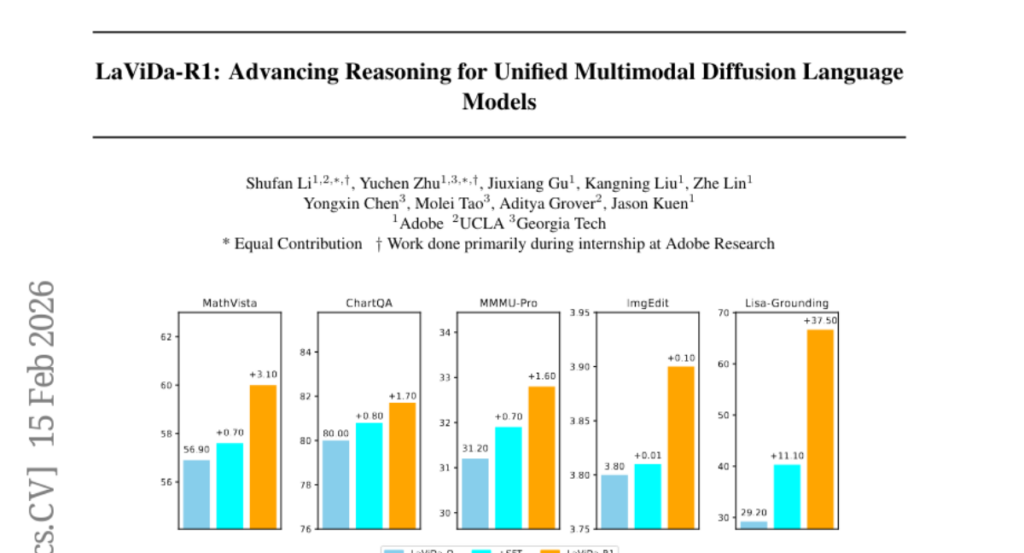
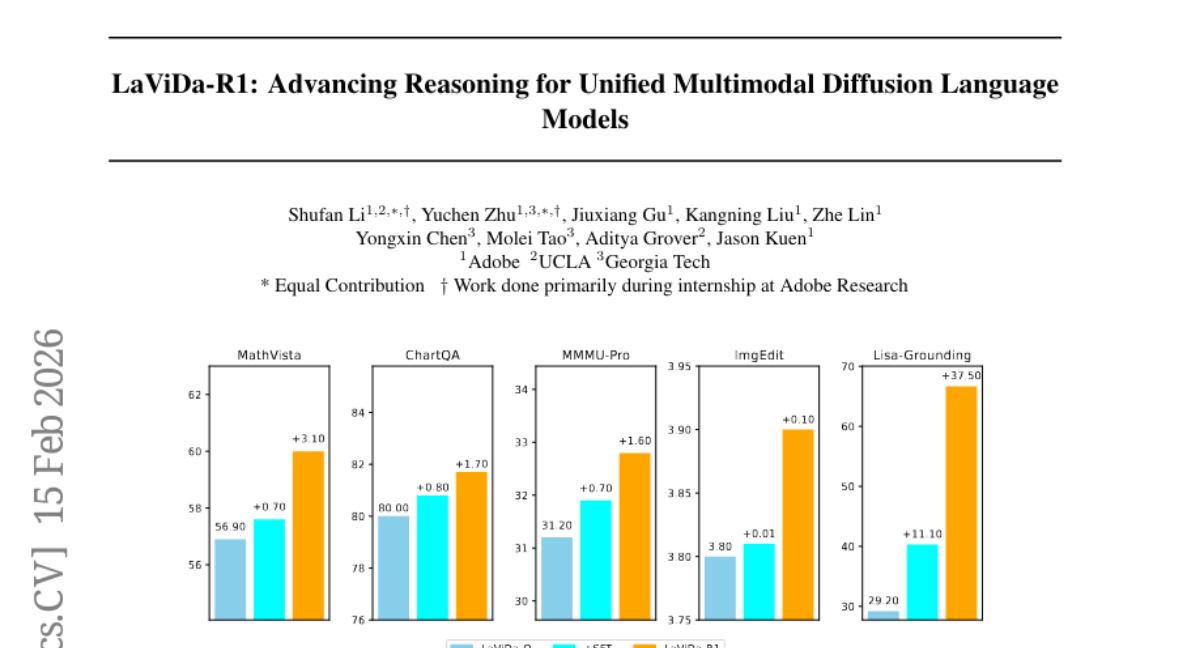
9. LaViDa-R1: Advancing Reasoning for Unified Multimodal Diffusion Language Models
🔑 Keywords: LaViDa-R1, multimodal reasoning, diffusion language model, multi-task reinforcement learning, unified post-training framework
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research introduces LaViDa-R1, a multimodal reasoning diffusion language model designed to unify supervised fine-tuning and multi-task reinforcement learning for enhanced performance across various tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes a novel unified post-training framework incorporating diversified multimodal understanding and generation tasks with innovative training techniques like answer-forcing, tree search, and complementary likelihood estimation.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Extensive experiments show that LaViDa-R1 performs strongly in a wide range of multimodal tasks, including visual math reasoning, reason-intensive grounding, and image editing.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.14147
10. WebWorld: A Large-Scale World Model for Web Agent Training
🔑 Keywords: WebWorld, AI-generated summary, cross-domain generalization, world model, inference-time search
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To introduce WebWorld, an open-web simulator leveraging over one million interactions for enhanced reasoning and simulation, comparable to advanced models like Gemini-3-Pro and GPT-4o.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizing a scalable data pipeline to train on extensive open-web interactions, supporting long-horizon reasoning and multi-format data.
– Implementing intrinsic and extrinsic evaluations to benchmark performance against existing models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– WebWorld achieves performance comparable to leading models in web simulation and extends cross-domain capabilities to code, GUI, and games.
– Offers a replicable formula for constructing efficient world models, excelling in inference-time search and outshining models like GPT-5 in certain aspects.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.14721

11. AIDev: Studying AI Coding Agents on GitHub
🔑 Keywords: AI Agent, Agentic AI, Coding Agent, Human-AI Collaboration, Developer Productivity
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to introduce AIDev, a large-scale dataset capturing agent-authored pull requests from real-world GitHub repositories, to fill the lack of comprehensive datasets that demonstrate AI coding agent usage in practical software development scenarios.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The dataset aggregates 932,791 agent-authored pull requests produced by AI agents including OpenAI Codex, Devin, GitHub Copilot, Cursor, and Claude Code, across over 116,211 repositories and involving 72,189 developers.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– AIDev serves as a foundation for future studies on AI adoption, developer productivity, and human-AI collaboration in modern software engineering. This dataset includes a curated subset of pull requests from notable repositories, adding depth with comments, reviews, commits, and related issues.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.09185

12. AnchorWeave: World-Consistent Video Generation with Retrieved Local Spatial Memories
🔑 Keywords: video generation consistency, AI-generated summary, local geometric memories, cross-view inconsistencies, multi-anchor weaving controller
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to improve long-term video generation consistency by replacing global 3D scene reconstruction with multiple local geometric memories and a multi-anchor weaving controller.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– AnchorWeave framework employs coverage-driven local memory retrieval aligned with the target trajectory and integrates local memories using a multi-anchor weaving controller.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– AnchorWeave significantly enhances scene consistency and visual quality in long-term video generation, with validation through extensive experiments on the effectiveness of local geometric conditioning, multi-anchor control, and coverage-driven retrieval.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.14941

13. DHPLT: large-scale multilingual diachronic corpora and word representations for semantic change modelling
🔑 Keywords: DHPLT, diachronic corpora, semantic change modelling, multilingual, word embeddings
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To present DHPLT, a multilingual diachronic corpus collection across 41 languages aimed at addressing gaps in semantic change modelling beyond high-resource languages.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized web-crawled HPLT datasets with timestamps to approximate document creation times and provided pre-computed word type and token embeddings along with lexical substitutions for selected target words.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– DHPLT enables new experimental setups in semantic change modelling across multiple languages, facilitating broader research by offering open access to resources.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11968

14. Can I Have Your Order? Monte-Carlo Tree Search for Slot Filling Ordering in Diffusion Language Models
🔑 Keywords: Masked Diffusion Models, Monte Carlo Tree Search, slot infilling, reasoning task performance
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to enhance Masked Diffusion Models by optimizing slot infilling order using Monte Carlo Tree Search to improve performance on reasoning tasks.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research uses McDiffuSE, a framework to formulate slot selection as decision-making optimized through Monte Carlo Tree Search, employing look-ahead simulations to evaluate partial completions and systematically explore generation orders.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The findings demonstrate an average improvement of 3.2% over autoregressive baselines and 8.0% over baseline plan-and-infill, with significant gains on MBPP and MATH500. The research identifies that effective orderings are discovered through larger exploration constants, suggesting MCTS-based planning effectively enhances generation quality in Masked Diffusion Models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12586

15. Benchmarking Knowledge-Extraction Attack and Defense on Retrieval-Augmented Generation
🔑 Keywords: Retrieval-Augmented Generation, knowledge-extraction attacks, attack and defense strategies, standardized protocols, privacy-preserving
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper aims to introduce a systematic benchmark for evaluating knowledge-extraction attacks on Retrieval-Augmented Generation systems, addressing gaps in the fragmented research landscape by using standardized evaluation protocols.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study presents a unified experimental framework covering diverse attack and defense strategies, multiple retrieval and generation models, and uses standardized protocols across a variety of datasets.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The benchmark offers valuable insights and a foundation for developing privacy-preserving RAG systems by enabling reproducible and comparable evaluations in response to knowledge extraction threats.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.09319

16. A Critical Look at Targeted Instruction Selection: Disentangling What Matters (and What Doesn’t)
🔑 Keywords: targeted instruction selection, large language models, data representation, gradient-based representations, selection algorithms
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To clarify and systematically analyze the components of targeted instruction selection for LLM fine-tuning, focusing on data representation and selection algorithms.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilized gradient-based data representations and a greedy round-robin selection algorithm to evaluate performance across datasets, tasks, and budgets.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Gradient-based representations with a greedy round-robin selection algorithm perform best at low budgets. Insights provide a foundation for more principled data selection in LLM fine-tuning.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.14696

17. VisPhyWorld: Probing Physical Reasoning via Code-Driven Video Reconstruction
🔑 Keywords: VisPhyWorld, physical reasoning, MLLMs, execution-based framework, semantic scene understanding
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Evaluate the capacity of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to genuinely reason about physical dynamics through an execution-based framework called VisPhyWorld.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of VisPhyWorld framework requiring models to generate executable simulator code from visual observations to assess physical reasoning.
– Introduction of VisPhyBench with 209 evaluation scenes derived from 108 physical templates to test model performance on reconstructing appearance and simulating motion.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– While MLLMs demonstrate strong semantic scene understanding, they struggle with accurately inferring physical parameters and simulating consistent physical dynamics.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.13294

18. SPILLage: Agentic Oversharing on the Web
🔑 Keywords: Web agents, Natural Agentic Oversharing, SPILLage, Behavioral Oversharing, Task Success
💡 Category: Human-AI Interaction
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper investigates the handling of user resources by web agents when performing tasks online, formalizing the concept of Natural Agentic Oversharing due to behavioral and content traces.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– A taxonomy distinguishing content and behavioral oversharing, involving 180 tasks across e-commerce websites, with agentic frameworks and LLMs, to separate task-relevant from irrelevant attributes.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Oversharing is significantly more prevalent behaviorally than content-wise, and reducing task-irrelevant information increases task success by up to 17.9%, emphasizing privacy challenges inherent in web agents.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.13516

19.

20. Found-RL: foundation model-enhanced reinforcement learning for autonomous driving
🔑 Keywords: AI Native, Vision-Language Models, Reinforcement Learning, asynchronous batch inference
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The main goal is to integrate Vision-Language Models with Reinforcement Learning for autonomous driving, focusing on enhancing sample efficiency and reducing latency issues.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The introduction of an asynchronous batch inference framework to handle VLM’s reasoning separately from the RL simulation loop.
– Implementation of diverse supervision mechanisms such as Value-Margin Regularization and Advantage-Weighted Action Guidance for improved policy formulation in RL.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Found-RL demonstrates that a streamlined RL model can achieve performance levels comparable to large-scale VLMs while maintaining real-time inference capabilities, approximately 500 FPS.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.10458

21. Preliminary sonification of ENSO using traditional Javanese gamelan scales
🔑 Keywords: Sonification, ENSO, dynamical systems, acoustic phase space, parameter-mapping
💡 Category: Foundations of AI
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective is to explore sonification as a means to represent complex dynamical systems, specifically mapping El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) data to audio through traditional musical scales.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study utilizes parameter-mapping sonification of the Niño 3.4 sea surface temperature anomaly index, effectively encoding variability into Javanese gamelan pentatonic systems and analyzing the resulting audio in a two-dimensional acoustic phase space.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The research concludes that the sonification preserves key dynamical signatures through recurrence-based diagnostics and coupling analysis, providing a geometric framework for comparing sonification designs within complex systems contexts.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.14560

22. Blind to the Human Touch: Overlap Bias in LLM-Based Summary Evaluation
🔑 Keywords: LLM judge, summarization bias, ROUGE, BLEU, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– To analyze the bias of LLM judges towards AI-generated summaries compared to human-written summaries, using a defined overlap metric in the domain of summarization.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Testing was conducted on 9 recent LLMs with parameter counts ranging from 1 billion to 12 billion, including variants of Gemma 3 and LLaMA 3, using ROUGE and BLEU as measures for summary overlap.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LLM judges exhibit a preference for AI-generated summaries as similarities to human references decrease. This preference was consistent across almost all models tested, indicating that additional techniques beyond simple comparison are needed for accurate judgment in summarization tasks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.07673

23. Acoustivision Pro: An Open-Source Interactive Platform for Room Impulse Response Analysis and Acoustic Characterization
🔑 Keywords: Room Acoustics, AcoustiVision Pro, RIR Analysis, Open-Source, Real-Time Auralization
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– To present AcoustiVision Pro, a comprehensive platform for room impulse response (RIR) analysis, offering both rigorous signal processing and intuitive visualization for architectural design and audio engineering.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Development of a web-based open-source platform that computes twelve distinct acoustic parameters, provides 3D visualizations, generates frequency-dependent decay characteristics, checks compliance with international standards, and supports FFT-based real-time auralization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– AcoustiVision Pro enhances room acoustics analysis by providing a detailed suite of tools suitable for applications ranging from classroom acoustics to healthcare facility design, demonstrated through preliminary case studies.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12299

24. CellMaster: Collaborative Cell Type Annotation in Single-Cell Analysis
🔑 Keywords: LLM-encoded knowledge, zero-shot cell-type annotation, interpretable rationales, human-in-the-loop refinement, AI-generated summary
💡 Category: AI in Healthcare
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aimed to improve the accuracy of cell-type annotation in single-cell RNA sequencing by utilizing LLM-encoded knowledge, bypassing the need for pre-training or fixed marker databases.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– CellMaster, an AI agent, uses on-the-fly annotation with interpretable rationales powered by LLM-encoded knowledge to surpass the performance of existing automated cell annotation tools.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– CellMaster demonstrated a significant accuracy improvement, showing a 7.1% increase over the best-existing tools in automatic mode and up to 18.6% with human refinement. It is particularly effective in identifying rare and novel cell states.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.13346

25. Exposing the Systematic Vulnerability of Open-Weight Models to Prefill Attacks
🔑 Keywords: Prefill attacks, Open-weight models, Large language models, Vulnerability, Model-specific strategies
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– Investigate the effectiveness and implications of prefill attacks on open-weight language models.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Conducted the largest empirical study on prefill attacks, evaluating over 20 strategies across various model families and state-of-the-art open-weight models.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Prefill attacks demonstrate consistent effectiveness against major open-weight models, revealing significant vulnerabilities.
– Some large reasoning models show partial robustness but remain susceptible to tailored strategies.
– Emphasizes the urgent need for developing defenses against prefill attacks in open-weight language models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.14689

26. EditCtrl: Disentangled Local and Global Control for Real-Time Generative Video Editing
🔑 Keywords: Video Inpainting, Generative Editing, Local Video Context, Temporal Global Context Embedder
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– The paper introduces EditCtrl, an efficient video inpainting framework that optimizes computation by focusing on masked regions for improved editing.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method uses a local video context module operating on masked tokens and a lightweight temporal global context embedder for ensuring context consistency with reduced computational cost.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– EditCtrl offers 10 times more computational efficiency than state-of-the-art methods and enhances editing quality. It enables capabilities like multi-region editing with text prompts and autoregressive content propagation.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.15031

27. LM-Lexicon: Improving Definition Modeling via Harmonizing Semantic Experts
🔑 Keywords: LM-Lexicon, definition modeling, data clustering, semantic expert learning, sparse mixture-of-experts architecture
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research introduces LM-Lexicon, an advanced approach to improve definition modeling by utilizing a novel combination of data clustering, semantic expert learning, and sparse mixture-of-experts architecture.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The method involves decomposing the task into specialized semantic domains with small language models trained as domain experts. It employs a clustering strategy for fine-grained expert specialization and utilizes semantic-aware domain-level routing.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– LM-Lexicon achieves significant improvements, including a 7% increase in BLEU score over the prior state-of-the-art, a nearly 10% enhancement in definition quality through expert specialization, and a 1% boost in expert efficacy compared to traditional methods. The study further suggests performance can be improved through test-time computation and semantic expert scaling.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.14060

28. FireRed-Image-Edit-1.0 Techinical Report
🔑 Keywords: FireRed-Image-Edit, diffusion transformer, instruction-based image editing, data curation, training methodology
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– To achieve state-of-the-art performance in instruction-based image editing using a diffusion transformer with optimized data curation and training methods.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed a diffusion transformer called FireRed-Image-Edit.
– Constructed a large training corpus through data curation techniques, including cleaning, stratification, and automatic labeling.
– Employed a multi-stage training pipeline with pre-training, supervised fine-tuning, and reinforcement learning for optimal data efficiency.
– Introduced innovative techniques like Multi-Condition Aware Bucket Sampler and Asymmetric Gradient Optimization.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– FireRed-Image-Edit demonstrates competitive or superior performance in several editing benchmarks, including REDEdit-Bench, showcasing advanced editing capabilities.
– Released code, models, and benchmark suite to encourage future research in the domain of instruction-based image editing.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.13344

29. Conversational Image Segmentation: Grounding Abstract Concepts with Scalable Supervision
🔑 Keywords: Conversational Image Segmentation, ConverSeg, Segmentation Priors, Language Understanding, AI-powered Data Engine
💡 Category: Computer Vision
🌟 Research Objective:
– Address the gap in current models by introducing a new benchmark called Conversational Image Segmentation (CIS) and a model named ConverSeg-Net that combines segmentation priors with language understanding.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Developed ConverSeg, a benchmark that includes various aspects such as entities, spatial relations, intent, affordances, functions, safety, and physical reasoning.
– Introduced an AI-powered data engine that generates prompt-mask pairs without human supervision.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Current language-guided segmentation models are inadequate for CIS.
– ConverSeg-Net, trained on the new data engine, achieves significant improvement on the ConverSeg benchmark and maintains strong performance on existing benchmarks.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.13195
30. BrowseComp-V^3: A Visual, Vertical, and Verifiable Benchmark for Multimodal Browsing Agents
🔑 Keywords: Multimodal large language models, multimodal browsing, deep search, cross-modal multi-hop reasoning, multimodal information integration
💡 Category: Multi-Modal Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to address the limitations in existing benchmarks for multimodal browsing by introducing BrowseComp-V3.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– BrowseComp-V3 is a benchmark with 300 challenging questions focusing on multi-level, cross-modal reasoning, requiring accessible public evidence.
– An expert-validated, subgoal-driven process evaluation mechanism is introduced for fine-grained analysis.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Even advanced models achieve only 36% accuracy on BrowseComp-V3, highlighting significant gaps in current model capabilities for robust multimodal deep search in real-world settings.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.12876
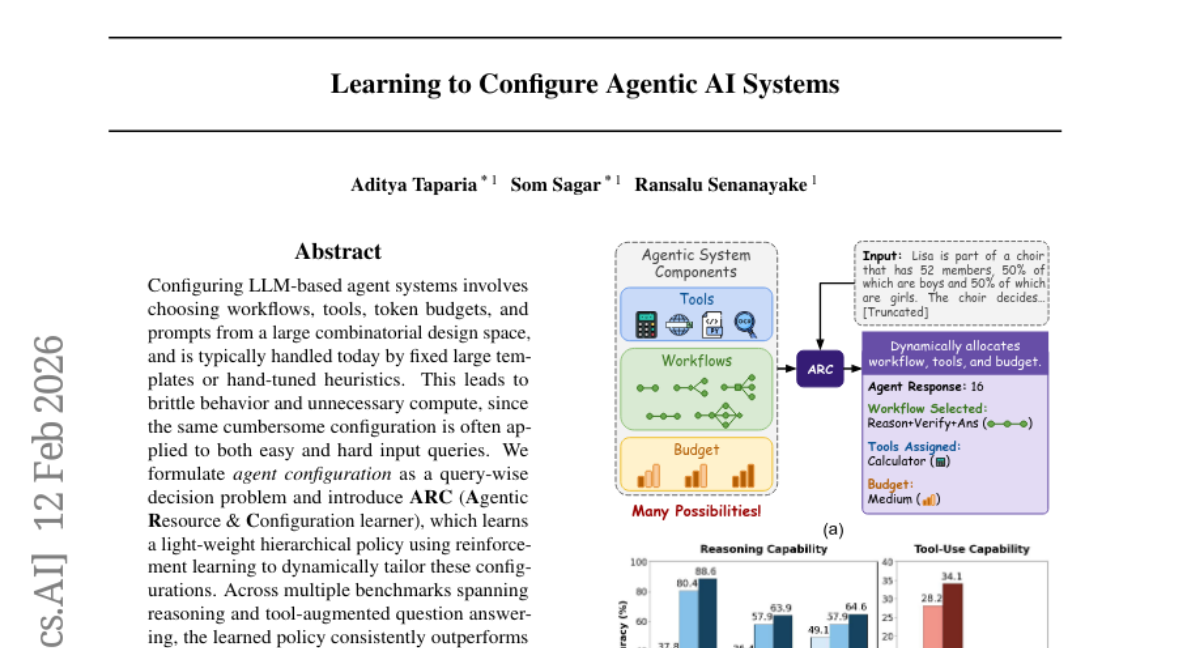
31. Learning to Configure Agentic AI Systems
🔑 Keywords: Reinforcement learning, Agent configuration, Task accuracy, Token budget, LLM-based agent systems
💡 Category: AI Systems and Tools
🌟 Research Objective:
– The study aims to improve task accuracy while reducing computational costs by learning per-query agent configurations through reinforcement learning.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Introduced ARC (Agentic Resource & Configuration learner), a system that employs reinforcement learning to learn a hierarchical policy for dynamically tailoring agent configurations per-query.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– The ARC system consistently outperforms traditional fixed templates and hand-tuned heuristics, achieving up to 25% higher task accuracy and reducing token and runtime costs, demonstrating its effectiveness as an alternative to “one size fits all” designs.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.11574
32. Nanbeige4.1-3B: A Small General Model that Reasons, Aligns, and Acts
🔑 Keywords: unified language model, agentic behavior, code generation, reward modeling, Reinforcement Learning
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The research aims to develop a versatile small language model, Nanbeige4.1-3B, that excels in agentic behavior, code generation, and reasoning using only 3 billion parameters.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The study employs advanced point-wise and pair-wise reward modeling, complexity-aware rewards in Reinforcement Learning, complex data synthesis, and turn-level supervision to enhance the model’s reasoning and decision-making capabilities.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Nanbeige4.1-3B outperforms other models of similar and larger scales, demonstrating that smaller models can achieve both broad competence and strong specialization, challenging the status quo of model parameter scalability.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.13367

33. Qute: Towards Quantum-Native Database
🔑 Keywords: Quantum Database, Quantum Computation, SQL, Qute, Fidelity-preserving Storage
💡 Category: Quantum Machine Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– This paper presents Qute, a quantum database designed to integrate quantum computation as a primary execution method, contrasting simulation-based methods.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The research employs a strategy that includes compiling extended SQL into quantum circuits, utilizing a hybrid optimizer, introducing quantum indexing, and employing fidelity-preserving storage to manage qubit limitations.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– Qute demonstrates superior performance compared to classical systems when deployed on an actual quantum processor, with results shared via an open-source prototype.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.14699

34. BitDance: Scaling Autoregressive Generative Models with Binary Tokens
🔑 Keywords: BitDance, autoregressive image generator, binary diffusion head, photorealistic images, high-entropy binary latents
💡 Category: Generative Models
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduction of BitDance, a scalable autoregressive image generator for efficient high-resolution image production.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Utilizes binary visual tokens and diffusion-based methods, employing a novel binary diffusion head to resolve sampling challenges, along with next-patch diffusion for parallel token prediction.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– BitDance achieves superior FID scores on ImageNet 256×256 with significantly reduced parameters and rapid computation. It demonstrates exceptional text-to-image generation performance and substantial speed improvements over previous AR models.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.14041

35. STATe-of-Thoughts: Structured Action Templates for Tree-of-Thoughts
🔑 Keywords: STATe, Interpretable ITC Method, Reasoning Patterns, Textual Interventions
💡 Category: Natural Language Processing
🌟 Research Objective:
– The objective of the paper is to introduce STATe, an interpretable Inference-Time-Compute (ITC) method that aims to enhance the generation of high-quality, diverse, and explainable text by utilizing reasoning patterns instead of stochastic sampling.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– The researchers developed STATe by integrating discrete textual interventions controlled by a selection process to encode reasoning choices, a generator to produce steps based on these choices, and an evaluator to score and guide the search.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– STATe demonstrated greater diversity in output compared to temperature-based sampling, captured interpretable features predictive of quality in argument generation, and identified unexplored action space regions to enhance text generation. The framework is available on GitHub.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.14265

36. Experiential Reinforcement Learning
🔑 Keywords: Experiential Reinforcement Learning, environmental feedback, behavioral revision, self-reflection, optimization
💡 Category: Reinforcement Learning
🌟 Research Objective:
– Introduce Experiential Reinforcement Learning (ERL) to improve learning efficiency and performance in sparse-reward environments by using an experience-reflection-consolidation loop.
🛠️ Research Methods:
– Implement a training paradigm where models generate initial attempts, receive feedback, and undergo reflection to guide improved attempts. This process strengthens the base policy without additional inference costs.
💬 Research Conclusions:
– ERL significantly enhances learning efficiency and final performance in complex environments and reasoning tasks, with gains up to +81% in multi-step environments and +11% in reasoning tasks through explicit self-reflection in policy training.
👉 Paper link: https://huggingface.co/papers/2602.13949
